Submitted:
21 February 2025
Posted:
24 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
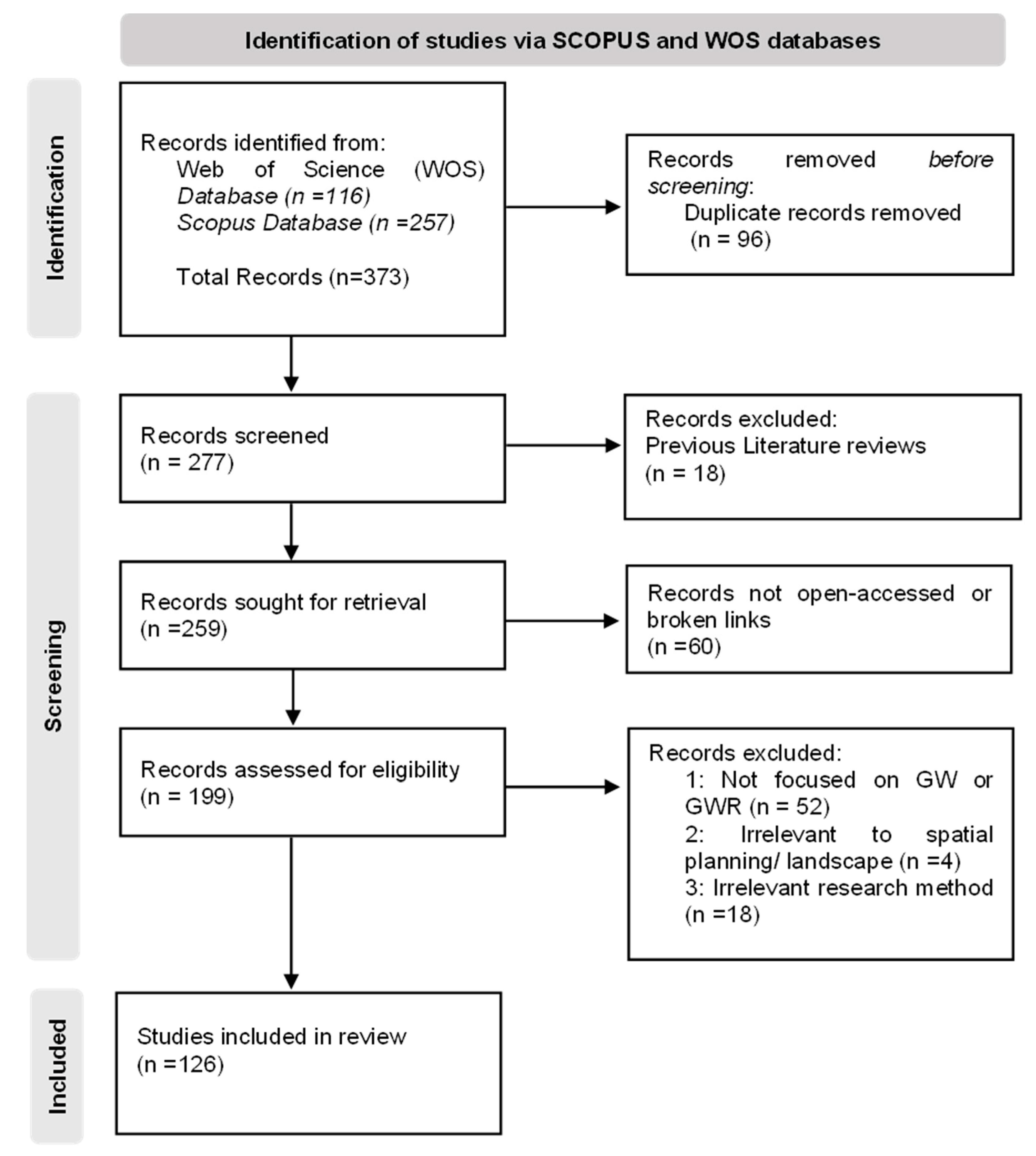
2. Materials and Methods
| KW-1 | KW-2 | KW-3 |
|---|---|---|
| (Groundwater recharge | Landscape | Spatial planning |
| Related Keywords | ||
| "Groundwater" OR "Groundwater recharge" OR "Aquifer recharge" OR "Groundwater Potential" OR "Managed Aquifer recharge" OR "Groundwater management" | "Landscape" OR "Landscape-scale planning" OR " Green space" OR "Landscape design" OR "Vegetation" OR "Landscape approach" OR "Nature-based solutions" | "Spatial planning" OR "Land-use planning" OR "Urban Design" OR "urban planning" OR "Regional planning" OR "Regional development" OR "Multiscale planning" |
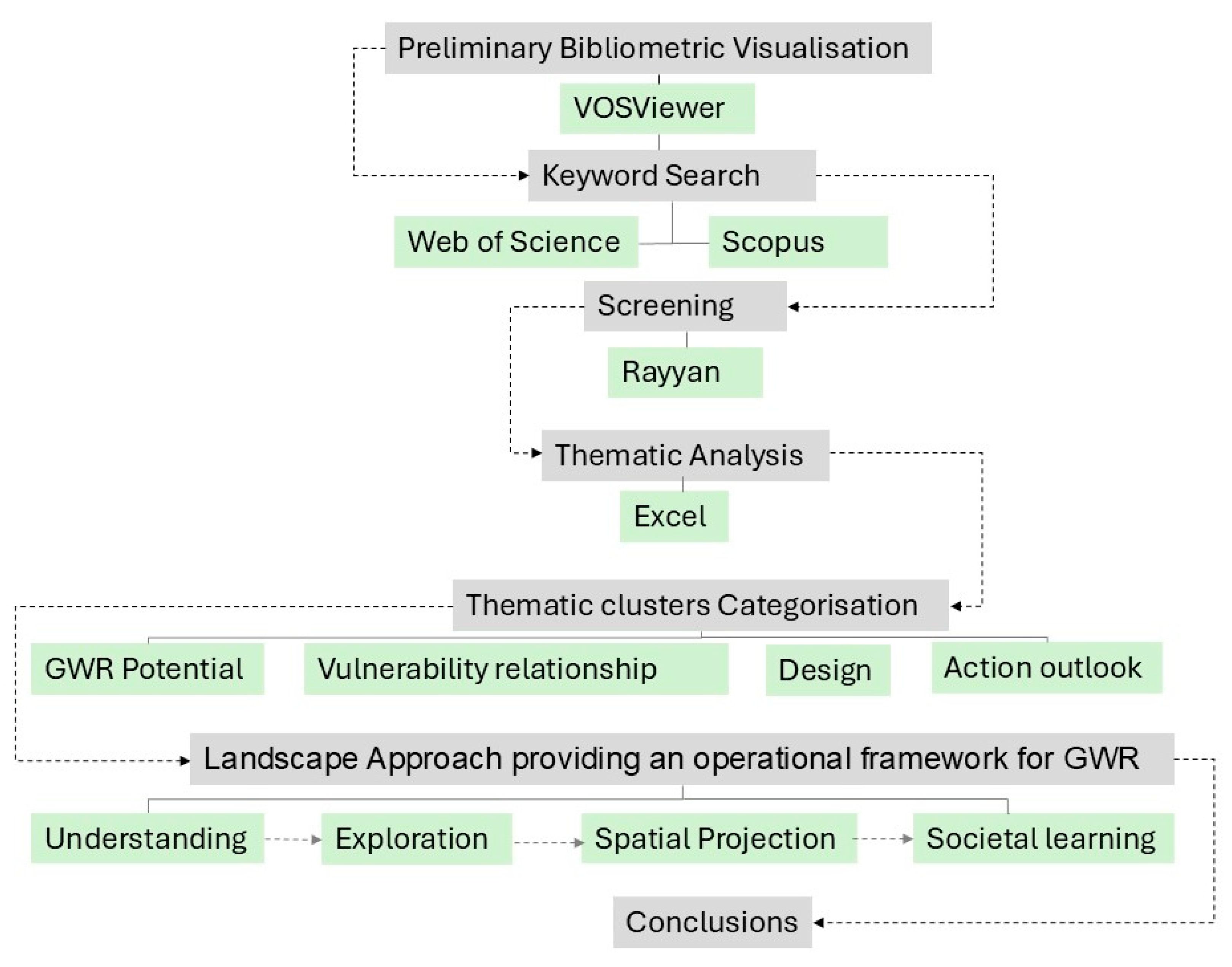
3. Results
3.1. Visualisation Analysis
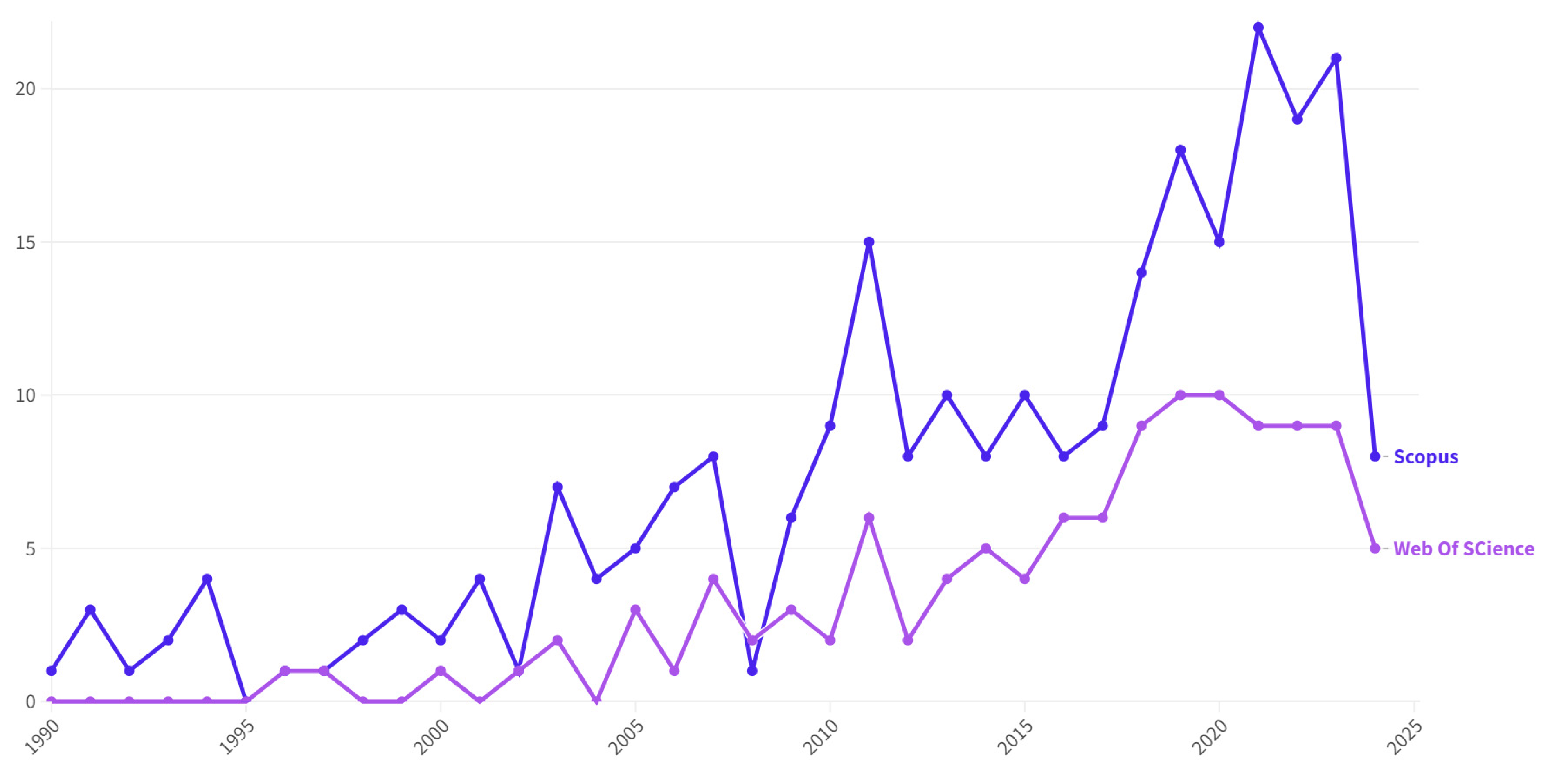
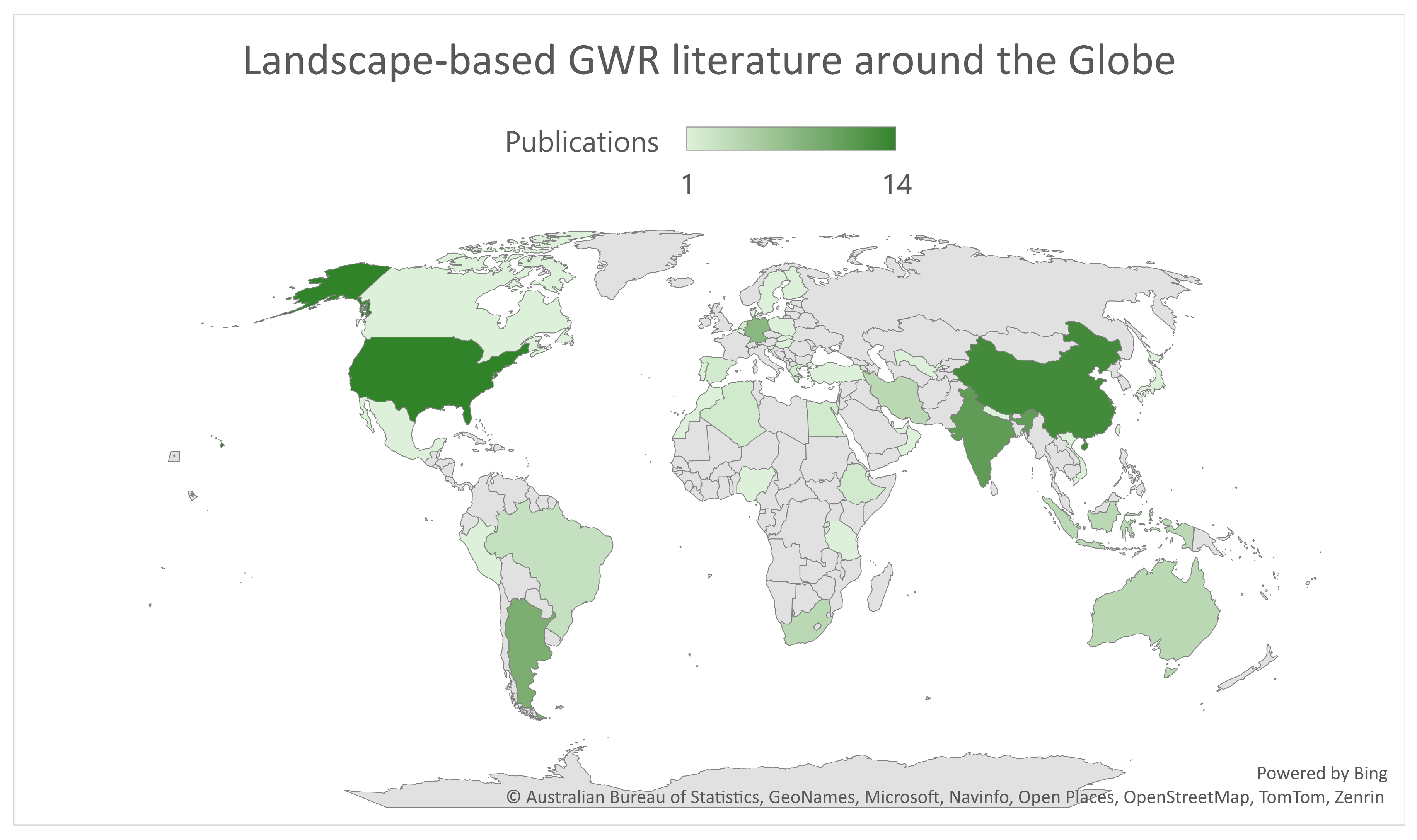
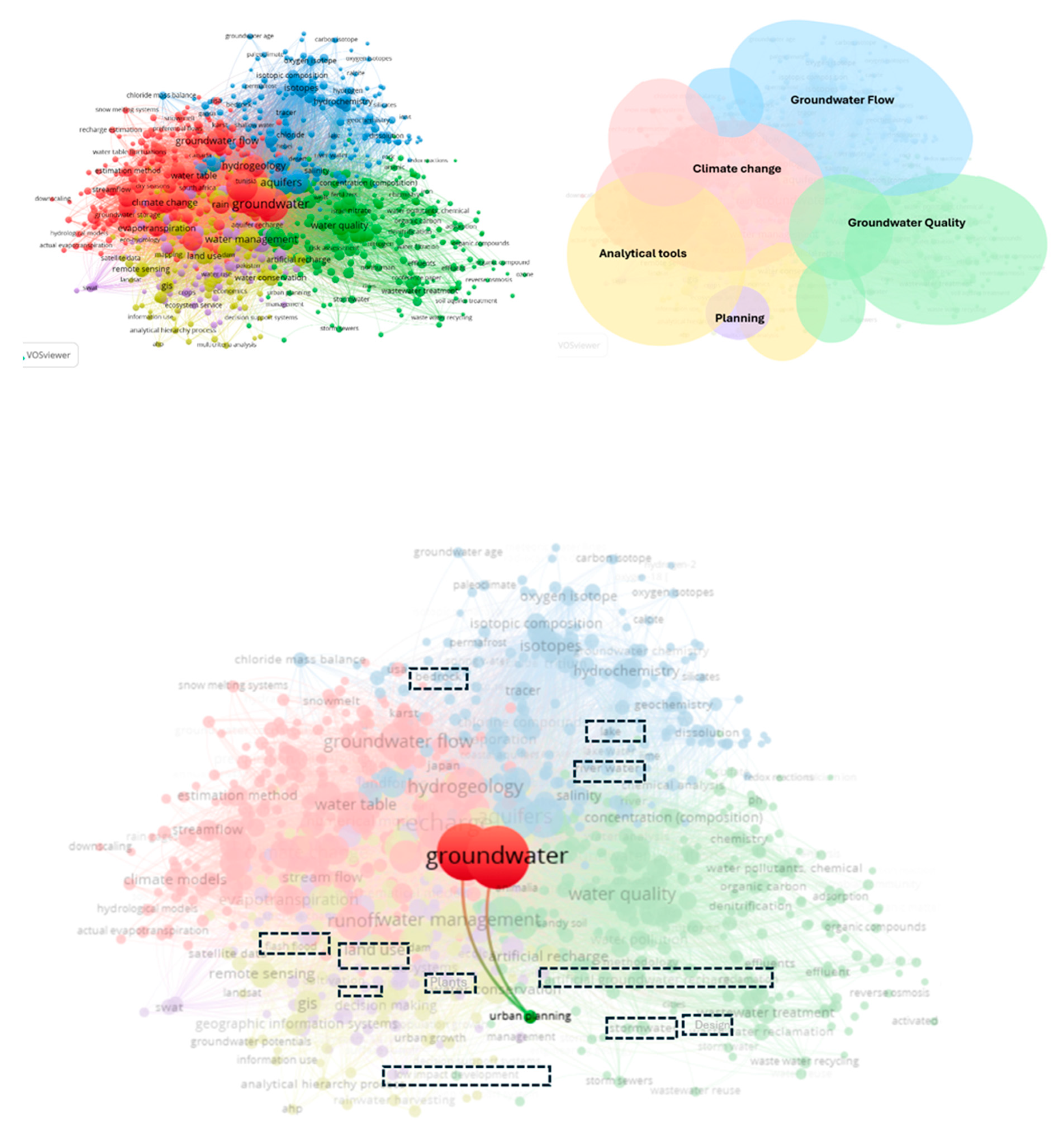
3.2. Thematic Categorisation in Groundwater Recharge Literature from a Spatial Planning and Landscape Perspective
- Groundwater Recharge Potential Mapping: Studies focusing on identifying and mapping areas with high groundwater recharge potential.
- Vulnerable relationship between climate change, urban landscape, and groundwater hydrology: Research underscoring the vulnerable relationship between climate change and urban landscapes, and factors affecting groundwater recharge and hydrological processes.
- Spatial Design in Groundwater Recharge: Studies exploring spatial design interventions such as green infrastructure, water-sensitive urban design (WSUD), and landscape planning to enhance groundwater recharge.
- Participatory outlook: Research focused on participatory approaches in groundwater management, emphasizing community and stakeholder engagement and collaborative decision-making processes.
| Clusters | Numbers (From the appendix) | Total number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GWR Potential mapping | 68,74, 78,91,98,117 | 6 | ||
| Vulnerable relationship between climate change, urban landscape, and groundwater hydrology | Landscape and climate conditions as Indicators of Groundwater Vulnerability | 7,8,10,11,12,14,15,16,18,20,21,25, 30,36,37,38,39,42,44,49,50,54,56,71, 72,88,89,90,92,93,99,101,102,104,107, 109,110,111,112,118,119,120 |
42 | 84 |
| Groundwater as a Marker of Landscape Fragility | 4,6,17,23,28,29,33,35,40,52,57,59,60,69, 73,75,77,80,82,83,84,87,94,95,97,100,114, 115,124,125 |
30 | ||
| Groundwater in ecosystem service evaluation | 34,43,47,53,55,61,63,64,65,85,106,126 | 12 | ||
| Spatial Design in Groundwater Recharge | Spatial Design to improve GWR | 5,27,46,67,70,76,108,127 | 8 | 23 |
| GW in integrated urban water management approach | 2,3,9,19,26,31,32,58,79,86,96, 103,113,116,121 |
15 | ||
| Participatory outlook | 13,22,24,41,45,48,51,62,66,81,105,122,123 | 13 | ||
3.2.1. GWR Potential Mapping
| No. | Author | Country | Scale | Input Parameters | Highest influencing Parameter | Model/ Methodology | Validation | Additional Associated dimension |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | De Souza et al. (2019) | Brazil | Basin | Elevation Rainfall, Land cover, Soil type, | Rainfall | Random Forest Model and BALSEQ Model | Soil Moisture Data | --- |
| 2 | Bara et. Al (2022) | India | Regional | Slope, Aspect, Altitude, Drainage Density, Pond Density, LULC, NDVI, Rainfall, Temp., Lithology, Geomorphology, Lineament, Soil type | LULC and Lithology | Weighted Overlay Method, AHP | Groundwater Elevation Datasets | --- |
| 3 | Das et. Al (2021) | India | Sub-district | Lithology, Geomorphology, Lineament, Soil type, LULC, Av. Slope, Drainage Density, | Geomor-phology | Weighted Overlay Method, AHP | Groundwater level | Human Adaptation behaviour |
| 4 | w. Chen et al. (2019) | China | Regional | Elevation, Slope, Aspect, Plan curvature, Profile curvature, TWI, SPI, STI, Lithology, LULC, NDVI, Distance to roads, Distance to streams | Lithology | FLDA, BFLDA, RFLDA | Friedman Test, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, ROC | --- |
| 5 | Gizaw et al. (2023) | Ethiopia | Sub-Basin/ catchment | slope, geomorphology, NDVI, elevation, geology, LULC, soil, rainfall, and drainage density |
Slope | Weighted Overlay, AHP | Boreholes and Spring yield data | --- |
| 6 | Singha and Pasupuleti (2020) | India | District | Aquifer, Soil, Geomorphology, Slope, Drainage Density, LULC, NDVI, Rainfall | Aquifer | ANP | Groundwater level | --- |
3.2.2. Vulnerability Studies- Understanding the Relationship Between Groundwater, Urban Landscape, and Climate Change
3.2.3. Spatial Design in Groundwater Recharge
3.2.4. Participatory Outlook
4. Discussion
4.1. Existing Research Trends and Gaps
4.2. Development of a Landscape-Based Framework for Integration of GWR in Spatial Planning
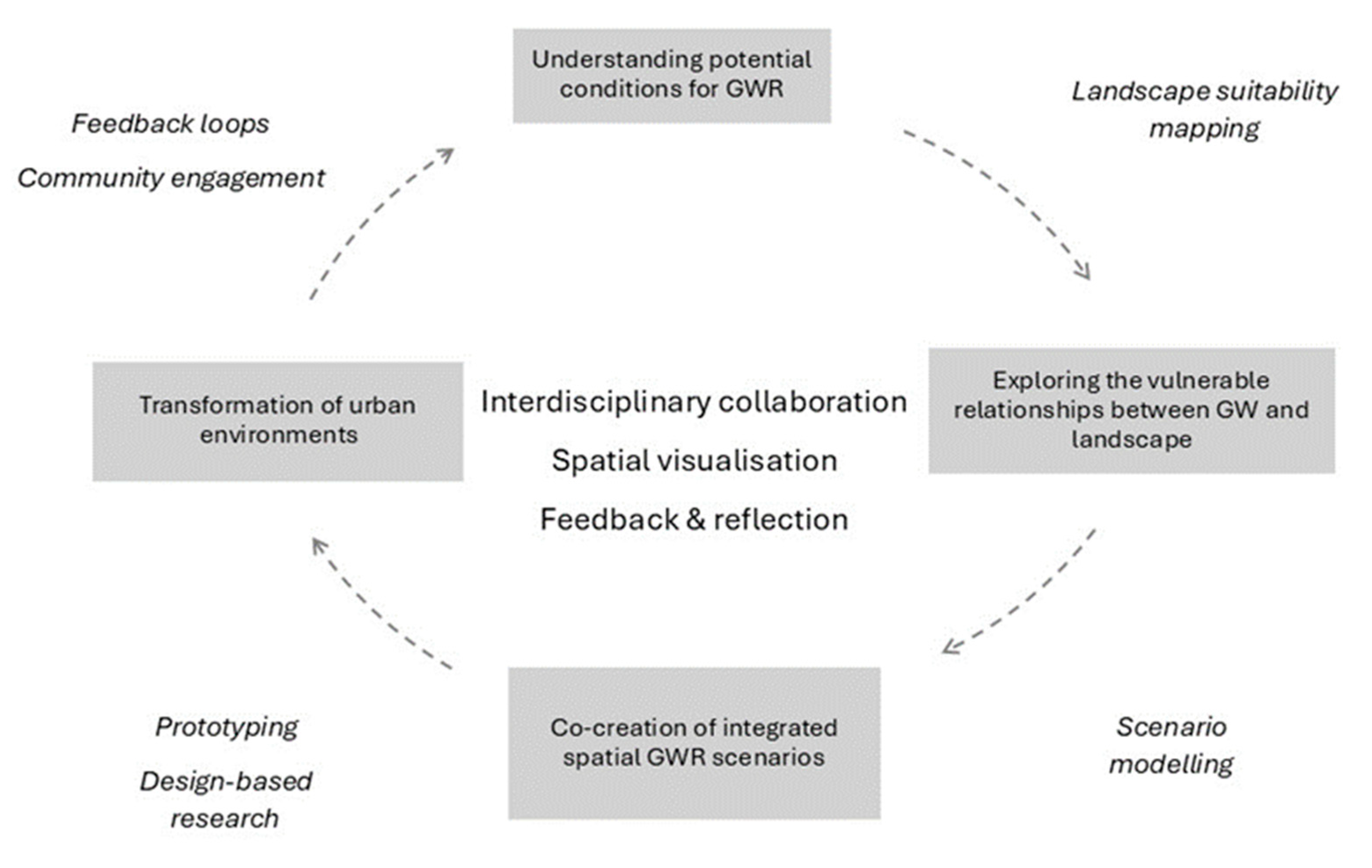
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, H. Hasan, M. M. Jilani, and S. I. Ahmed, “Mapping potential groundwater accumulation zones for Karachi city using GIS and AHP techniques,” Environ Monit Assess, vol. 195, no. 3, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- UNESCO, “The United Nations World Water Development Report 2022: Groundwater- Making the invisible visible Executive Summary,” 2022.
- Y. Chen, Z. Li, Y. Fan, H. Wang, and H. Deng, “Progress and prospects of climate change impacts on hydrology in the arid region of northwest China,” Environ Res, vol. 139, pp. 11–19, May 2015. [CrossRef]
- A.C. R. Braga, S. A.C. R. Braga, S. Serrao-Neumann, and C. de Oliveira Galvão, “Groundwater Management in Coastal Areas through Landscape Scale Planning: A Systematic Literature Review,” Environ Manage, vol. 65, no. 3, pp. 321–333, 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Damania, S. Desbureaux, A.-S. Rodella, J. Russ, and E. Zaveri, Quality Unknown: The Invisible Water Crisis. Washington, DC: World Bank, 2019. [CrossRef]
- V. Masson-Delmotte et al., Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Edited by. 2021. [Online]. Available: www.ipcc.
- Dai, “Increasing drought under global warming in observations and models,” Nat Clim Chang, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 52–58, Jan. 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. N. Galloway et al., “The Nitrogen Cascade,” 2003.
- S. S. D. Foster and P. J. Chilton, “Groundwater: The processes and global significance of aquifer degradation,” Dec. 29, 2003, Royal Society. [CrossRef]
- W. M.. Alley, T. E.. Reilly, and O. Lehn. Franke, Sustainability of ground-water resources. U.S. Dept. of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey ; U.S. G.P.O. ; U.S. Geological Survey, Branch of Information Services [distributor], 1999.
- J. J. de Vries and I. Simmers, “Groundwater recharge: An overview of process and challenges,” Hydrogeol J, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 5–17, Feb. 2002. [CrossRef]
- Ian, L. McHarg, Design with Nature. Philadelphia: Natural History Press, 1969. Accessed: Jan. 16, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://archive.
- J. Reed, L. Deakin, and T. Sunderland, “What are ‘Integrated Landscape Approaches’ and how effectively have they been implemented in the tropics: A systematic map protocol,” Jan. 07, 2015, BioMed Central Ltd. [CrossRef]
- A.Kirby, “Exploratory Bibliometrics: Using VOSviewer as a Preliminary Research Tool,” Publications, vol. 11, no. 1, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Page et al., “The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews,” International Journal of Surgery, vol. 88, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Ouzzani, H. Hammady, Z. Fedorowicz, and A. Elmagarmid, “Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews,” Syst Rev, vol. 5, no. 1, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- V. Braun and V. Clarke, “Using thematic analysis in psychology,” Qual Res Psychol, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 77–101, 2006. [CrossRef]
- J. Lian, S. Nijhuis, G. Bracken, X. Wu, X. Wu, and D. Chen, “Conservation and development of the historic garden in a landscape context: A systematic literature review,” Jun. 01, 2024, Elsevier B.V. [CrossRef]
- M. Das, T. Parveen, D. Ghosh, and J. Alam, “Assessing groundwater status and human perception in drought-prone areas: a case of Bankura-I and Bankura-II blocks, West Bengal (India),” Environ Earth Sci, vol. 80, no. 18, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Bera, M. E. Newcomer, and P. Banik, “Groundwater recharge site suitability analysis through multi-influencing factors (MIF) in West Bengal dry-land areas, West Bengal, India,” Acta Geochimica, vol. 41, no. 6, pp. 1030–1048, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. A. Gizaw, G. T. Bawoke, M. M. Alemu, and Z. L. Anteneh, “Spatial analysis of groundwater potential using remote sensing and GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis method in Fetam-Yisir catchment, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia,” Applied Geomatics, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 659–681, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Singha and S. Pasupuleti, “Delineation of Groundwater Prospect Zones in Arang Block, Raipur District, Chhattisgarh, Central India, Using Analytical Network Process,” Journal of the Geological Society of India, vol. 95, no. 6, pp. 609–615, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- E. De Souza, L. M. Pontes, E. I. Fernandes Filho, C. E. G. R. Schaefer, and E. E. Dos Santos, “Spatial and temporal potential groundwater recharge: The case of the doce river basin, Brazil,” Rev Bras Cienc Solo, vol. 43, 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. Chen et al., “Novel Hybrid Integration Approach of Bagging-Based Fisher’s Linear Discriminant Function for Groundwater Potential Analysis,” Natural Resources Research, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 1239–1258, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. L. Collin and A. J. Melloul, “Assessing groundwater vulnerability to pollution to promote sustainable urban and rural development,” J Clean Prod, vol. 11, no. 7, pp. 727–736, Nov. 2003. [CrossRef]
- N. S. Nalini, “Urbanisation and changing temperature patterns in the city of Bengaluru,” Environ Dev Sustain, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 9090–9109, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Tomaškinová and J. Tomaškin, “Assessment of anthropogenic activity negative impact on the karst landscape and a proposal for revitalization measures,” Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 117–123, 2014.
- E. Falkowska, “The significance of morphogenetic analysis in the assessment of soil-water conditions in Quaternary sediments,” Geomorphology, vol. 246, pp. 420–432, 2015. [CrossRef]
- L.-M. Kuhlemann, D. Tetzlaff, A. Smith, B. Kleinschmit, and C. Soulsby, “Using soil water isotopes to infer the influence of contrasting urban green space on ecohydrological partitioning,” Hydrol Earth Syst Sci, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 927–943, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. M. G. Lumongsod, N. T. Ramos, and C. B. Dimalanta, “Mapping the karstification potential of central Cebu, Philippines using GIS,” Environ Earth Sci, vol. 81, no. 18, 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. L. Pereira, P. Galvão, T. Lucon, and M. A. Fujaco, “Adapting the EPIK method to Brazilian Hydro(geo)logical context of the São Miguel watershed to assess karstic aquifer vulnerability to contamination,” J South Am Earth Sci, vol. 90, pp. 191–203, Mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A.E. El-Rayes, M. O. Arnous, E.-A. H. Shendi, M. H. Geriesh, and R. A. Gharib, “Morphotectonic controls on hydro-environmental hazards in rift basins: a case study from Southern Suez Canal Province, Egypt,” Geoenvironmental Disasters, vol. 10, no. 1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Noriega-Puglisevich and K. I. Eckhardt, “Hydrological effects of the conversion of tropical montane forest to agricultural land in the central Andes of Peru,” Environmental Quality Management, 2024. [CrossRef]
- T. W. Negash, F. K. Abagale, and B. N. Baatuuwie, “Impact of land-use and land-cover change on watershed hydrology: a case study of Mojo watershed, Ethiopia,” Environ Earth Sci, vol. 81, no. 23, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Busch, “The impact of Short Rotation Coppice cultivation on groundwater recharge - a spatial (planning) perspective,” LANDBAUFORSCHUNG VOLKENRODE, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 207–221, 2009.
- M. Wu and M.-A. Ha, Incorporating conservation practices into the future bioenergy landscape: Water quality and hydrology. 2017. [CrossRef]
- V. L. Versace, D. Ierodiaconou, F. Stagnitti, and A. J. Hamilton, “Appraisal of random and systematic land cover transitions for regional water balance and revegetation strategies,” Agric Ecosyst Environ, vol. 123, no. 4, pp. 328–336, Feb. 2008. [CrossRef]
- R. Li et al., “Effects of urbanization on the water cycle in the Shiyang River basin: based on a stable isotope method,” Hydrol Earth Syst Sci, vol. 27, no. 24, pp. 4437–4452, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Dagar, “Opportunities for Alternate Land Uses in Salty and Water Scarcity Areas,” 2009. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate. 2284.
- G. N. de Lima, M. A. Fonseca-Salazar, and J. Campo, “Urban growth and loss of green spaces in the metropolitan areas of São Paulo and Mexico City: effects of land-cover changes on climate and water flow regulation,” Urban Ecosyst, vol. 26, no. 6, pp. 1739–1752, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A.Balha, A. Singh, S. Pandey, R. Kumar, J. Mallick, and C. K. Singh, “Assessing the Impact of Land-Use Dynamics to Predict the Changes in Hydrological Variables Using Effective Impervious Area (EIA),” Water Resources Management, vol. 37, no. 10, pp. 3999–4014, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. M. Al-Kindi, A. F. Alqurashi, A. Al-Ghafri, and D. Power, “Assessing the Impact of Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Aflaj Systems over a 36-Year Period,” Remote Sens (Basel), vol. 15, no. 7, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. C. Vaddiraju and R. T, “Urbanization implications on hydro-meteorological parameters of Saroor Nagar Watershed of Telangana,” Environmental Challenges, vol. 8, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. O. Randhir and O. Tsvetkova, “Spatiotemporal dynamics of landscape pattern and hydrologic process in watershed systems,” J Hydrol (Amst), vol. 404, no. 1–2, pp. 1–12, Jun. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Achmad, A. Anhar, and A. Izzaty, “Landscape patterns changes and relation to water infiltration of Krueng Peusangan Watershed in Aceh,” Dec. 02, 2021, IOP Publishing Ltd. [CrossRef]
- A.S. Bhaskar et al., “Will it rise or will it fall? Managing the complex effects of urbanization on base flow,” in Freshwater Science, University of Chicago Press, Mar. 2016, pp. 293–310. [CrossRef]
- L. S. Leonard, “Assessment of groundwater quality along cemeteries and associated potential health concerns in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania,” Water Pract Technol, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 1218–1229, May 202. [CrossRef]
- S. Lyu, W. Chen, J. Qian, X. Wen, and J. Xu, “Prioritizing environmental risks of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in reclaimed water on urban green space in Beijing,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 697, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. L. Bester, E. O. Frind, J. W. Molson, and D. L. Rudolph, “Numerical investigation of road salt impact on an urban wellfield,” Ground Water, vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 165–175, Mar. 2006. [CrossRef]
- D. Fatta, D. Naoum, and M. Loizidou, “Integrated environmental monitoring and simulation system for use as a management decision support tool in urban areas,” J Environ Manage, vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 333–343, 2002. [CrossRef]
- N. N. Gao, F. Li, H. Zeng, and Y. R. Zheng, “The impact of human activities, natural factors and climate time-lag effects over 33 years in the heihe river basin, china,” Appl Ecol Environ Res, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 1589–1606, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A.Lagro, B. T. Vowels, and B. Vondra, “Exurban housing development, onsite wastewater disposal, and groundwater vulnerability within a changing policy context,” 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Baker, Y. Everett, L. Liegel, and R. Van Kirk, “Patterns of Irrigated Agricultural Land Conversion in a Western U.S. Watershed: Implications for Landscape-Level Water Management and Land-Use Planning,” Soc Nat Resour, vol. 27, no. 11, pp. 1145–1160, Nov. 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Martín Muñoz, J. Schoelynck, D. Tetzlaff, R. Debbaut, M. Warter, and J. Staes, “Assessing biodiversity and regulatory ecosystem services in urban water bodies which serve as aqua-Nature-based Solutions,” Front Environ Sci, vol. 11, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Lu et al., “The impacts of the ecological water diversion project on the ecology-hydrology-economy nexus in the lower reaches in an inland river basin,” Resour Conserv Recycl, vol. 164, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Attig, and T. McDermott, “Inondation par les eaux souterraines d’une terrasse fluvial dans le sud-ouest du Wisconsin, Etats Unis d’Amérique,” Hydrogeol J, vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 1421–1432, 2014. [CrossRef]
- A.Batelaan, F. De Smedt, and L. Triest, “Regional groundwater discharge: Phreatophyte mapping, groundwater modelling and impact analysis of land-use change,” J Hydrol (Amst), vol. 275, no. 1–2, pp. 86–108, Apr. 2003. [CrossRef]
- S. I. Elmahdy and M. M. Mohamed, “Groundwater of Abu Dhabi Emirate: A regional assessment by means of remote sensing and geographic information system,” Arabian Journal of Geosciences, vol. 8, no. 12, pp. 11279–11292, Dec. 2015. [CrossRef]
- F. Böttcher and K. Zosseder, “Thermal influences on groundwater in urban environments – A multivariate statistical analysis of the subsurface heat island effect in Munich,” Science of The Total Environment, vol. 810, p. 152193, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- N. Gunawardhana and S. Kazama, “Using subsurface temperatures to derive the spatial extent of the land use change effect,” J Hydrol (Amst), vol. 460–461, pp. 40–51, 2012. [CrossRef]
- P. E. V Van Walsum, J. Runhaar, and J. F. M. Helming, “Spatial planning for adapting to climate change.” [Online]. Available: http://iwaponline.com/wst/article-pdf/51/5/45/435015/45.
- R. U. Syrbe, O. Bastian, M. Röder, and P. James, “A framework for monitoring landscape functions: The Saxon Academy Landscape Monitoring Approach (SALMA), exemplified by soil investigations in the Kleine Spree floodplain (Saxony, Germany),” Landsc Urban Plan, vol. 79, no. 2, pp. 190–199, Feb. 2007. [CrossRef]
- A.Ghosh, S. Bhattacharjee, and B. Bera, “Hydro-Geomorphological Mapping of Manbhum-Singhbhum Plateau (Part of Singhbhum Protocontinent, India) for Water Resource Development and Landuse Planning,” Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, vol. 51, no. 8, pp. 1757–1775, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Avtar, C. K. Singh, G. Singh, R. L. Verma, S. Mukherjee, and H. Sawada, “Landslide susceptibility zonation study using remote sensing and GIS technology in the Ken-Betwa River Link area, India,” Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, vol. 70, no. 4, pp. 595–606, Nov. 2011. [CrossRef]
- F. Benzenine, M. A. Allal, C. Abdelbaki, N. Kumar, M. Goosen, and J. M. Gathenya, “Multi-Hazard Risk Assessment and Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: A Case Study from Bensekrane in Algeria,” Sustainability (Switzerland), vol. 15, no. 3, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Q. Liu, W. Jian, and W. Nie, “Sustainable Cities and Society 69 (2021) 102817 Rainstorm-induced landslides early warning system in mountainous cities based on groundwater level change fast prediction,” 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. Wen et al., “Land-subsidence susceptibility mapping: assessment of an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system–genetic algorithm hybrid model,” Geocarto Int, vol. 37, no. 26, pp. 12194–12218, 2022. [CrossRef]
- V. Marchionni, A. Guyot, N. Tapper, J. P. Walker, and E. Daly, “Water balance and tree water use dynamics in remnant urban reserves,” J Hydrol (Amst), vol. 575, pp. 343–353, Aug. 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Arden, X. Ma, and M. Brown, “An ecohydrologic model for a shallow groundwater urban environment,” Water Science and Technology, vol. 70, no. 11, pp. 1789–1797, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Koren, “Management of Landslides in Small Settlements in Slovenia,” in Advancing Culture of Living with Landslides, Springer International Publishing, 2017, pp. 989–998. [CrossRef]
- L. Falconi, G. Leoni, P. M. Arestegui, C. Puglisi, and S. Savini, “Geomorphological processes and cultural heritage of Maca and Lari Villages: An opportunity for sustainable tourism development in the Colca Valley (Province of Caylloma, Arequipa, South Perù),” in Landslide Science and Practice: Risk Assessment, Management and Mitigation, Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH, 2013, pp. 459–465. [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, S. Wu, S. Zhang, C. Nie, Y. Li, and Y. Huang, “Optimization of land reuse structure in coal mining subsided areas considering regional economic development: A case study in Pei County, China,” Sustainability (Switzerland), vol. 12, no. 8, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, “GIS based susceptibility mapping of karst depression in gypsum: A case study from Sivas basin (Turkey),” Eng Geol, vol. 90, no. 1–2, pp. 89–103, Mar. 2007. [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, “Estimation of intrinsic aquifer vulnerability with index-overlay and statistical methods: the case of eastern Kopaida, central Greece,” Appl Water Sci, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 2215–2229, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- A.Fatoyinbo et al., “Municipal solid waste landfill site selection: a geotechnical and geoenvironmental-based geospatial approach,” Environ Earth Sci, vol. 79, p. 231, 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. C. Crivelenti, C. R. P. Bueno, J. S. R. Pires, J. Francisco, and B. F. Lessi, “Ecological-economic zoning of the city of altinópolis - SP, Brazil,” Engenharia Agricola, vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 1218–1228, 2016. [CrossRef]
- A.Bao et al., “Ecological problems and ecological restoration zoning of the Aral Sea,” J Arid Land, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 315–330, Mar. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Malekmohammadi, “Site selection of sustainable urban drainage systems using fuzzy logic and multi-criteria decision-making,” Water and Environment Journal, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 584–599, Nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Esterhuyse et al., “Vulnerability mapping as a tool to manage the environmental impacts of oil and gas extraction,” R Soc Open Sci, vol. 4, no. 11, 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Xue, C. Wang, Y. Wu, Q. Zhou, Z. Song, and Y. Wu, “Revised zoning method for environmental fragility evaluation to desertification in arid–semiarid areas: a case of Dousitu river basin,” Environ Earth Sci, vol. 80, no. 17, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. Sefati, B. Khalilimoghadam, and H. Nadian, “Assessing urban soil quality by improving the method for soil environmental quality evaluation in a saline groundwater area of Iran,” Catena (Amst), vol. 173, pp. 471–480, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Nielsen-Pincus et al., “Predicted effects of residential development on a northern Idaho landscape under alternative growth management and land protection policies,” Landsc Urban Plan, vol. 94, no. 3–4, pp. 255–263, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chen and Z. Paydar, “Evaluation of potential irrigation expansion using a spatial fuzzy multi-criteria decision framework,” Environmental Modelling and Software, vol. 38, pp. 147–157, Dec. 2012. [CrossRef]
- H. Susilo, D. Purwantoro, and S. Rahadiansyah, “Model Performance Index of Ground Water Irrigation Systems in the Karst Mountain Region: Case Study in Gunung Kidul Regency, Yogyakarta,” in IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, IOP Publishing Ltd, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Khamzina, B. Tischbein, P. Knöfel, C. Conrad, and J. P. A. Lamers, “Spatio-temporal supply–demand of surface water for agroforestry planning in saline landscape of the lower Amudarya Basin,” J Arid Environ, vol. 162, pp. 53–61, Mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Lasch, <italic></italic>; et al. “Regional impact analysis of climate change on natural and managed forests in the Federal State of Brandenburg, Germany,” 1999.
- S. H. M. Langroodi, M. G. Masoum, H. Nasiri, and S. T. Javi, “Spatial and temporal variability analysis of groundwater quantity to land-use/land-cover change in the Khanmirza agricultural plain in Iran,” Arabian Journal of Geosciences, vol. 8, no. 10, pp. 8385–8397, Oct. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Å. Kasimir, H. He, J. Coria, and A. Nordén, “Land use of drained peatlands: Greenhouse gas fluxes, plant production, and economics,” Glob Chang Biol, vol. 24, no. 8, pp. 3302–3316, 2018. [CrossRef]
- V. Hermoso, L. Cattarino, S. Linke, and M. J. Kennard, “Catchment zoning to enhance co-benefits and minimize trade-offs between ecosystem services and freshwater biodiversity conservation,” Aquat Conserv, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 1004–1014, Aug. 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Lupp, R. Steinhäußer, O. Bastian, and R.-U. Syrbe, “Impacts of increasing bioenergy use on ecosystem services on nature and society exemplified in the German district of Görlitz,” Biomass Bioenergy, vol. 83, pp. 131–140, 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. C. Zipper, M. E. Soylu, C. J. Kucharik, and S. P. Loheide, “Quantifying indirect groundwater-mediated effects of urbanization on agroecosystem productivity using MODFLOW-AgroIBIS (MAGI), a complete critical zone model,” Ecol Modell, vol. 359, pp. 201–219, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Santos, S. Díaz-Alcaide, A. De la Hera-Portillo, and V. Gómez-Escalonilla, “Mapping groundwater-dependent ecosystems by means of multi-layer supervised classification,” J Hydrol (Amst), vol. 603, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. McLaughlin and M. J. Cohen, “Realizing ecosystem services: Wetland hydrologic function along a gradient of ecosystem condition,” Ecological Applications, vol. 23, no. 7, pp. 1619–1631, Oct. 2013. [CrossRef]
- W. Xiao, Y. Fu, T. Wang, and X. Lv, “Effects of land use transitions due to underground coal mining on ecosystem services in high groundwater table areas: A case study in the Yanzhou coalfield,” Land use policy, vol. 71, pp. 213–221, Feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. Aevermann and J. Schmude, “Quantification and monetary valuation of urban ecosystem services in Munich, Germany,” Z Wirtschgeogr, vol. 59, pp. 188–200, 2015.
- Z. Pinke, M. Kiss, and G. L. Lövei, “Developing an integrated land use planning system on reclaimed wetlands of the Hungarian Plain using economic valuation of ecosystem services,” Ecosyst Serv, vol. 30, pp. 299–308, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Tammi, K. Mustajärvi, and J. Rasinmäki, “Integrating spatial valuation of ecosystem services into regional planning and development,” Ecosyst Serv, vol. 26, pp. 329–344, Aug. 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. L. Bremer et al., “Bringing multiple values to the table: Assessing future land-use and climate change in North Kona, Hawaiʻi,” Ecology and Society, vol. 23, no. 1, 2018. [CrossRef]
- L. T. Ha and W. G. M. Bastiaanssen, “Determination of Spatially-Distributed Hydrological Ecosystem Services (HESS) in the Red River Delta Using a Calibrated SWAT Model,” Sustainability (Switzerland), vol. 15, no. 7, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Doyle, P. Thalmann, and A. Parriaux, “Underground potential for urban sustainability: Mapping resources and their interactions with the Deep City method,” Sustainability (Switzerland), vol. 8, no. 9, Aug. 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Teal, C.-S. Huang, and J. Rodiek, “Open space planning for Travis Country, Austin, Texas: A collaborative design,” Landsc Urban Plan, vol. 42, no. 2–4, pp. 259–268, 1998. [CrossRef]
- Mclachlan, <italic></italic>; et al. “Pathways to water resilient South African cities – from mono-functional to multi-functional stormwater infrastructure,” Sci Afr, vol. 20, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- C. Matos, A. Briga Sá, I. Bentes, S. Pereira, and R. Bento, “An approach to the implementation of Low Impact Development measures towards an EcoCampus classification,” J Environ Manage, vol. 232, pp. 654–659, Feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Burlakovs, I. Grinfelde, J. Pilecka, Y. Jani, and W. Hogland, “Phytoremediation as tool for prevention of contaminant flow to hydrological systems,” in Research for Rural Development, 2018, pp. 188–194. [CrossRef]
- Z. Boukalová, J. Těšitel, and B. D. Gurung, “Nature-based water treatment solutions and their successful implementation in kathmandu valley, nepal,” WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment, vol. 242, pp. 121–132, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Tang, H. feng Jia, Q. gui Jiang, and J. Wang, “Comprehensive rehabilitation planning of deserted pits and the case study in plain area of Beijing, China,” Landsc Urban Plan, vol. 99, no. 2, pp. 123–132, Feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- A. Brenner, H. Cohen, O. Gradus, O. Koren, S. Shandalov, and Y. Zinger, “INCORPORATION OF HYBRID BIOFILTERS IN WATER-SENSITIVE URBAN DESIGN,” Present Environment and Sustainable Development, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 167–177, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Kadaverugu, S. Dhyani, R. Dasgupta, P. Kumar, and C. Matli, “Urban sustainability and resilience building: Blue-green infrastructure for air pollution abatement and realizing multiple co-benefits,” in Blue-Green Infrastructure Across Asian Countries: Improving Urban Resilience and Sustainability, Springer Nature, 2022, pp. 397–417. [CrossRef]
- Singh and, V. Bakshi, “Geospatial approach for reducing water stress: case study of Delhi,” in Climate Change, Community Response and Resilience: Insight for Socio-Ecological Sustainability, Elsevier, 2023, pp. 467–497. [CrossRef]
- V. Novotny and K. Hill, “Diffuse pollution abatement - A key component in the integrated effort towards sustainable urban basins,” in Water Science and Technology, IWA Publishing, 2007, pp. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Tjallingii, “Water flows and urban planning,” in Sustainable Urban Environments: An Ecosystem Approach, Springer Netherlands, 2012, pp. 91–111. [CrossRef]
- A.J. Melloul and S. H. Wollman, “Qualitative hydrological and land-use planning tool for the Israel Coastal aquifer,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 309, no. 1–3, pp. 1–17, Jun. 2003. [CrossRef]
- B.Fryd et al., “Water sensitive urban design retrofits in Copenhagen - 40% to the sewer, 60% to the city,” Water Science and Technology, vol. 67, no. 9, pp. 1945–1952, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Lancia, C. Zheng, X. He, D. N. Lerner, C. Andrews, and Y. Tian, “Hydrogeological constraints and opportunities for ‘Sponge City’ development: Shenzhen, southern China,” J Hydrol Reg Stud, vol. 28, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Chandran, S. R. Thiruchelve, and M. Dhanasekarapandian, “Integrated urban water resources management strategy for a smart city in India,” Water Sci Technol Water Supply, vol. 21, no. 2, pp. 736–749, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Palmer, D. P. Lettenmaier, N. L. Poff, S. L. Postel, B. Richter, and R. Warner, “Climate change and river ecosystems: Protection and adaptation options,” Dec. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, “Long-range planning for water reuse in the city of Los Angeles,” Water Science and Technology, vol. 24, no. 9, pp. 11–17, 1991. [CrossRef]
- Panayi, “USE OF A PUBLIC PERCEPTIONS STUDY TO ASSIST POLICY MAKING FOR RECLAIMED WATER REUSE Water Development Department Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources and Environment Republic of Cyprus 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology.
- L. Fertas, M. Alouat, and H. Benmahamed, “The Emergence of Irrigated Agriculture in Semi-Arid Zones in the Face of Climate Change and Urbanization in Peri-Urban Areas in Setif, Algeria,” Sustainability (Switzerland), vol. 16, no. 3, Feb. 2024. [CrossRef]
- R. Roggema and K. Bruin-Baerts, Waterman, vol. Part F8. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Alaerts, “Water, physically connected yet institutionally fragmented—Investing in its strategies, asset classes, and organizations,” in Financing Investment in Water Security: Recent Developments and Perspectives, Elsevier, 2022, pp. 17–55. [CrossRef]
- Everard, <italic></italic>; et al. , “Assessing the feasibility of integrating ecosystem-based with engineered water resource governance and management for water security in semi-arid landscapes: A case study in the Banas catchment, Rajasthan, India,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 612, pp. 1249–1265, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Newman; et al. , “Citizen science-informed community master planning: Land use and built environment changes to increase flood resilience and decrease contaminant exposure,” Int J Environ Res Public Health, vol. 17, no. 2, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Terribile et al., “A Web-based spatial decision supporting system for land management and soil conservation,” Solid Earth, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 903–928, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- D. Milz, M. Zellner, C. Hoch, J. Radinsky, K. Pudlock, and L. Lyons, “Reconsidering Scale: Using Geographic Information Systems to Support Spatial Planning Conversations,” Planning Practice and Research, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 291–308, May 2018. [CrossRef]
- Mukuyu, N. Nyambe, M. S. Magombeyi, and G. Y. Ebrahim, “Polycentric Groundwater Governance: Insights from the Kavango-Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area,” Int J Commons, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 322–336, 2024. [CrossRef]
- X. Yang, J. Dong, and P. D. White, “The key role of water resources management in ecological restoration in Western China,” Geographical Research, vol. 44, no. 2, pp. 146–154, Jun. 2006. [CrossRef]
- P. Dhakal and L. R. Chevalier, “Urban Stormwater Governance: The Need for a Paradigm Shift,” Environ Manage, vol. 57, no. 5, pp. 1112–1124, 16. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- D. Vollmer, D. O. Pribadi, F. Remondi, E. Rustiadi, and A. Grêt-Regamey, “Prioritizing ecosystem services in rapidly urbanizing river basins: A spatial multi-criteria analytic approach,” Sustain Cities Soc, vol. 20, pp. 237–252, Jan. 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. Rivas-Tabares, A. M. Tarquis, Á. De Miguel, A. Gobin, and B. Willaarts, “Enhancing LULC scenarios impact assessment in hydrological dynamics using participatory mapping protocols in semiarid regions,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 803, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Braune and Y. Xu, “The role of ground water in sub-Saharan Africa,” Ground Water, vol. 48, no. 2, pp. 229–238, Mar. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Vejre, J. P. Vesterager, L. S. Kristensen, and J. Primdahl, “Stakeholder and expert-guided scenarios for agriculture and landscape development in a groundwater protection area,” Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, vol. 54, no. 9, pp. 1169–1187, Nov. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Kmoch, A. Bou-Lahriss, and T. Plieninger, “Drought threatens agroforestry landscapes and dryland livelihoods in a North African hotspot of environmental change,” Landsc Urban Plan, vol. 245, 24. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- S. Nijhuis, “Landscape-Based Urbanism: Cultivating Urban Landscapes Through Design,” in Contemporary Urban Design Thinking, vol. Part F7, Springer Nature, 2022, pp. 249–277. [CrossRef]
- S. Nijhuis, L. Xiong, and D. Cannatella, “Towards a Landscape-based Regional Design Approach for Adaptive Transformation in Urbanizing Deltas,” Research in Urbanism Series, vol. 6, pp. 55–80, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Bürgi; et al. “Integrated landscape approach: Closing the gap between theory and application,” Sustainability (Switzerland), vol. 9, no. 8, p. 1371, Aug. 2017. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Alpak, D. G. Özkan, and T. Düzenli, “Systems approach in landscape design: a studio work,” Int J Technol Des Educ, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 593–611, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. Backhaus, O. fryd, and T. Dam, “Research in landscape architecture_methods and methodology,” in Research in landscape architecture_methods and methodology, A. Van den Brink, D. Bruns, H. Tobi, and S. Bell, Eds., Routledge, 2017, pp. 285–304.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





