1. Introduction
It is true that database systems are the most important component of any modern application as they perform the necessary functions of data management, retrieval, and storage. A well-designed database is a critical point of concern for the organization in order to uphold the integrity of data and efficient operations for maintaining decision-making. This study looks into the design and implementation of a relational database system that enables effective facility management and bookings. The premise on which this whole process takes place is robust database architecture, adhering to the requirements of dynamic application environments, with the intention of scalability, efficiency, and reliability [
1,
2].
The design process begins with the identification of key entities, relationships, and attributes, which would form the basis for the database structure. An Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) provides an abstraction of the relationships among the data elements so as to give the system a logical representation. The process of normalization is used to eliminate redundancy, increase the consistency of data and facilitate better query performances. Significant entities like primary keys as well as foreign keys are assigned properly in order to establish referential integrity and to allow seamless data retrieval across multiple tables [
3,
4,
5].
The complete database implementation holds several different modules like facility information, clients, bookings, and even staff management. All these modules are constructed by using Structured Query Language-created queries which are used in schema creation, data insertion, and retrieval operations. The system accommodates different booking types in place from accommodation reservation, sports facility rental, and event management. Complex reporting and analytics are integrated into the database by using advanced SQL queries, and this enables stakeholders to generate valuable insights into booking trends, customer preferences, and financial performance [
7].
This project will also investigate the effects of unforeseen global events, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, on the database design and development process. The pandemic has resulted in a requirement for more health-related information, remote work tracking, and flexible pricing models. The data system is, therefore, designed to address the dynamic needs of business operations and enhance operational resilience [
8,
9].
This project is thus a well-rounded outline for the design of a facility management database that will ensure data accuracy, improve workflow efficiency, and assist with strategic decision-making. This method in database development ensures that the significance of the integration of SQL-based functions with organized developments is demonstrated in the relational database systems in real-world application optimization [
10].
2. Literature Review
In modern applications, relational database systems (RDBMS) are required to store, retrieve, and manage data efficiently. These database systems adopt structured query languages (SQL) to organize and manipulate data while ensuring data integrity and backing up decision-making processes (Elmasri & Navathe, 2020). The facility and booking management system discussed in this work is congruent with the relational model by employing Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERD) to specifically conceptualize relationships among entities: facilities, clients, bookings, and employees [
11].
ERDs promote the orderly construction of relational systems, whereby entities, attributes, and relationships are mapped. These diagrams ensure the systems are scalable, consistent, and logically flow (Chen, 1976). The facility and booking management system utilizes ERDs to completely remove redundancy and run within a data normalization schema. The aim of normalization is to reduce redundancy and enhance consistency within a relational database [
12]. The designed system has adhered to normalization criteria since the schema was designed in a way that will efficiently support the management of facility, client, and booking data. Constraints on primary and foreign keys are applied for the consistency of data, thus providing an easy way for the interrelated data to be retrieved. SQL queries are essential to defining the schema, inserting data, and developing reports for decision-making purposes. Previous authors have highlighted SQL as capable of executing intricate data operations [
13,
14,
15]. The facility management system employs SQL queries in table creation and population work with 'Facilities Information,' 'Bookings,' and 'Client Details' concerning the various booking categories like sports facilities, lodgings, and event management.
Modern-day database systems integrate business intelligence tools for analyzing trends and generating insights. The system being studied contains SQL-based analytics meant for monitoring booking trends, client preferences, and financial performance. The literature on predictive analytics and decision support highlights databases' roles in them [
16].
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the design of many database systems and brought in considerations for health data, remote work monitoring, and adaptive pricing schemes [
17]. The actual system is adaptable with additional data fields, such as health monitoring records, to ensure adaptability to global happenings that cannot be foreseen.
Scalability is one of the main features of database architecture; the assumption is that as time passes, the load of data will grow, and the database will hold it. Cloud-based relational databases, today, great scalability, as well as the modern best access, will offer all of these [
18]. The next step in the facility booking database development will then include the use of cloud solutions for remote access and processing even larger transaction volumes. Relational databases are decidedly required for structured data management, especially for the facility and booking system [
19,
20,
21]. By using ERDs and normalization techniques, and finally performing analytics based on SQL, the efficiency, integrity, and adaptability of the developing system stand to grow with the needs of the business. Future research can lead to the application of machine learning algorithms in forecasting booking trends and optimization techniques [
22,
23].
3. Proposed Methodology
The development of a relational database management system for facilities and bookings invariably uses a structured methodology for system design, implementation, and evaluation. The methodology starts with an exhaustive requirement analysis to identify key entities, relationships, and attributes based on sufficient concepts for the efficient management of data. By means of an Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), the logical relationships between facilities, clients, bookings, and employees are modeled in a way to ensure a structured and scalable database design. Normalization techniques are introduced to eliminate redundancy and maintain data integrity, declaring Primary and Foreign keys to ensure Referential Integrity.
The implementation phase consists of creating several database tables in structured query language (SQL) to define the schema, input data, and allow data querying. The database is designed with the capability to incorporate different aspects of bookings such as accommodation bookings, sports facilities rentals, and event management to offer a complete facility management solution. To that effect, advanced SQL queries are implemented for complex reporting and analytics, providing stakeholders with insights into the trend of bookings, customer preferences, and fiscal performance.
Being foreseen for adaptability, the system is mindful of unforeseen global circumstances along the lines of COVID-19. Additional fields and tables have been added to track health-related information, remote work monitoring, and flexible price adjustments. Furthermore, the database scales well for possible future migration into the cloud for better access and performance.
The evaluation phase includes testing for functionality, performance, and integrity of the data within the database system. SQL queries are executed to ensure that the retrieval of certain pieces of data is possible within optimal time, and the system is put through stress testing to assess its ability to perform effectively with large datasets. End-user feedback is also being obtained to optimally refine the system in line with the operational requirements of management for facilities and bookings.
This methodology will ensure a robust, scalable, and efficient database system, able to support business intelligence functions while optimal in maintaining data accuracy and security. Future enhancements could involve machine learning techniques to predict booking trends and optimize utilization of the faculties.
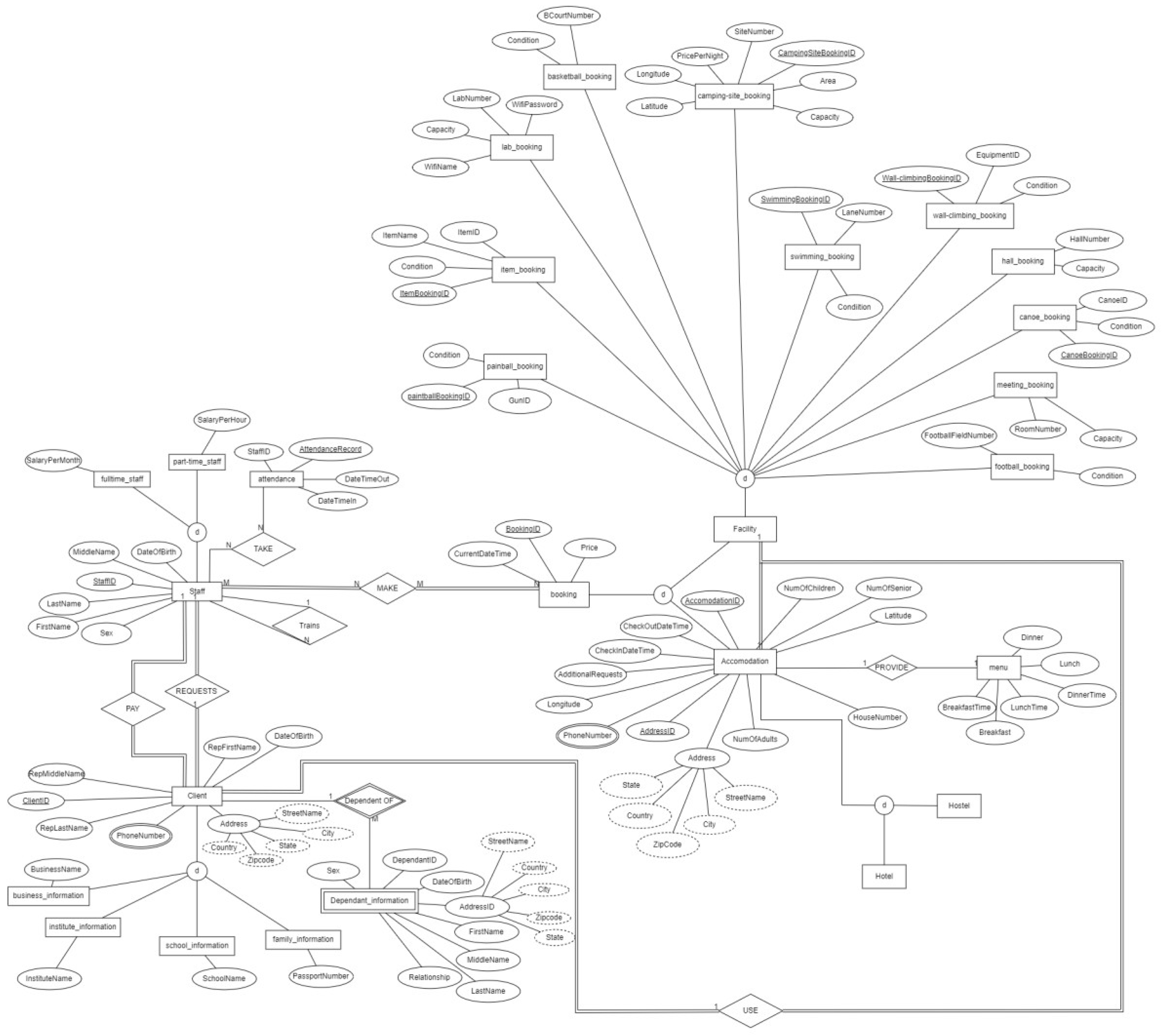
4. Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD)
Figure 1.
(Entity-Relationship Diagram).
Figure 1.
(Entity-Relationship Diagram).
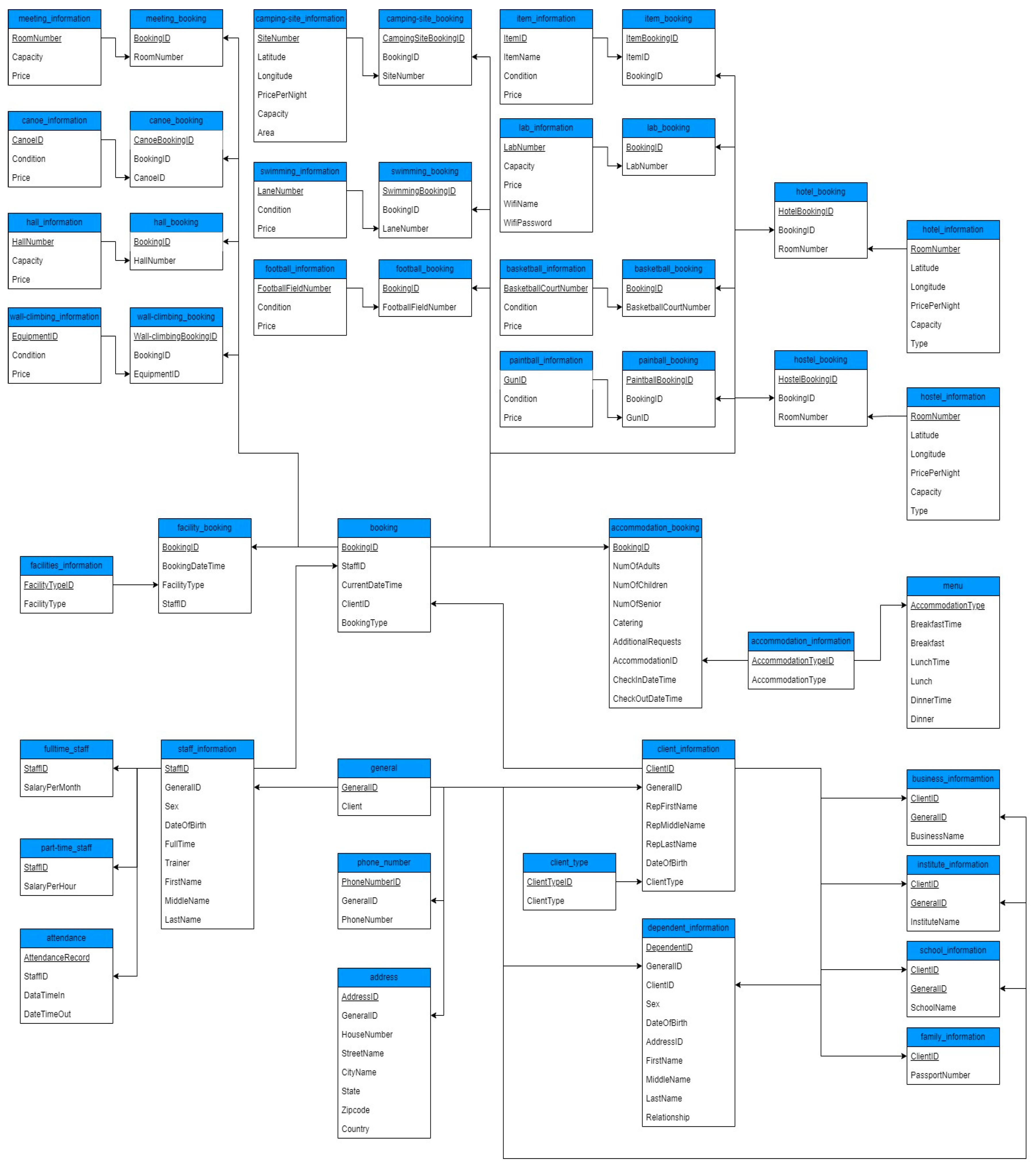
4.1. Physical Model
Figure 2.
(Physical Diagram).
Figure 2.
(Physical Diagram).
4.2. Results and Discussion
Various performance measurements, such as data retrieval efficiency, query execution time, data integrity, and scaling ability, were considered in the evaluation of the relational database system's implementation; the main objective of the system was facility and booking management. Queries were structured to test the working of the system in the evaluation of the accuracy and efficiency with which the data are stored and retrieved.
Database Performance and Query Execution
Using SQL queries, this included data insertion, updates, and retrieval operations which performed optimally with minimal latency. The primary and foreign key indexing improved query execution speed by ensuring rapid access to booking records and facility information. Complex queries involving multiple tables joins and aggregations were processed without difficulties, and they provided significant information about the trends of bookings and financial transactions.
4.2.1. Data Integrity and Consistency
Normalization is performed on the data to reduce redundancy and keep the data consistent. Referential integrity constraints kept the entity's relationships, like those of a client and a booking. Transaction consistency adhered to atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID) for the transactional wrongs that resulted from concurrent transactions.
4.2.2. Scalability and Adaptability of the System
The system's performance is assessed through stress testing and performance testing to see if it can accommodate very large datasets. It was discovered that the database can continue to increase in terms of bookings and client records without considerable degradation in performance. The system is also amenable to enhancements to include new attributes and tables with the changing business requirements, for example, to cater to health-monitoring fields that have been necessitated due to COVID-19.
4.2.3. Analytical Insights and Business Intelligence
The advanced SQL query integration to create analytical reports analyzed customer details such as peak booking time and revenue generation. Also, the reports aided in providing information valuable for decision-making among stakeholders to optimize resource allocation and consequently improve operational efficiencies.
4.2.4. Challenges and Limitations
However, there are some challenges the system encounters, and the complexity of large-scale transaction management and data security will now be covered by some functionality enhancement in the future, such as encryption for data confidentiality or a cloud for better access and scalability.
5. Unforeseen Challenges
Building and Designing a database system would take a lot of constructively due to the influences of the global pandemic to mitigate the fallout from the crisis that began early in 2019. The database would need to integrate other health data like vaccination status and health monitoring metrics for a complete view of patient records. For instance, beyond COVID-19 tests, in view of changing health requirements, it may also need to have specialized tables like Health Monitoring. Specialized tables start to take shape for the monitoring of possible exposure, like Compromise Rooms. Tables like Facility and Activity become superfluous due to lockdown regulations, and the system now needs to be reviewed concerning costs. In this regard, anticipatory changes must be adopted with post-pandemic dimensions. For example, contingent marketing approaches should be balanced into smooth operation with the database design to provide resilience against unforeseen constraints.
A few tables, among which the Employee Remote Work Log Table, are intended to keep track of remote work activity of employees. Supply Chain Inventory Table follows. It is essential for controlling and keeping an eye on supply chain inventory levels. Employee Health Screening Table is another. It is intended to keep an eye on workers' health through routine screenings. Fields like Boolean field where true refers to sanitized and false refers to unsensitized to keep track of covid 19 sanitization. A varchar field like Well-being Score can be added into Employee Health Screening table where marks>70 is considered as passed.
The shift toward remote work and online teamwork also requires strong connectivity features, focusing on safe communication channels within the database. The importance of data redundancy and backup systems is enhanced to assure business continuity against disruptions. Furthermore, the database should enable real-time analytic features to empower timely ad hoc decisions based on insights about pandemic days and changing health trends.
The database financial modules require revaluation considering the economic effects to be in line with moving prices and changing customer needs. The database system, too, should be designed with scale-up capabilities in anticipation of sudden upsurges in user activity, such as increased online reservations or telehealth consultations during peaks of health concern.
6. Conclusions
The database system has brought tremendous improvements in the organization of data for operations, efficiency, and decision-making processes in the implementation and development of a relational database system for scheduling and facility management. This paper considers the critical importance of database architecture in providing apt data management in a scalable manner with the possibility of reusing the system. The entity-relationship design in the ERD formed the basis of the logical structure of the system since it envisaged the proper identification of key entities, relationships, and attributes. The normalizations performed eliminated redundancies from the data resolved within the well-structured and optimized database. In this way, referring integrity through primary and foreign linkages guarantees consistent data across various and related tables and smooth data retrieval. Implementation involved creating a large number of interrelated tables using structured query language (SQL) to capture information about facilities, bookings, clients, and employees. SQL queries were performed successfully the schema creation, insertion, and retrieval processes were transactional. The system was developed with different types of bookings in mind: sports facilities, meeting rooms, and accommodation rentals; therefore, the system was flexible enough for various institutional and business applications.
The incorporation of business intelligence into the database system has provided further enhancements to the overall system functionality. It allowed advanced SQL queries to give stakeholders valuable reports on booking trends, customer preferences, and earnings analysis. These analytical findings were important for strategic planning and optimizing available resources. Tracking financial performance using SQL analytical tools further aided the organization's decision-making process. An emerging factor that was given special attention in this project was how unpredictable global scenarios such as the COVID-19 pandemic would affect the database design. The system was purposely designed to cater for adaptability in terms of allowing for the introduction of more fields on health, remote work tracking, and flexible pricing models. Such a feature guaranteed the resilience of the database in meeting rapid changes in business requirements. The performance assessment of the database system validated its efficiency, scalability, and resiliency. It could manage large amounts of data very quickly with short query execution times and could withstand increasing transactional loads. Stress testing results showed that the database could effectively handle tons of bookings with no or very little degradation in performance. The system has had some successes, but like any other, it has its challenges, including issues of concurrent transactions and issues of data security. While the system has ACID properties in providing transaction integrity, future advances could include adopting encryption techniques for sensitive clients' and financial data. Also, cloud-based database solutions would mean better accessibility and real-time processing of the data to users from different locations. It can be concluded that the relational database system developed in this study provides a broad, usable, and efficient solution to facility and booking management, ensuring accurate data storage and transaction processing while enabling reporting. It is scalable and easily adaptable, which makes it a reliable tool for institutions and businesses that have many bookings. Future extensions, for example adding predictive analytics through machine learning integration, will enhance booking trend optimization and enrich user experience. This study further affirms the importance of a well-structured relational database in modern application environments and its effect on efficiency gains and strategic decision-making.
References
- Lee, J. M., Jung, I. H., & Hwang, K. (2022). Design and Implementation of Database for Shared Facility Reservation System in School. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6(8), 7033-7041.
- Williams, K., & Micheal, A. (2018). Design and Implementation of Reservation Management System Case Study: Grand Ville Hotels. Journal of Information Technology & Software Engineering, 8(04), 1-10.
- Chogo, O. J., & Musinga, J. (2012). Design and implementation of an interactive secure patient appointment booking information system: a case study Kibuli Muslim Hospital (Doctoral dissertation, Kampala International University, School of Computing and Information Technology (SCIT)).
- Amin, N. U., Alsukhailah, A. A., Ghaleb, A. A. F., Mobarak, M. A. A., Algaafari, H. A., Algaafari, H. W., & Zaman, S. (2025). Design and Implementation of a Database System for Event Management Customizer (EMC): A Case-Based Approach.
- Kamil, J., & Amer, M. (2023). An Integrated Room Booking and Access Control System for Public Spaces.
- Saeed, S., & Abdullah, A. (2021). Combination of brain cancer with hybrid K-NN algorithm using statistical analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surgery. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, 21(2), 120-130.
- Saeed, S., & Abdullah, A. (2019). Analysis of lung cancer patients for data mining tool. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, 19(7), 90-105.
- Saeed, S., Abdullah, A., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Naqvi, M., & Nayyar, A. (2022). New techniques for efficiently k-NN algorithm for brain tumor detection. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 81(13), 18595-18616. [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S. (2021). Optimized hybrid prediction method for lung metastases. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.
- Saeed, S., Abdullah, A., & Naqvi, M. (2019). Implementation of Fourier transformation with brain cancer and CSF images. Indian Journal of Science & Technology, 12(37), 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Ronald, W. E., & Fredrick, J. (2009). Design and implementation of an online airline booking system using PHP, MYSQL, JAVA script and cascading style sheets (Doctoral dissertation, Kampala International University, School of Computing and Information Technology).
- Magnifique, U. M. U. R. E. R. W. A. (2024). ONLINE BOOKING WEDDING VENUE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Case study: AmaliTech (Doctoral dissertation, ULK).
- Maulana, R. A., Fatih, M. A., Suto, L. A., & Darwis, M. (2024). Development of Paramadina Roomhub Application As Room Booking System Using Waterfall Method. JISA (Jurnal Informatika dan Sains), 7(2), 176-185.
- Kumar, M. S., Vimal, S., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Dhanabalan, S. S., & Alhumyani, H. A. (2021). Blockchain-based peer-to-peer communication in autonomous drone operation. Energy Reports, 7, 7925-7939. [CrossRef]
- Jhanjhi, N. Z., Humayun, M., & Almuayqil, S. N. (2021). Cybersecurity and privacy issues in industrial Internet of Things. Computer Systems Science & Engineering, 37(3). [CrossRef]
- Lee, S., Abdullah, A., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2020). A review on honeypot-based botnet detection models for smart factory. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 11(6). [CrossRef]
- Khan, N. A., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Brohi, S. N., Almazroi, A. A., & Almazroi, A. A. (2022). A secure communication protocol for unmanned aerial vehicles. CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, 70(1), 601-618. [CrossRef]
- Brohi, S. N., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Brohi, N. N., & Brohi, M. N. (2023). Key applications of state-of-the-art technologies to mitigate and eliminate COVID-19. Authorea Preprints.
- Gill, S. H., Razzaq, M. A., Ahmad, M., Almansour, F. M., Haq, I. U., Jhanjhi, N. Z., ... & Masud, M. (2022). Security and privacy aspects of cloud computing: a smart campus case study. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing, 31(1), 117-128. [CrossRef]
- Muzafar, S., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2020). Success stories of ICT implementation in Saudi Arabia. In Employing Recent Technologies for Improved Digital Governance (pp. 151-163). IGI Global.
- Shah, I. A., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Laraib, A. (2023). Cybersecurity and blockchain usage in contemporary business. In Handbook of Research on Cybersecurity Issues and Challenges for Business and FinTech Applications (pp. 49-64). IGI Global.
- Aldughayfiq, B., Ashfaq, F., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Humayun, M. (2023). Explainable AI for retinoblastoma diagnosis: interpreting deep learning models with LIME and SHAP. Diagnostics, 13(11), 1932. [CrossRef]
- Aherwadi, N., Mittal, U., Singla, J., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Yassine, A., & Hossain, M. S. (2022). Prediction of fruit maturity, quality, and its life using deep learning algorithms. Electronics, 11(24), 4100.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).