Submitted:
28 February 2025
Posted:
03 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
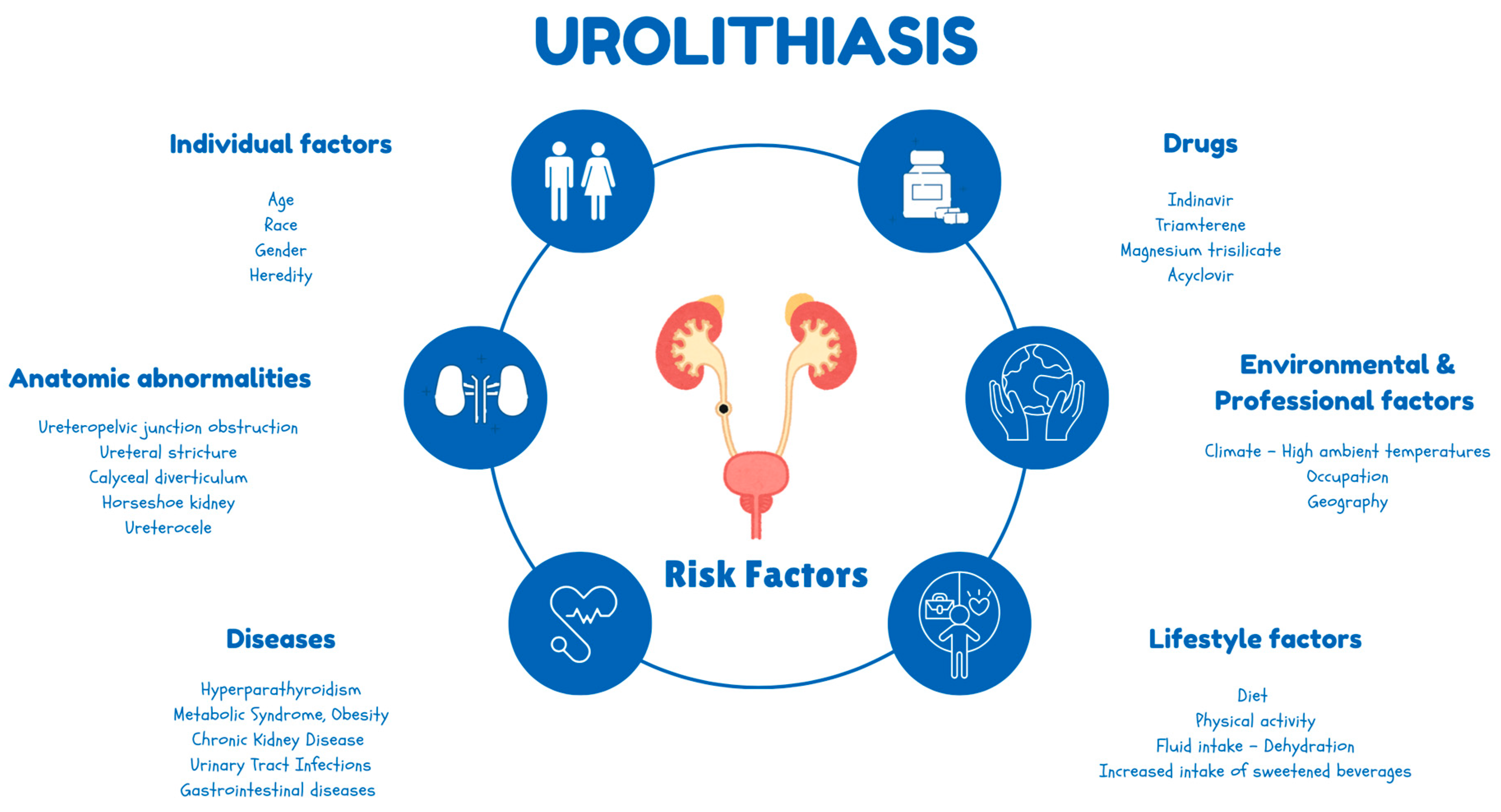
1. Introduction
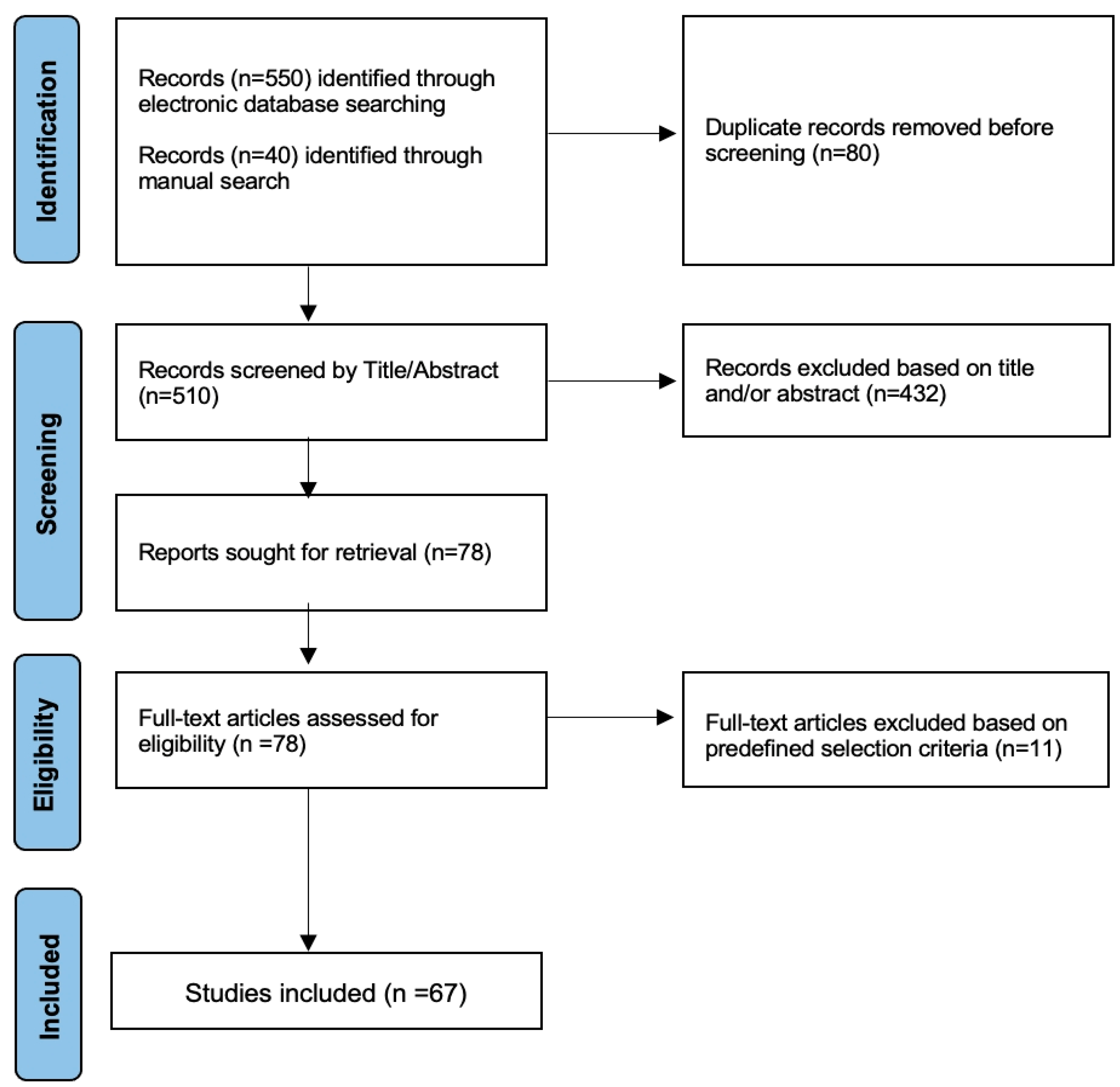
2. Materials and Methods
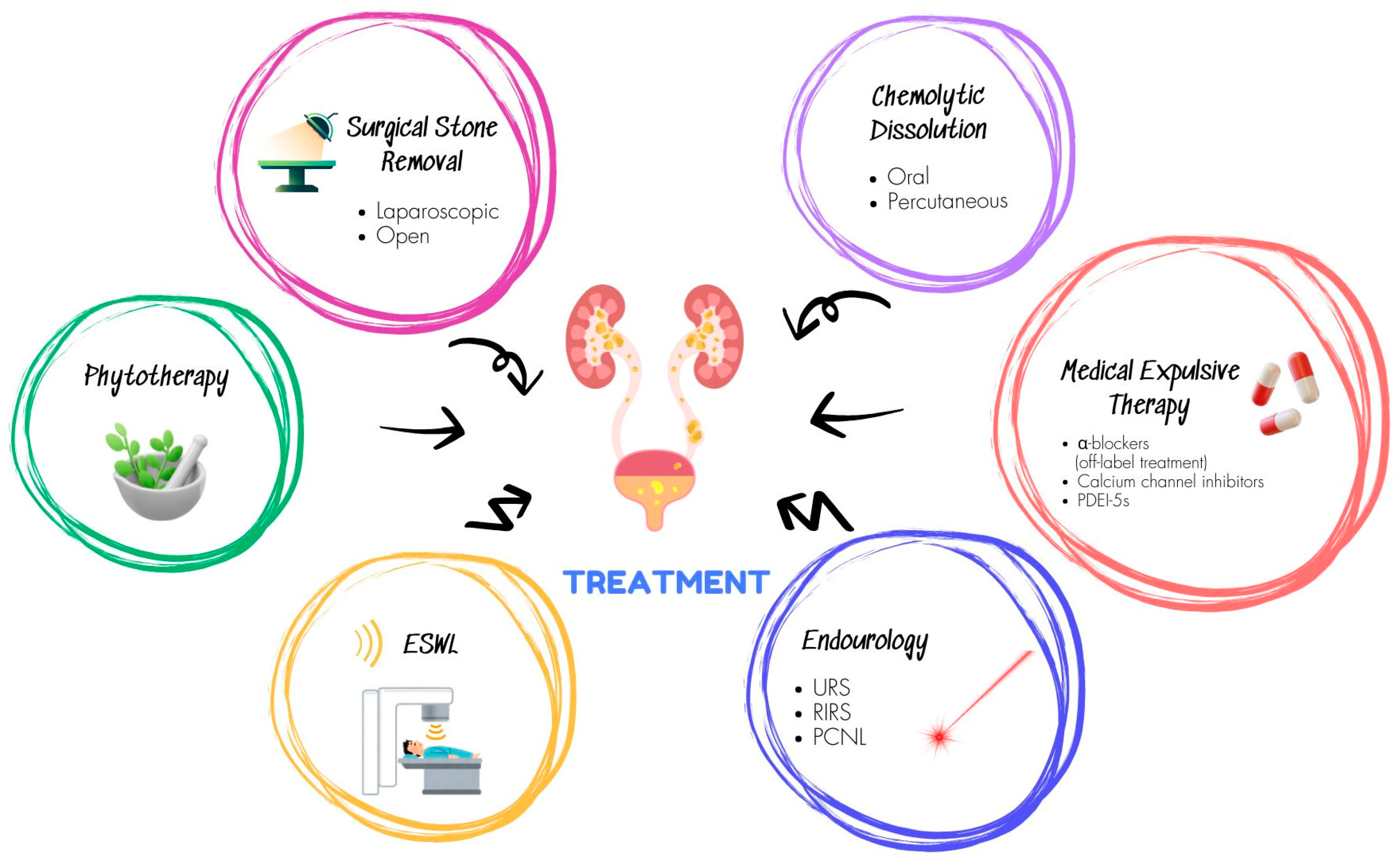
3. Phytotherapy: Current evidence from clinical trials
| Authors, year | Study Type | Regimen | Stone size (mm) | Imaging modality | Recruited/Randomised | Maximum period (months) |
Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singh et al., 2011 [28] | RCT | Sitivaraka Vs Potassium Citrare | ≥8mm | US | 21/ 23 | 6 | -Stone size reduction |
| Pucci et al., 2018 [30] | RCT |
Phyllanthus Niruri (Stone breaker) |
<10mm | USCT | 56 | 26 * | -Increased urinary excretion of magnesium and potassium |
| Cealan et al., 2019 [33] | RCT | P. niruri + Mg + VitB6 | <15mm | NCCT | 48 | 3 | -No change |
| Movaghati et al., 2019 [35] | RCT |
Nigella Sativa (Black Seed) |
≥5mm | US | 30/30 | 10* | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Jalal et al., 2020 [36] |
RCT | Phaseolus vulgaris | ≤10mm | US | 60 | 6* | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Erickson et al., 2011 [37] | RCT and Crossover |
Cystone® | NS | CT | 10 † | 12 | Not effective |
| Palaniyamma and Jeyaraman 2017 [39] | RCT | Cystone® | 5-12mm | US | 65 | 3 | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Patki et al., 2010 [40] | RCT | Cystone® | 5-10mm | X ray US |
26/26 | 6 | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Patankar et al., 2020 [46] | RCT | Subap Plus | 4-9mm | NCCT | 34/31 | 6 | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Samandarian et al., 2023 [47] | RCT | 5 herbal extracts | ≤10mm | US | 27/27 | 4 | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Brardi et al., 2012 [48] | RCT | Potassium citrate + Agropyron repens | NS | US | 25/25 | 5 | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Kristyantoro et al., 2012 [49] | RCT | Renalof vs Kalkurenal vs Placebo | <20mm | X ray US |
13/8/9 | 1 | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Chamorro et al., 2021 [51] | RCT | Renalof vs Placebo | <10mm | US CT |
120/35 | 3 | Increased stone expulsion |
| Sánchez et al., 2012 [52] | RCT | Renalof vs Placebo | <10mm | X ray US CT |
52/58 | 3 | -Stone size reduction -Stone expulsion |
| Caione et al., 2022[53] | RCT | Herniaria hirsuta and Peumus boldus | Small stone fragments | NS | 15/19 | 3 | Stone expulsion post endourology |
| Sountoulides et al, 2024 [54] | RCT | Renalof vs placebo | <2 cm | CT | 82/82 | 3 | -stone surface and stone volume reduction |
4. Phythotherapy: Something to Worry About or Much ado About Nothing?
5. Evidence from Systematic Reviews
6. Strengths, Limitations, and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCNL | Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy |
| RIRS | Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery |
| URS | Ureteroscopy |
| SWL | Shockwave Lithotripsy |
| MET | Medical Expulsive Therapy |
| UTI | Urinary Tract Infections |
| RCTs | Randomized-controlled trials |
References
- Tiselius, H.-G. Epidemiology and medical management of stone disease: EPIDEMIOLOGY and MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF STONE DISEASE. BJU Int. 2003, 91, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, M.; Hoppe, B. History, epidemiology and regional diversities of urolithiasis. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2010, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, H.A.; Wilt, T.J.; Eidman, K.E.; Garimella, P.S.; MacDonald, R.; Rutks, I.R.; Brasure, M.; Kane, R.L.; Ouellette, J.; Monga, M. Medical Management to Prevent Recurrent Nephrolithiasis in Adults: A Systematic Review for an American College of Physicians Clinical Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türk, C.; Petřík, A.; Sarica, K.; Seitz, C.; Skolarikos, A.; Straub, M.; Knoll, T. EAU Guidelines on Interventional Treatment for Urolithiasis. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribarri, J.; Oh, M.S.; Carroll, H.J. The first kidney stone. Ann. Intern. Med. 1989, 111, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswal, M.; Varghese, R.; Zagade, T.; Dhatrak, C.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, D. Dietary supplements and medicinal plants in urolithiasis: diet, prevention, and cure. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2023, 75, 719–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiris, D.; Adamou, K.; Kallidonis, P. Diet and stone formation: a brief review of the literature. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2018, 28, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.W.; Stoller, M.L. Urinary stone disease: a practical guide to metabolic evaluation. Geriatrics 1997, 52, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Karakoç, O.; Karakeçi, A.; Ozan, T.; Fırdolaş, F.; Tektaş, C.; Özkarataş, Ş.E.; Orhan, İ. Comparison of retrograde intrarenal surgery and percutaneous nephrolithotomy for the treatment of renal stones greater than 2 cm. Turk. J. Urol. 2015, 41, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alelign, T.; Petros, B. Kidney Stone Disease: An Update on Current Concepts. Adv. Urol. 2018, 2018, 3068365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.; Ho, H.C.; Pietropaolo, A.; Somani, B.K. Guideline of guidelines for kidney and bladder stones. Turk. J. Urol. 2020, 46, S104–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokubo, I.I.; Wiseman, O. Management of urolithiasis. Surg. Oxf. 2022, 40, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearle, M.S.; Calhoun, E.A.; Curhan, G.C. ; the UROLOGIC DISEASES OF AMERICA PROJECT UROLOGIC DISEASES IN AMERICA PROJECT: UROLITHIASIS. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scales, C.D.; Smith, A.C.; Hanley, J.M.; Saigal, C.S. Prevalence of Kidney Stones in the United States. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patle, A.; Hatware, K.V.; Patil, K.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, G. Role of Herbal Medicine in the Management of Urolithiasis— A Review for Future Perspectives. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2019, 38, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürocak, S.; Küpeli, B. Consumption of historical and current phytotherapeutic agents for urolithiasis: a critical review. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirumand, M.; Hajialyani, M.; Rahimi, R.; Farzaei, M.; Zingue, S.; Nabavi, S.; Bishayee, A. Dietary Plants for the Prevention and Management of Kidney Stones: Preclinical and Clinical Evidence and Molecular Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Yang, H.; Peng, J. Therapeutic effects of Chinese herbal medicines for treatment of urolithiasis: A review. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, R.; Monga, M. Use of traditional Chinese medicine in the management of urinary stone disease. Int. Braz J Urol Off. J. Braz. Soc. Urol. 2009, 35, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Idrees, M. Progress and prospects in the management of kidney stones and developments in phyto-therapeutic modalities. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 205873841984822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, G.; Akram, M.; Jabeen, F.; Ali Shah, S.M.; Munir, N.; Daniyal, M.; Riaz, M.; Tahir, I.M.; Ghauri, A.O.; Sultana, S.; et al. Therapeutic potential of medicinal plants for the management of urinary tract infection: A systematic review. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterweck, V.; Khan, S.R. Herbal medicines in the management of urolithiasis: alternative or complementary? Planta Med. 2009, 75, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Mishra, A.; Chandel, S.S.; Agarwal, M.; Chawra, H.S.; Singh, M.; Dubey, G. Unlocking New Approaches to Urolithiasis Management ViaNutraceuticals. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2024, 25, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Xi, Y.; Jiang, W. Protective roles of flavonoids and flavonoid-rich plant extracts against urolithiasis: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.; Aro, T.; Matlaga, B.R. Buyer Beware: Evidence-Based Evaluation of Dietary Supplements for Nephrolithiasis. J. Endourol. 2020, 34, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasote, D.M.; Jagtap, S.D.; Thapa, D.; Khyade, M.S.; Russell, W.R. Herbal remedies for urinary stones used in India and China: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 203, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupisti, A.; Giannese, D.; D’Alessandro, C.; Benedetti, A.; Panichi, V.; Alfieri, C.; Castellano, G.; Messa, P. Kidney Stone Prevention: Is There a Role for Complementary and Alternative Medicine? Nutrients 2023, 15, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Bishnoi, I.; Agarwal, V.; Bhatt, S. Prospective randomized clinical trial comparing phytotherapy with potassium citrate in management of minimal burden (≤8 mm) nephrolithiasis. Urol. Ann. 2011, 3, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, J.B.; Santos, A.R.; Cechinel Filho, V.; Yunes, R.A. A review of the plants of the genus Phyllanthus: their chemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic potential. Med. Res. Rev. 1998, 18, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, N.D.; Marchini, G.S.; Mazzucchi, E.; Reis, S.T.; Srougi, M.; Evazian, D.; Nahas, W.C. Effect of phyllanthus niruri on metabolic parameters of patients with kidney stone: a perspective for disease prevention. Int. Braz J Urol Off. J. Braz. Soc. Urol. 2018, 44, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boim, M.A.; Heilberg, I.P.; Schor, N. Phyllanthus niruri as a promising alternative treatment for nephrolithiasis. Int. Braz J Urol Off. J. Braz. Soc. Urol. 2010, 36, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiliani, E.; Jara, A.; Kanashiro, A.K. Phytotherapy and Herbal Medicines for Kidney Stones. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cealan, A.; Coman, R.-T.; Simon, V.; Andras, I.; Telecan, T.; Coman, I.; Crisan, N. Evaluation of the efficacy of Phyllanthus niruri standardized extract combined with magnesium and vitamin B6 for the treatment of patients with uncomplicated nephrolithiasis. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2019, 92, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.; Olweny, E.O. Phyllanthus niruri (stone breaker) herbal therapy for kidney stones; a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical efficacy, and Google Trends analysis of public interest. Can. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 10162–10166. [Google Scholar]
- Ardakani Movaghati, M.R.; Yousefi, M.; Saghebi, S.A.; Sadeghi Vazin, M.; Iraji, A.; Mosavat, S.H. Efficacy of black seed (Nigella sativa L.) on kidney stone dissolution: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Phytother. Res. PTR 2019, 33, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, S.M.; Alsultan, A.A.; Alotaibi, H.H.; Mary, E.; Alabdullatif, A.A.I. Effect of Phaseolus Vulgaris on Urinary Biochemical Parameters among Patients with Kidney Stones in Saudi Arabia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, S.B.; Vrtiska, T.J.; Lieske, J.C. Effect of Cystone® on Urinary Composition and Stone Formation Over a One Year Period. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2011, 18, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patki, P.S. Cystone in cystine stone formers. Urol. Res. 2011, 39, 323–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniyamma, D.; Jeyaraman, R. Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of a Herbal Formulation Cystone Forte in the Management of Urolithiasis. 2017.
- Patki, P. Safety and Efficacy of an Ayurvedic Formulation Cystone in Management of Ureteric Calculi: A Prospective Randomized Placebo Controlled Study. Am. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, N.K.; Nayak, R.L.; Patki, P.S. Safety and Efficacy of an Ayurvedic Formulation Cystone in Management of Ureteric Calculi: A Prospective Randomized Placebo Controlled Study. Am. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 5, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar Kumaran, M.G.; Patki, P.S. Evaluation of an Ayurvedic formulation (Cystone), in urolithiasis: A double blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2011, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarfar, A.; Rafiee, Z.; Ravanshad, Y.; Saber Moghadam, N.; Bakhtiari, E. Effect of Herbal Formulation “Cystone®” on Urolithiasis. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Tsai, K.-S.; Chiang, J.-H.; Muo, C.-H.; Sung, F.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, W.-C. Long-Term Therapy With Wu-Ling-San, a Popular Antilithic Chinese Herbal Formula, Did Not Prevent Subsequent Stone Surgery. Inq. J. Med. Care Organ. Provis. Financ. 2016, 53, 0046958016681148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Ho, L.; Lin, M.-S.; Huang, M.-H.; Chen, W.-C. Wu-Ling-San Formula Prophylaxis Against Recurrent Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis - A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Patankar, S.B.; Mujumdar, A.M.; Bernard, F.; Supriya, P. Safety and efficacy of an herbal formulation in patients with renal calculi - A 28 week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2020, 11, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samandarian, S.; Soltani, R.; Hajhashemi, V.; Dehghani, M.; Matinfar, M.; Mahboubi, M.; Mohsenzadeh, A. Efficacy of an Oral Solution Containing Five Herbal Extracts in the Treatment of Urolithiasis: A Randomized, Single-blind, Placebo-controlled Clinical Trial. J. Res. Pharm. Pract. 2023, 12, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brardi, S.; Imperiali, P.; Cevenini, G.; Verdacchi, T.; Ponchietti, R. Effects of the association of potassium citrate and agropyrum repens in renal stone treatment: results of a prospective randomized comparison with potassium citrate. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. Organo Uff. Soc. Ital. Ecogr. Urol. E Nefrol. 2012, 84, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kristyantoro, B.; Alif, S.; Djojodimedjo, T.; Budiono, B. THE EFFECTIVENESS OF RENALOF® COMPARED TO KALKURENAL® AND PLACEBO. Indones. J. Urol. 2012, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolami, M.; Di Matteo, P.; Rocco, D.; Feroci, M.; Petrucci, R. Metabolic Profile of Agropyron repens (L.) P. Beauv. Rhizome Herbal Tea by HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS/MS Analysis. Molecules 2022, 27, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, M.M.A.; Collado, S.A.V.; Márquez, D. Effectiveness of Using Renalof® in the Elimination of Kidney Stones under 10 mm Located in the Renal-Ureteral Tract. Open J. Nephrol. 2021, 11, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.C.A.; Villanueva, V.E.; Vázquez, R.A. Randomized double-blind study with Renalof in patients with calcium oxalate renal lithiasis. Rev. Cuba. Investig. Biomed. 2012, 31, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Caione, P.; Salerno, A.; Collura, G.; De Dominicis, M.; Innocenzi, M.; Martucci, C.; Capozza, N. Phytotherapy as ancillary treatment after urinary stone lithotripsy in pediatric age. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2022, 92, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Petros, S. A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study of Agropyron Repens, Mannitol and Magnesium Supplement for the Treatment of Calcium Oxalate Upper Urinary Tract Stones: The AMMOS Study; clinicaltrials.gov, 2023.
- Aydιn, A.; Aktay, G.; Yesilada, E. A Guidance Manual for the Toxicity Assessment of Traditional Herbal Medicines. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekor, M. The growing use of herbal medicines: issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jităreanu, A.; Trifan, A.; Vieriu, M.; Caba, I.-C.; Mârțu, I.; Agoroaei, L. Current Trends in Toxicity Assessment of Herbal Medicines: A Narrative Review. Processes 2023, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbens, A.; Pearle, M.S. Causes and prevention of kidney stones: separating myth from fact. BJU Int. 2021, 128, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegra, S.; De Francia, S.; Turco, F.; Bertaggia, I.; Chiara, F.; Armando, T.; Storto, S.; Mussa, M.V. Phytotherapy and Drugs: Can Their Interactions Increase Side Effects in Cancer Patients? J. Xenobiotics 2023, 13, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, E.; Trinchieri, A.; Magri, V.; Cleves, A.; Perletti, G. Herbal medicines for urinary stone treatment. A systematic review. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. Organo Uff. Soc. Ital. Ecogr. Urol. E Nefrol. 2016, 88, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, E.A.H.; Sabra, M.S. Plant-based therapies for urolithiasis: a systematic review of clinical and preclinical studies. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2024, 56, 3687–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Bashir, S.; Khan, S.R. Antiurolithic effects of medicinal plants: results of in vivo studies in rat models of calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis-a systematic review. Urolithiasis 2021, 49, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Thorne, S.; Malterud, K. Time to challenge the spurious hierarchy of systematic over narrative reviews? Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 48, e12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhera, J. Narrative Reviews: Flexible, Rigorous, and Practical. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2022, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Bhatia, G. Writing and appraising narrative reviews. J. Clin. Sci. Res. 2021, 10, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borumandnia, N.; Fattahi, P.; Talebi, A.; Taheri, M.; Alvani, M.S.; Balani, M.M.; Ashrafi, S.; Alavimajd, H. Longitudinal trend of urolithiasis incidence rates among world countries during past decades. BMC Urol. 2023, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Urolithiasis from 1990 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Clin. Epidemiol. 2022, 14, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





