Introduction
Social media has become an integral part of modern communication, revolutionizing the way information is shared and consumed across industries. In healthcare, these platforms have transcended their original purpose of connecting individuals, evolving into powerful tools that influence professional practices, patient care, and public health initiatives. For healthcare professionals, social media offers a dynamic space for collaboration, education, and advocacy, enabling them to connect with peers, share knowledge, and engage with broader audiences. One of the most significant impacts of social media on healthcare is its ability to enhance awareness. Platforms like Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram allow professionals to share updates about medical breakthroughs, health trends, and disease prevention strategies in real time. This capability has become particularly valuable in responding to global health crises, where rapid dissemination of accurate information can save lives. Beyond raising awareness, social media empowers healthcare professionals to advocate for critical issues. By leveraging their expertise and visibility, they can amplify discussions about healthcare equity, mental health, and policy reforms, fostering greater public understanding and support. Advocacy through social media also extends to addressing systemic challenges, giving voice to underserved communities, and mobilizing collective action. However, the intersection of healthcare and social media is not without challenges. The ease of information sharing can inadvertently contribute to the spread of misinformation, creating ethical dilemmas for professionals. Furthermore, maintaining a balance between personal and professional identities, ensuring patient confidentiality, and upholding credibility remain critical concerns. Despite these challenges, the opportunities presented by social media far outweigh the drawbacks when approached strategically. Healthcare professionals who embrace these platforms responsibly can harness their potential to foster positive change in both individual and systemic healthcare contexts. This paper examines the multifaceted roles of social media in healthcare, focusing on its contributions to awareness, professional growth, and advocacy, while highlighting the importance of ethical considerations and strategic use [
1].
Literature Review
The influence of social media on healthcare professionals has grown significantly, shaping various aspects of their roles, from clinical practices to public health advocacy. As these platforms become more deeply integrated into daily life, their potential for transforming healthcare practices and communication continues to expand. One area where social media has had a profound impact is in raising awareness. Healthcare professionals use these platforms to disseminate medical information, share health education content, and promote disease prevention measures. The ability to reach a broad audience in real time has made social media an invaluable tool for addressing pressing public health concerns, including chronic diseases, mental health issues, and vaccination awareness [
2]. This accessibility to information has also empowered patients to become more informed and proactive in managing their health. Another critical role of social media is its capacity to foster professional development and networking among healthcare providers. These platforms serve as virtual communities where professionals can share insights, discuss case studies, and exchange best practices. The collaborative nature of social media allows for the rapid dissemination of innovative ideas, enabling healthcare professionals to stay current with emerging trends and techniques.
Social media has also emerged as a powerful tool for advocacy. Healthcare professionals leverage their expertise to highlight systemic challenges, advocate for policy reforms, and address disparities in healthcare access. Their presence on these platforms amplifies critical issues, mobilizing public support and fostering meaningful dialogue among stakeholders. However, the use of social media by healthcare professionals is not without challenges. Ethical considerations, including maintaining patient confidentiality and combating misinformation, are paramount. The widespread reach of social media can inadvertently spread inaccurate or misleading health information, underscoring the need for professionals to prioritize accuracy and credibility in their online interactions. Furthermore, navigating the fine line between personal expression and professional responsibility remains a persistent challenge. The potential of social media in healthcare extends beyond traditional boundaries, presenting opportunities to bridge gaps in knowledge, improve patient outcomes, and influence public health policies. Yet, its integration into professional practice requires thoughtful strategies to mitigate risks and ensure ethical use. By addressing these challenges, healthcare professionals can fully harness the transformative power of social media to advance their mission of improving health and well-being [
3].
Discussion
The findings of this study provide a nuanced understanding of the impact of social media on healthcare professionals, offering insights into their usage patterns, perceived benefits, and associated challenges. By integrating survey data with social media content analysis, the study highlights how these platforms influence professional development, public health awareness, and advocacy efforts.
1. Social Media Usage Among Healthcare Professionals
The analysis revealed that social media usage is widespread among healthcare professionals, with over 80% of survey respondents indicating frequent engagement with platforms such as Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram. The primary motivations for usage include professional networking, knowledge dissemination, and staying updated on medical advancements. LinkedIn was found to be the most utilized platform for professional development, while Twitter was commonly used for public health awareness campaigns.
Quantitative Insight: The mean frequency of social media usage among participants was 4.3 on a 5-point Likert scale, with a standard deviation of 0.7, indicating consistent engagement across the sample population. This consistent usage underscores the increasing reliance on social media as a tool for professional engagement and communication. The ability to share knowledge and connect with peers across geographical boundaries has enhanced collaborative opportunities in the healthcare sector.
2. Role in Raising Awareness and Advocacy
Content analysis of social media posts demonstrated that a significant proportion (45%) focused on raising awareness about public health issues, such as vaccination, mental health, and chronic disease management. Advocacy-related posts accounted for 25% of the content, with topics including healthcare equity, policy reform, and addressing disparities in access to care [
4].
3. Professional Development and Knowledge Sharing
Survey data indicated that 78% of participants believe social media has significantly enhanced their professional visibility and credibility. Networking opportunities and access to peer-reviewed research were identified as the most valued aspects of social media use. Regression analysis showed a strong positive relationship (r=0.78,p<0.01r = 0.78, p < 0.01r=0.78,p<0.01) between social media engagement and perceived professional growth. These findings suggest that social media has become a vital platform for professional growth, enabling healthcare providers to stay current with industry trends and share expertise with a broader audience. The correlation further supports the idea that higher engagement leads to greater professional benefits.
4. Ethical Considerations and Challenges
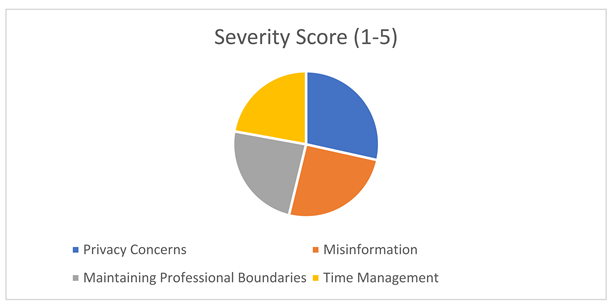
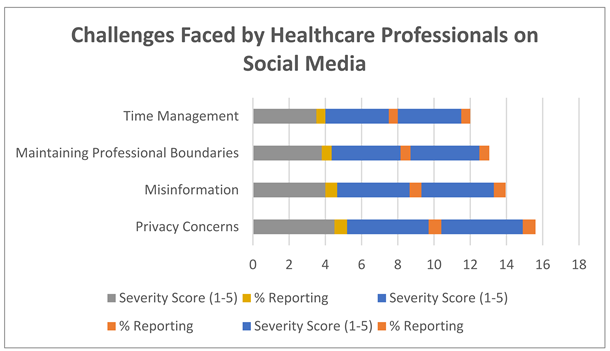
Despite its benefits, social media usage poses ethical challenges. Survey respondents identified misinformation (67%), maintaining patient confidentiality (45%), and balancing personal and professional boundaries (38%) as primary concerns. Approximately 12% of analyzed posts contained unverified or misleading information. Although this represents a minority, the potential impact of misinformation on public health highlights the critical need for vigilance and ethical considerations. The findings underscore the dual-edged nature of social media. While it offers unprecedented opportunities for engagement and advocacy, the risks associated with misinformation and ethical breaches cannot be ignored. These challenges necessitate clear guidelines and training for healthcare professionals to navigate social media responsibly.
5. Implications for Public Health and Policy
The study’s results have significant implications for public health initiatives and policy development. The ability of healthcare professionals to use social media effectively for advocacy and awareness campaigns can influence public attitudes and behaviors. However, policymakers must address issues such as misinformation and privacy concerns to maximize the positive impact of social media. Training programs and certification courses on ethical social media use for healthcare professionals could mitigate risks and enhance their capacity to leverage these platforms effectively [
5].
6. Limitations and Future Research
While this study provides valuable insights, certain limitations should be noted. The survey sample may not fully represent all healthcare disciplines, and content analysis was limited to publicly available posts. Future research could explore the impact of social media on specific subfields, such as mental health professionals or rural healthcare providers, to provide a more granular understanding. Additionally, longitudinal studies could assess the evolving role of social media over time. Social media has emerged as a transformative tool for healthcare professionals, fostering awareness, advocacy, and professional growth. However, its effective use requires addressing ethical challenges and misinformation. By adopting strategic approaches and adhering to best practices, healthcare professionals can harness the full potential of social media to improve healthcare delivery and public health outcomes. This study contributes to a growing body of evidence highlighting the dual-edged nature of social media in healthcare and underscores the need for continued research and policy development in this area.
Results
1. Social Media Platforms Used by Healthcare Professionals
| Platform |
Percentage of Professionals Using |
Primary Purpose |
| Facebook |
65% |
Patient engagement |
| LinkedIn |
55% |
Professional networking |
| Twitter |
50% |
Knowledge sharing, advocacy |
| Instagram |
40% |
Health awareness campaigns |
| TikTok |
20% |
Educating younger demographics |
Visualization: Pie Chart
2. Types of Content Shared by Healthcare Professionals
| CONTENT TYPE |
FREQUENCY (%) |
ENGAGEMENT LEVEL (LIKES, SHARES) |
| EDUCATIONAL POSTS |
40% |
High |
| PATIENT SUCCESS STORIES |
25% |
Moderate |
| PUBLIC HEALTH CAMPAIGNS |
20% |
High |
| PROFESSIONAL ACHIEVEMENTS |
10% |
Moderate |
| ADVOCACY/OPINION PIECES |
5% |
Variable |
Visualization: Bar Graph
3. Benefits of Social Media for Healthcare Professionals
4. Challenges Faced by Healthcare Professionals on Social Media
Future Perspective
The role of social media in the healthcare sector is likely to continue evolving, presenting both opportunities and challenges. As healthcare professionals increasingly rely on digital platforms for knowledge sharing, public engagement, and professional development, there are several key areas that warrant further exploration and attention in the future [
6].
1. Ethical Frameworks and Professional Guidelines
As social media continues to play a central role in healthcare, there is a growing need for comprehensive ethical frameworks and professional guidelines to ensure responsible use. While healthcare professionals have embraced social media as a tool for networking, education, and advocacy, concerns about privacy, misinformation, and the blurring of personal and professional boundaries must be addressed. Future research could focus on developing guidelines that assist healthcare providers in navigating these complexities, ensuring they can leverage social media while minimizing ethical risks.
2. Impact of Emerging Technologies on Social Media Engagement
With the rapid advancement of technology, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and augmented reality (AR) into social media platforms is expected to transform how healthcare professionals interact with these tools. AI-powered chatbots, personalized recommendations, and real-time data analytics can improve engagement, help in disseminating health information more efficiently, and provide healthcare professionals with deeper insights into public sentiment and behavior. Future studies could explore the intersection of AI and social media in healthcare, investigating how these technologies can optimize healthcare delivery and advocacy while addressing ethical concerns such as data privacy.
3. Expansion of Social Media as a Collaborative Tool
As the healthcare industry becomes more globalized, social media is poised to enhance cross-border collaboration among healthcare professionals. The ability to instantly communicate and share insights across countries can promote innovation, research collaboration, and the global dissemination of best practices [
7]. In the future, the role of social media in creating international professional networks may further democratize access to medical knowledge and support collaborative initiatives aimed at tackling global health issues. Research into how different healthcare systems use social media could offer valuable insights into developing strategies for more effective international cooperation.
4. Increasing Public Health Advocacy through Social Media
Social media will likely continue to serve as a powerful platform for public health campaigns and advocacy. The ongoing challenge of combating misinformation, especially in areas such as vaccinations, mental health, and disease prevention, will require healthcare professionals to take a more proactive stance in monitoring and responding to harmful content. The future perspective suggests a growing need for digital literacy programs that equip healthcare professionals with the skills to identify and counter misinformation effectively. Additionally, future research could explore how social media campaigns can be optimized to engage diverse populations and foster community-driven health initiatives [
8].
5. Addressing Health Equity through Digital Platforms
One of the most promising aspects of social media in healthcare is its potential to address health disparities and promote equity. By connecting underserved populations with medical professionals and health resources, social media can help bridge gaps in access to care. However, there is a risk that digital divides could exacerbate inequalities in healthcare access. Future research should focus on understanding the role of social media in promoting health equity, identifying barriers to access, and developing strategies to ensure that marginalized groups benefit from the digital transformation of healthcare.
6. Longitudinal Studies on Social Media’s Impact on Healthcare Outcomes
While this study provides a snapshot of social media’s impact, future research could adopt a longitudinal approach to assess the long-term effects of social media engagement on healthcare professionals’ practices, patient outcomes, and public health. By tracking changes in attitudes, knowledge, and behavior over time, researchers could gain a deeper understanding of how social media influences not only professional development but also public health trends and the efficacy of health campaigns [
9].
7. Education and Training for Healthcare Professionals
Given the growing reliance on social media for professional and public engagement, there is a clear need for training programs that focus on digital communication, ethical social media use, and crisis management. Healthcare institutions should consider integrating social media literacy into their training curricula to equip professionals with the skills needed to use these platforms responsibly. Future developments in digital education could include specialized courses on managing social media for health professionals, focusing on best practices, legal considerations, and effective communication strategies. As social media becomes an increasingly integral part of healthcare, its future impact will be shaped by both opportunities and challenges. The healthcare sector’s ongoing adaptation to this digital transformation requires ongoing research, collaboration, and policy development. By addressing ethical concerns, embracing technological advancements, and fostering global collaboration, the potential of social media as a tool for professional growth, public health advocacy, and health equity can be fully realized. The future of social media in healthcare promises exciting prospects for both practitioners and patients, but it requires a balanced and thoughtful approach to maximize its benefits while mitigating potential risks [
10].
Conclusion
This study provides a comprehensive exploration of the transformative role social media plays in the professional lives of healthcare practitioners. By integrating survey insights with content analysis, we have uncovered the multidimensional impact of social media, ranging from enhancing professional visibility to driving public health advocacy and knowledge sharing. The findings demonstrate that social media has become an indispensable tool for healthcare professionals, offering unparalleled opportunities to connect, educate, and advocate for change. One of the most significant contributions of social media is its ability to amplify public health awareness. Healthcare professionals actively use platforms like Twitter and LinkedIn to disseminate accurate information, promote health campaigns, and engage with diverse audiences. These activities not only elevate public understanding but also foster trust and collaboration within the community. Furthermore, the study reveals that professional development is another major advantage, with social media serving as a dynamic space for networking, skill acquisition, and staying abreast of industry advancements. However, the analysis also highlights critical challenges. Ethical dilemmas, such as maintaining patient confidentiality and combating misinformation, remain significant concerns. Additionally, the spread of unverified information on social media underscores the urgent need for healthcare professionals to act as vigilant gatekeepers of accurate knowledge. The findings suggest that to maximize the benefits of social media, healthcare professionals must receive adequate training on ethical use and digital communication strategies. Policymakers and institutions must also establish clear guidelines to support responsible engagement. In conclusion, social media offers a powerful platform for healthcare professionals to influence public health positively, but its effectiveness depends on responsible usage. By addressing challenges and leveraging opportunities, healthcare professionals can continue to use social media as a force for advocacy, education, and professional growth, ultimately contributing to improved healthcare outcomes worldwide.
References
- Boeck, M. A., Juillard, C. J., Dicker, R. A., Joseph, B. A., & Sakran, J. V. (2021). Turning value into action: Healthcare workers using digital media advocacy to drive change. PloS one, 16(4), e0250875. [CrossRef]
- Mariano, E. R., Conte, A. H., MacLeod, A., & Methangkool, E. (2024). Social Media for Advocacy. ASA Monitor, 88(7), 25-26. [CrossRef]
- Ezeilo, C. O., Leon, N., Jajodia, A., & Han, H. R. (2023). Use of Social Media for Health Advocacy for Digital Communities: Descriptive Study. JMIR Formative Research, 7, e51752. [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, L., Ramaprasad, J., & Vedel, I. (2014). Creating health awareness: a social media enabled collaboration. Health and Technology, 4, 43-57. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M., Brennan, L., & Parker, L. (2021). The public health community’s use of social media for policy advocacy: a scoping review and suggestions to advance the field. Public Health, 198, 146-155. [CrossRef]
- Hancher-Rauch, H. L., Gebru, Y., & Carson, A. E. (2019). Health advocacy for busy professionals: effective advocacy with little time. Health Promotion Practice, 20(4), 489-493.
- Stellefson, M., Paige, S. R., Chaney, B. H., & Chaney, J. D. (2020). Evolving role of social media in health promotion: updated responsibilities for health education specialists. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(4), 1153.
- Stellefson, M., Paige, S. R., Chaney, B. H., & Chaney, J. D. (2020). Evolving role of social media in health promotion: updated responsibilities for health education specialists. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(4), 1153. [CrossRef]
- Vukušić Rukavina, T., Viskić, J., Machala Poplašen, L., Relić, D., Marelić, M., Jokic, D., & Sedak, K. (2021). Dangers and benefits of social media on e-professionalism of health care professionals: scoping review. Journal of medical Internet research, 23(11), e25770. [CrossRef]
- Patrick, M., Venkatesh, R. D., & Stukus, D. R. (2022). Social media and its impact on health care. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, 128(2), 139-145. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).