Submitted:
11 April 2025
Posted:
15 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
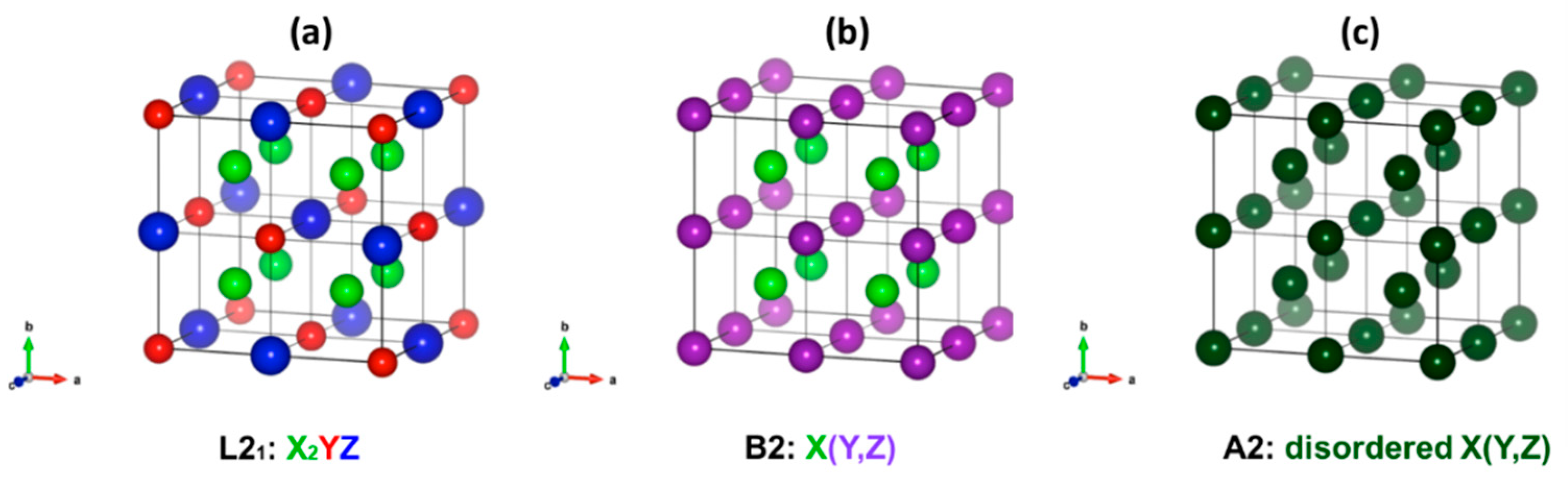
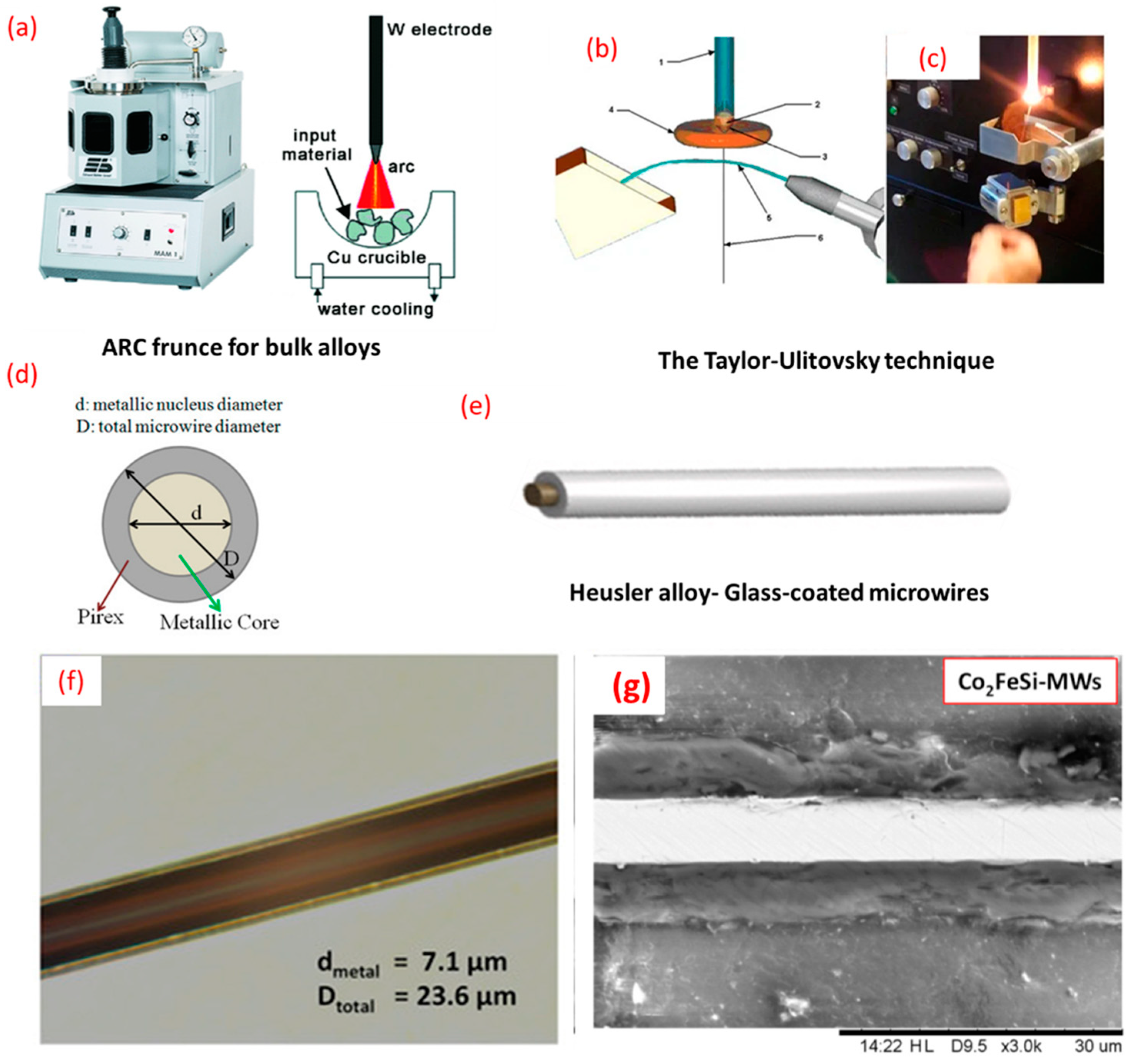
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
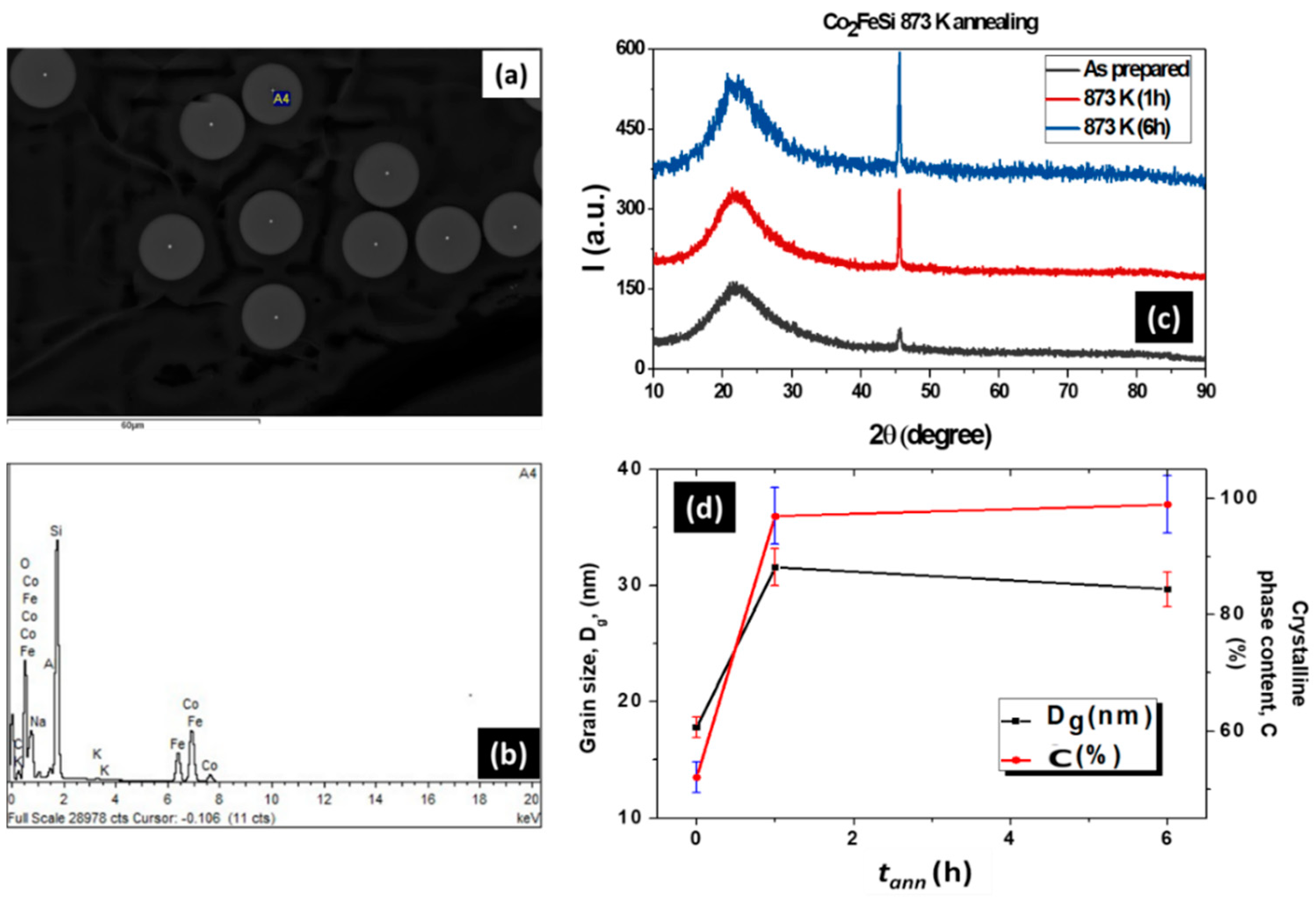
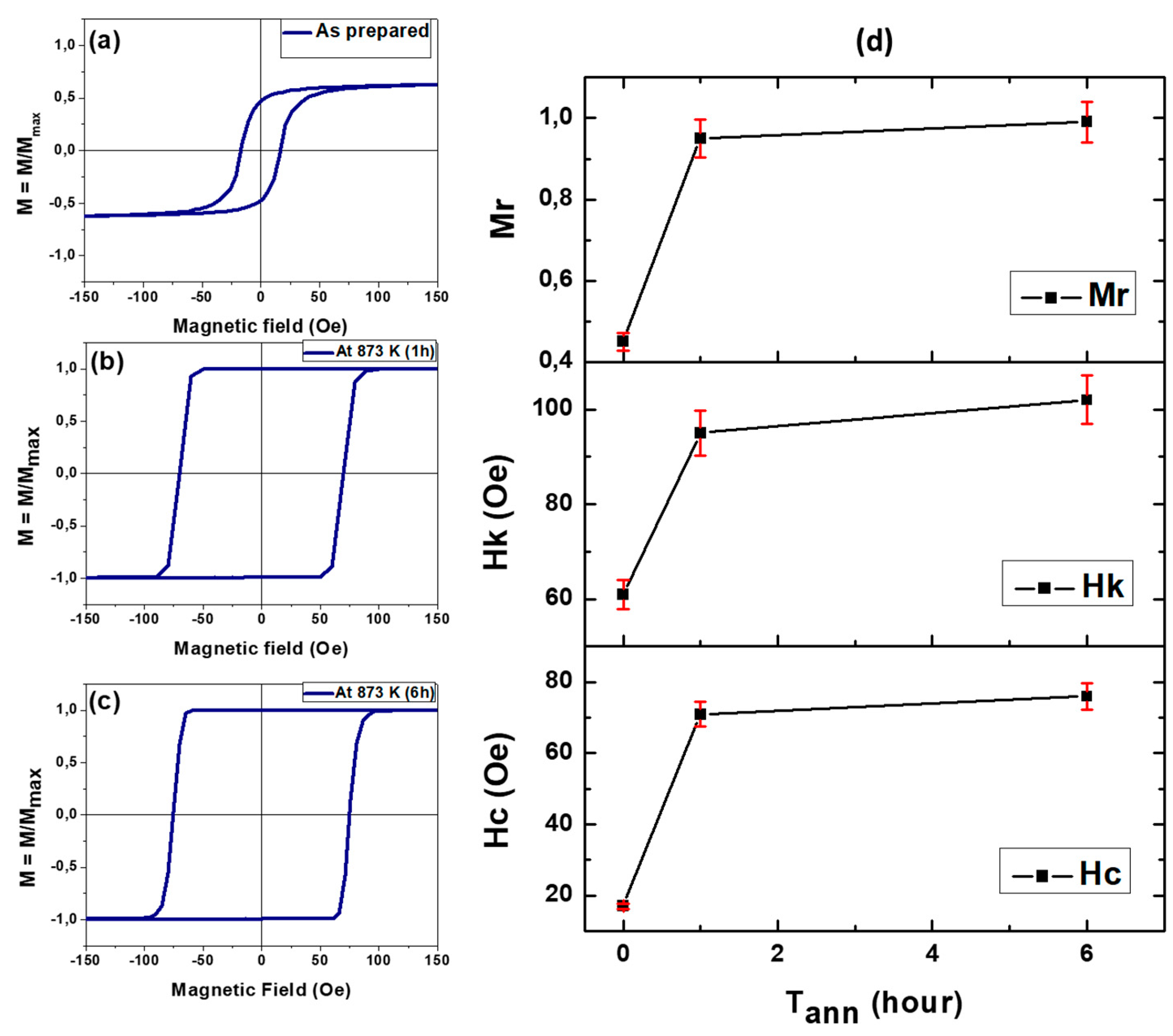
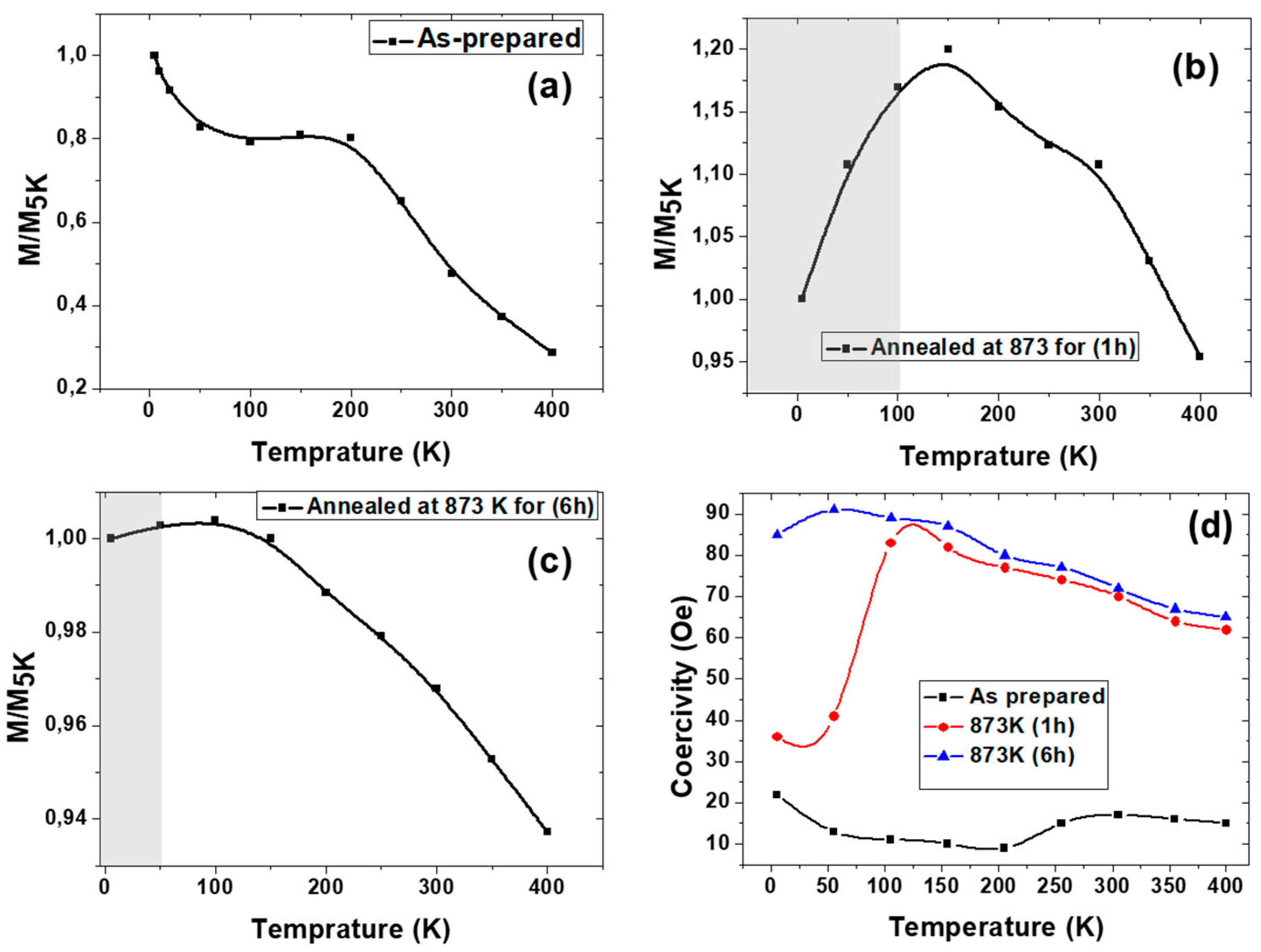
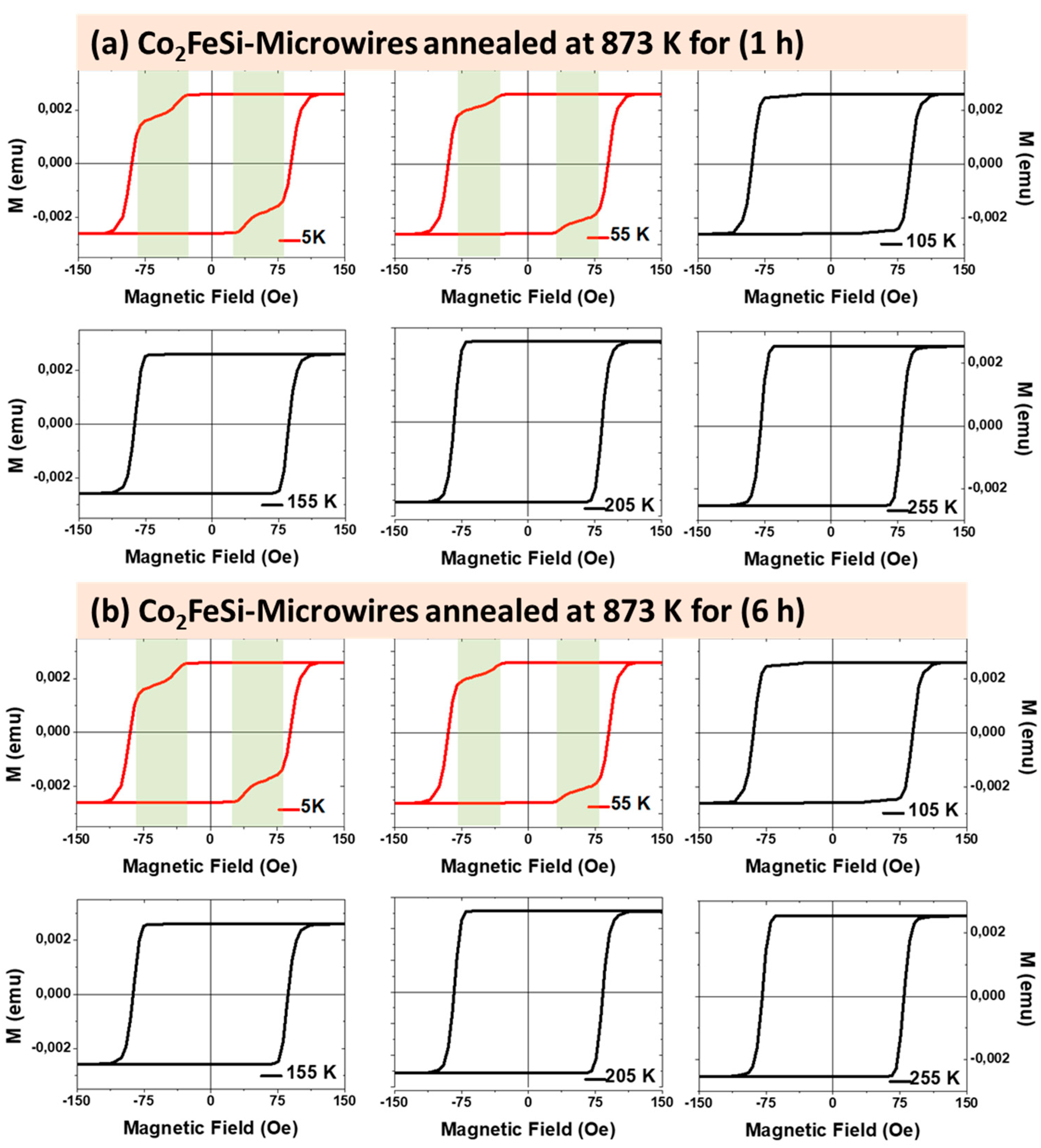
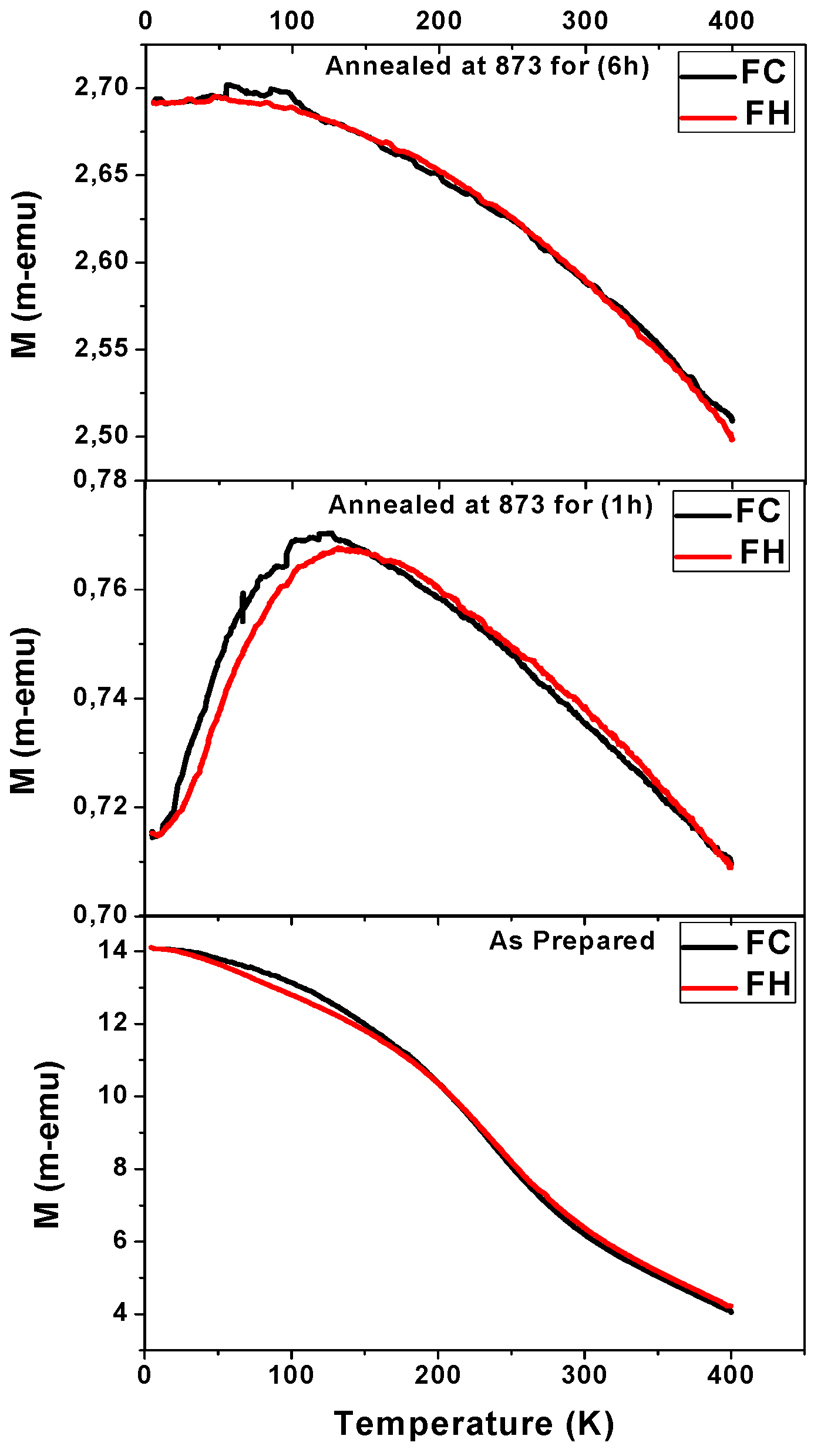
3.1. Effect of Annealing Conditions
3.1.1. Effect of Time Annealing in Co2FeSi Glass Coated Microwires
- (a).
- XRD analysis
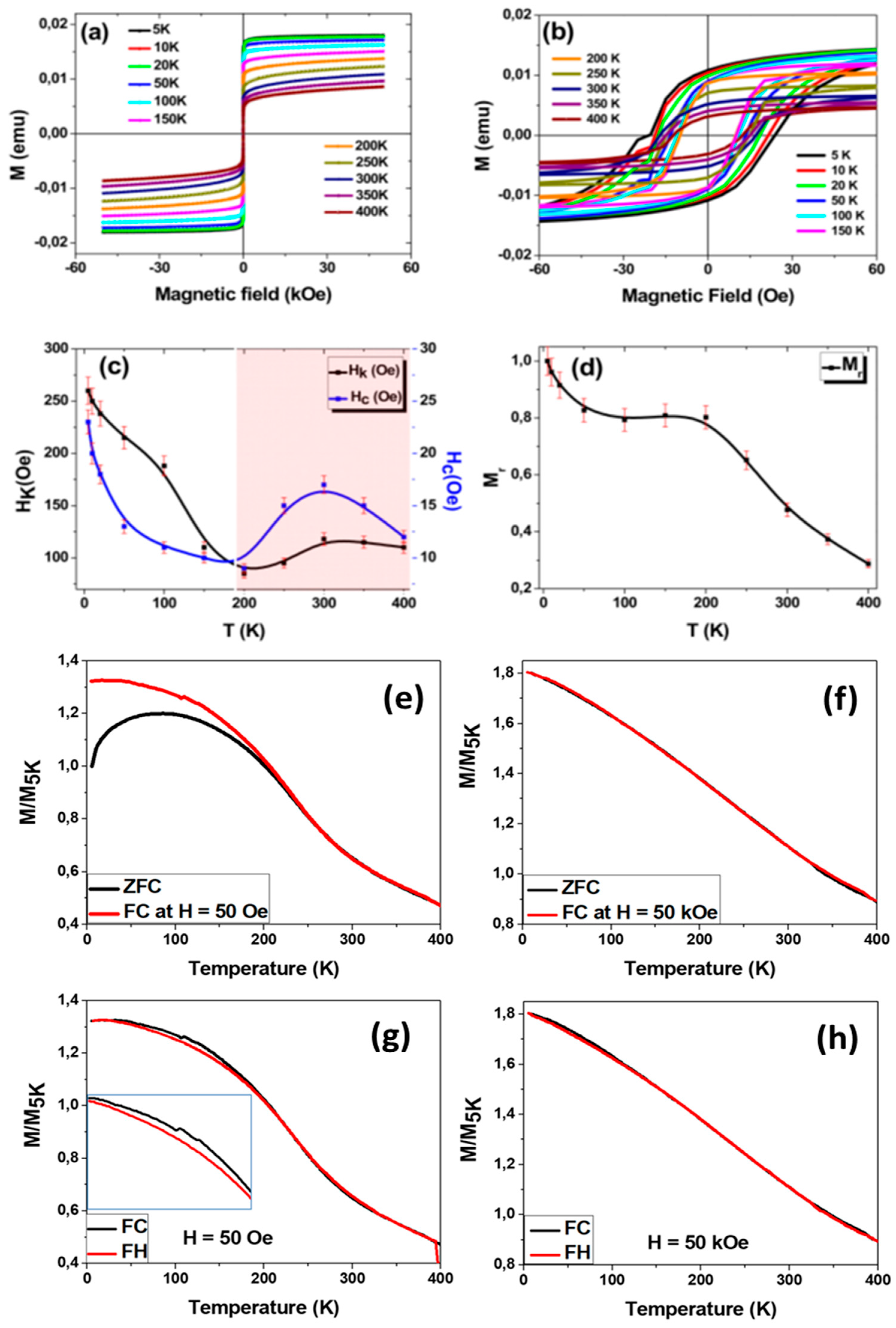
- (b). Magnetic properties
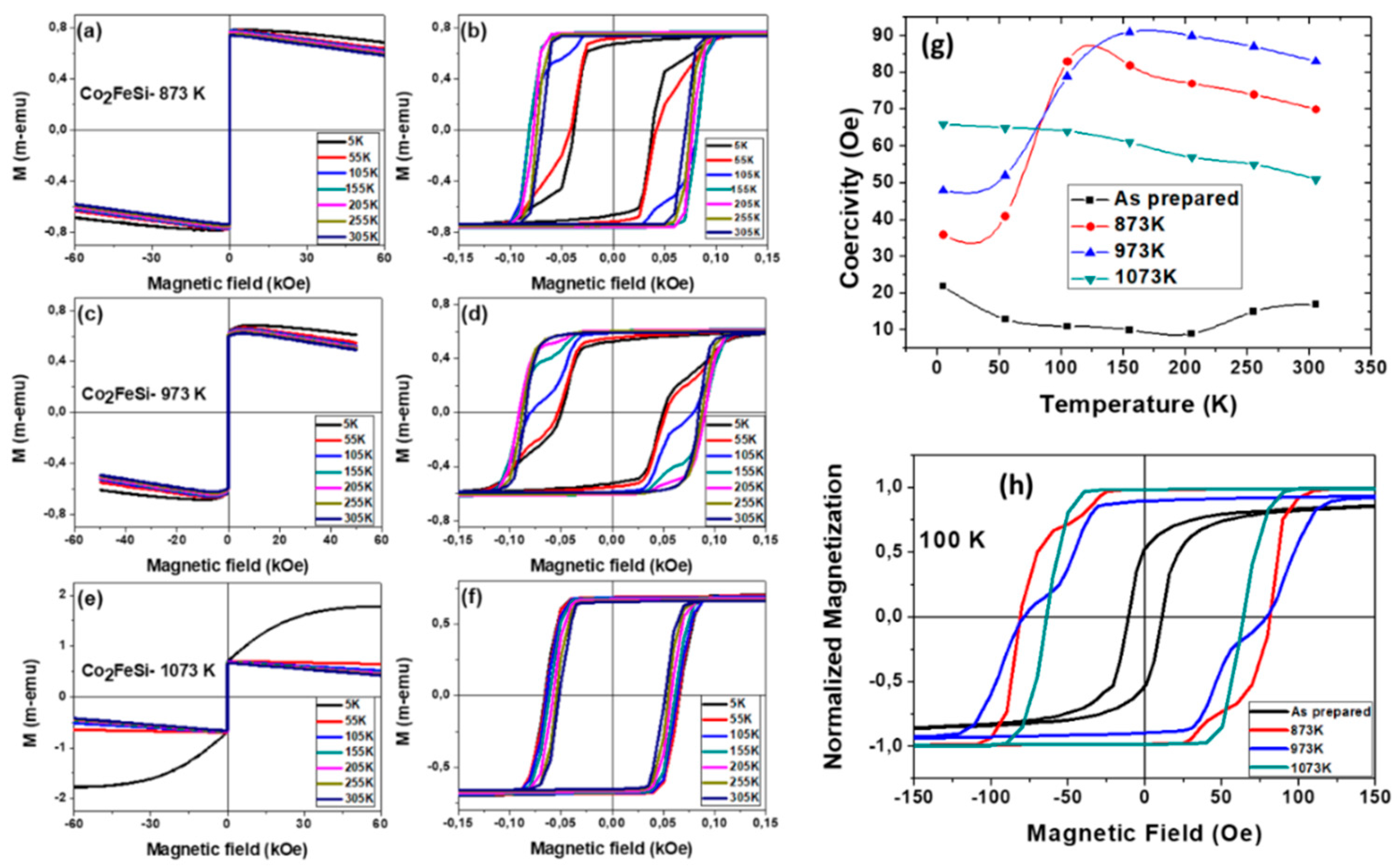
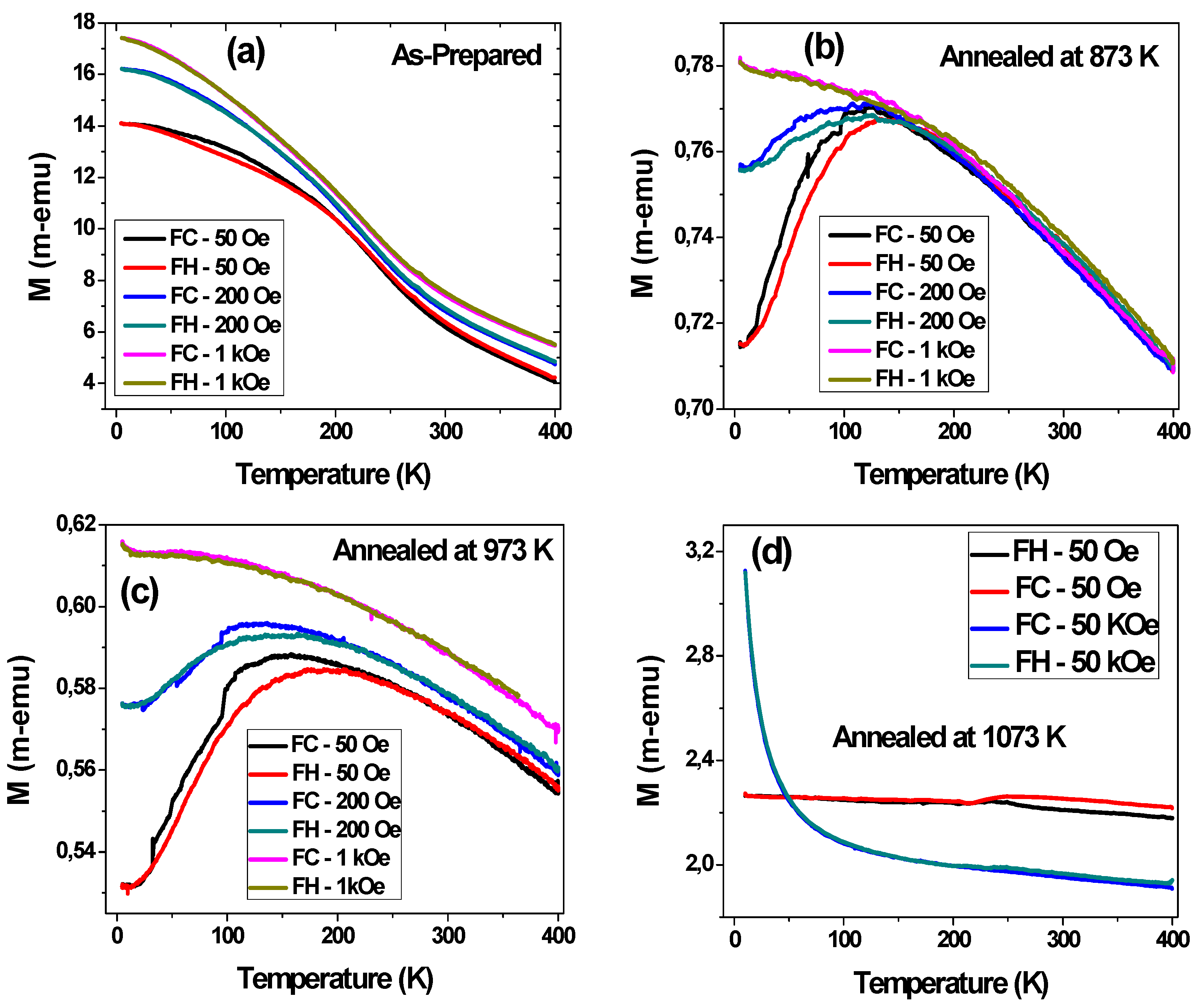
3.1.2. Effect of Annealing Temperature in Co2FeSi Glass Coated Microwires
- Strong magnetic coupling between distinct magnetic phases (in this case, hard Co and soft Fe regions), leading to an oxidation-induced imbalance.
- Reordering of ferromagnetic spins below the critical temperature under an applied magnetic field, causing domain wall pinning and influencing hysteresis loop distortions.
- Superposition of an external magnetic field and the stray field from the microwire array, induced by factors such as metallic nucleus diameter fluctuations, or mixed crystalline structure.
4. Potential Applications
4.1. Spintronic Devices
- Spin valves and magnetic tunnel junctions: The ability to control the magnetic properties through annealing and compositional variations allows for the fine-tuning required in these devices.
- Magnetic random access memory (MRAM): The stability of the magnetic properties and the potential for miniaturization provided by the microwire structure are potentially advantageous for MRAM development.
- Domain wall devices: The observed magnetic behavior, including the multi-step magnetization reversal, suggests potential for use in domain wall-based logic and memory devices.
4.2. Magnetic Sensors
- Magnetic field sensors: The soft magnetic behavior and the ability to tailor the coercivity and anisotropy provide a basis for sensitive magnetic field detection.
- Temperature sensors: The temperature dependence of the magnetic properties, particularly the observed magnetic phase transitions, can be exploited for temperature sensing.
4.3. Biomedical Engineering
- Magnetic hyperthermia: The ability to generate heat under an alternating magnetic field can be utilized for targeted cancer therapy.
- Biosensors: The sensitivity of the magnetic properties to biological molecules can be exploited for developing novel biosensors.
4.4. Other Potential Application
- Microactuators: The magnetic field-induced shape memory effects observed in some Heusler alloys could be utilized for microactuators.
- Energy harvesting: The magnetocaloric effect in Heusler alloys suggests potential applications in energy harvesting devices.
5. Challenges and Future Works
5.1. Precise Control of Microstructure
- Achieving precise control over the microstructure, particularly the degree of L2₁ ordering and the grain size distribution, remains a challenge.
- Future work should focus on optimizing fabrication parameters, such as annealing conditions and cooling rates, to enhance structural order and tailor the microstructure for specific applications.
5.2. Understanding Complex Magnetic Behavior
- The complex magnetic behavior observed in these microwires, including the multi-step magnetization reversal and the interplay between different magnetic anisotropies, requires further investigation.
- Future studies should aim to develop a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms governing these phenomena, potentially through advanced micromagnetic modeling and simulation.
5.3. Integration into Devices
- While the potential applications of Heusler alloy microwires are promising, their integration into actual spintronic devices, sensors, and biomedical technologies presents challenges.
- Future research should focus on developing reliable methods for device fabrication, addressing issues such as microwire alignment, electrical contacting, and compatibility with other device components.
5.4. Exploring New Materials and Compositions
- The current review primarily focuses on Co₂FeSi alloys. Future work should explore other Heusler alloy compositions and even quaternary or quinary alloys to discover new materials with enhanced properties.
- Investigating the effects of doping or introducing other elements into the microwires could also lead to novel functionalities.
5.5. In-Situ Characterization
- In-situ characterization techniques, such as real-time monitoring of microstructure evolution during annealing or magnetic measurements under applied stress, would provide valuable insights into the structure-property relationships in these materials.
- Developing and utilizing such techniques should be a priority for future research.
5.6. Modeling and Simulation
- Computational modeling and simulation can play a crucial role in complementing experimental studies.
- Future efforts should focus on developing accurate models to predict the structural, magnetic, and electronic properties of Heusler alloy microwires, aiding in the design of materials with tailored properties.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, T.; Pickel, A.D.; Yao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Lacey, S.D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Thermoelectric properties and performance of flexible reduced graphene oxide films up to 3000 K. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjipanayis, G.C.; Gabay, A.M.; Schönhöbel, A.M.; Martín-Cid, A.; Barandiaran, J.M.; Niarchos, D. ThMn12-Type Alloys for Permanent Magnets. Engineering 2020, 6, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacko, P.; Duranka, P.; Varga, R. Advantages of Bistable Microwires in Digital Signal Processing. Sensors 2024, 24, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M. Salaheldeen, V. M. Salaheldeen, V. Zhukova, A. Wederni, M. Ipatov and A. Zhukov, "Magnetic Properties of Co2MnSi-Based Heusler Alloy Glass-Coated Microwires," in IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 59, no. 11, pp. 1-4, Nov. 2023, Art no. 7300904. [CrossRef]
- Hasmonay, E.; Depeyrot, J.; Sousa, M.H.; Tourinho, F.A.; Bacri, J.C.; Perzynski, R.; Raikher, Y.L.; Rosenman, I. Magnetic and optical properties of ionic ferrofluids based on nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukova, V.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. The Effect of High-Temperature Annealing on the Magnetic and Structural Properties of (MnFePSi)-Based Glass-Coated Microwires. Crystals 2025, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Senani, G.M.; Al-Fawzan, F.F.; Almufarij, R.S.; Abd-Elkader, O.H.; Deraz, N.M. Magnetic Behavior of Virgin and Lithiated NiFe2O4 Nanoparticles. Crystals 2023, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukova, V.; Rosero-Romo, J.J.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukov, A. Preparation and magnetic properties of MnFePSi-based glass-coated microwires. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 015350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, A.; Hakim, M.L.; Alam, T.; Islam, M.T.; Alshammari, A.S.; Mat, K.; M. , M.S.; Almalki, S.H.A.; Islam, M.S. Polarization Independent Metamaterial Absorber with Anti-Reflection Coating Nanoarchitectonics for Visible and Infrared Window Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, W.-Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.-S.; Deng, X.-C.; Gu, Y. A Metamaterial Absorber Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Suitable for Earth’s Atmospheric Transparency Window. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 92941–92951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; El-Dabea, T. Functionalization of Nanomaterials for Energy Storage and Hydrogen Production Applications. Materials 2025, 18, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borders, W.A.; Pervaiz, A.Z.; Fukami, S.; Camsari, K.Y.; Ohno, H.; Datta, S. Integer factorization using stochastic magnetic tunnel junctions. Nature 2019, 573, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukova, V.; Blanco, J.M.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. The Impact of High-Temperature Annealing on Magnetic Properties, Structure and Martensitic Transformation of Ni2MnGa-based Glass-Coated Microwires. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 4378–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoop, M.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Rösch, D.; Weinand, P.; Mendes, N.; Mushtaq, F.; Chen, X.Z.; Shen, Y.; Pujante, C.F.; Puigmartí-Luis, J.; et al. Mobile Magnetic Nanocatalysts for Bioorthogonal Targeted Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilkamy, H.A.E.-S.; Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukov, A.; El-Kasaby, R.A.; Feizi-Dehnayebi, M.; Alharas, M.M.A.; Abo-Dief, H.M.; El-Khatib, R.M.; Abu-Dief, A.M. Enhanced Corrosion Protection as a Sustainable Approach for Nickel Using Novel FeL Salen Complex: Electrochemical Investigation and DFT Insights. Metals 2025, 15, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukova, V.; Rosero-Romo, J.J.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukov, A. Preparation and magnetic properties of MnFePSi-based glass-coated microwires. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 015350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Recent Developments in RFe12-Type Compounds for Permanent Magnets. Scr. Mater. 2018, 154, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmadi, M.; Mohamed, W.S.; Zhukov, A.; Salaheldeen, M.; Alsaedi, W.H.; Alhashmialameer, D.; Al-Ghamdi, K.; Abu Dief, A.M. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of flower-like MoS2/VS2 nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 157, 111336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khilwani, D.; Moghe, V.; Saraswat, V.; Kumbhare, P.; Baghini, M.J.; Jandhyala, S.; Subramoney, S.; Ganguly, U. PrxCa1-xMnO3 based neuron for Boltzmann machine to solve “maximum cut” problem. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 091112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Mendez, M.; Vega, V.; Fernández, A.; Prida, V.M. Tuning Nanohole Sizes in Ni Hexagonal Antidot Arrays: Large Perpendicular Magnetic Anisotropy for Spintronic Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccone, M.; Scholl, A.; Velten, S.; Dhuey, S.; Hofhuis, K.; Wuth, C.; Huang, Y.-L.; Chen, Z.; Chopdekar, R.V.; Farhan, A. Towards artificial Ising spin glasses: Thermal ordering in randomized arrays of Ising-type nanomagnets. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 99, 224403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Nafady, A.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Díaz Crespo, R.; Fernández-García, M.P.; Andrés, J.P.; López Antón, R.; Blanco, J.A.; Álvarez-Alonso, P. Enhancement of Exchange Bias and Perpendicular Magnetic Anisotropy in CoO/Co Multilayer Thin Films by Tuning the Alumina Template Nanohole Size. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiwi, M. Exchange Bias Theory. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 234, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjærvø, S.H.; Marrows, C.H.; Stamps, R.L.; Heyderman, L.J. Advances in artificial spin ice. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2019, 2, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Salaheldeen, A.M. M. Salaheldeen, A.M. Abu-Dief, L. Martínez-Goyeneche, S.O. Alzahrani, F. Alkhatib, P. Álvarez-Alonso, J.A. Blanco, Dependence of the Magnetization Process on the Thickness of Fe70Pd30 Nanostructured Thin Film, Materials. 2020, 13, 5788. [CrossRef]
- Maniv, E.; Murphy, R.A.; Haley, S.C.; Doyle, S.; John, C.; Maniv, A.; Ramakrishna, S.K.; Tang, Y.-L.; Ercius, P.; Ramesh, R.; et al. Exchange bias due to coupling between coexisting antiferromagnetic and spin-glass orders. Nat. Phys. 2021, 17, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; Salaheldeen, M.; El-Dabea, T. Recent advances in the development of gold nanoparticles for drug delivery systems. J. Mod. Nanotechnol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Takahashi, Y.K.; Hirosawa, S.; Hono, K. Intrinsic Hard Magnetic Properties of Sm(Fe1−xCox)12 Compound with the ThMn12 Structure. Scr. Mater. 2017, 138, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finocchio, G.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Lin, P.; Pan, G.; Yang, J.J.; Tomasello, R.; Panagopoulos, C.; Carpentieri, M.; Puliafito, V.; Åkerman, J.; et al. Roadmap for unconventional computing with nanotechnology. Nano Futures 2024, 8, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prida, V.; Salaheldeen, M.; Pfitzer, G.; Hidalgo, A.; Vega, V.; González, S.; Teixeira, J.; Fernández, A.; Hernando, B. Template Assisted Deposition of Ferromagnetic Nanostructures: From Antidot Thin Films to Multisegmented Nanowires. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 131, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiklejohn, W.H.; Bean, C.P. New Magnetic Anisotropy. Phys. Rev. 1957, 105, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukin, K.; Zemlyanyi, O.; Lukin, S. Generation of chaotic and random signals for noise radar-brief overview. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Radar Symposium (IRS), Gdansk, Poland, 12–14 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Salaheldeen, M. , Zhukova, V., Ipatov, M., Zhukov, A. GdFe-based nanostructured thin films with large perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for spintronic applications. AIP Advances 2024, 14(2), 025308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-H.; Ryu, K.-S.; Parkin, S. Domain-wall velocities of up to 750 m s-1 driven by exchange-coupling torque in synthetic antiferromagnets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Goyeneche, M.L.M.; Alvarez-Alonso, P.; Fernandez, A. Enhancement the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy of nanopatterned hard/soft bilayer magnetic antidot arrays for spintronic application. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 485708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.A.; Awschalom, D.D.; Buhrman, R.A.; Daughton, J.M.; von Molnár, S.; Roukes, M.L.; Chtchelkanova, A.Y.; Treger, D.M. Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 2001, 294, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.M.K.; Ahmed, H.M.A.E.-L.; Salaheldeen, M.; Abu-Dief, A.M. Ultra-density nanostructure GdFe thin film with large perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for a new generation of spintronic device. U.S. Patent 11,804,322 B1, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tarnawski, J.; Buszman, K.; Woloszyn, M.; Puchalski, B. The Influence of the Geographic Positioning System Error on the Quality of Ship Magnetic Signature Reproduction Based on Measurements in Sea Conditions. Measurement 2024, 229, 114405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; M. Abu-Dief, A.; El-Dabea, T. Functionalization of Nanomaterials for Energy Storage and Hydrogen Production Applications. Materials 2025, 18, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, K.; Frost, W.; Samiepour, M.; Kubota, T.; Takanashi, K.; Sukegawa, H.; Mitani, S.; Hirohata, A. Heusler Alloys for Spintronic Devices: Review on Recent Development and Future Perspectives. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2021, 22, 235–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Pickel, A.D.; Yao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Lacey, S.D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Thermoelectric properties and performance of flexible reduced graphene oxide films up to 3,000 K. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccone, M.; Scholl, A.; Velten, S.; Dhuey, S.; Hofhuis, K.; Wuth, C.; Huang, Y.-L.; Chen, Z.; Chopdekar, R.V.; Farhan, A. Towards artificial Ising spin glasses: Thermal ordering in randomized arrays of Ising-type nanomagnets. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 99, 224403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Vega, V.; Ibabe, A.; Jaafar, M.; Asenjo, A.; Fernandez, A.; Prida, V.M. Tailoring of Perpendicular Magnetic Anisotropy in Dy13Fe87 Thin Films with Hexagonal Antidot Lattice Nanostructure. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-H.; Ryu, K.-S.; Parkin, S. Domain-wall velocities of up to 750 m s−1 driven by exchange-coupling torque in synthetic antiferromagnets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.L.; Nam Nguyen, H.; Hai Nguyen, H.; Quynh Luu, M.; Hieu Nguyen, M. Nanoparticles: Synthesis and applications in life science and environmental technology. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telegin, A.; Sukhorukov, Y. Magnetic Semiconductors as Materials for Spintronics. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barner, K. New Trends in the Characterization of CMR-Manganites and Related Materials; Research Signpost: Gottingen, Germany, 2005; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Telegin, A.V.; Sukhorukov, Y.P.; Bessonov, V.D.; Naumov, S.V. The Faraday effect in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite in the IR range. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2019, 45, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telegin, A.V.; Sukhorukov, Y.P.; Loshkareva, N.N.; Mostovshchikova, E.V.; Bebenin, N.G.; Gan’shina, E.A.; Granovsky, A.B. Giant magnetotransmission and magnetoreflection in ferromagnetic materials. JMMM 2015, 383, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Ueno, K.; Fukumura, T.; Yuan, H.T.; Shimotani, H.; Iwasa, Y.; Kawasaki, M. Electrically induced ferromagnetism at room temperature in cobalt-doped titanium dioxide. Science 2011, 332, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizal, C.; Shimizu, H.; Mejía-Salazar, J.R. Magneto-Optics effects: New trends and future prospects for technological developments. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, S.; Yang, K.; Meyers, M.A. Heusler alloys: Past, properties, new alloys, and prospects. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 132, 101017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelkerding, K.V.; Dames, S.A.; Durtschi, J.D. Next-generation sequencing: From basic research to diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Garcia-Gomez, A.; Corte-Leon, P.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. Anomalous Magnetic Behavior in Half-Metallic Heusler Co2FeSi Alloy Glass-Coated Microwires with High Curie Temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 923, 166379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, I.; Dederichs, P.H.; Papanikolaou, N. Slater-Pauling Behavior and Origin of the Half-Metallicity of the Full-Heusler Alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 174429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, B.K.; Kaul, S.N.; Srinath, S.; Raja, M.M. Uniaxial Anisotropy, Intrinsic and Extrinsic Damping in Co2FeSi Heusler Alloy Thin Films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 325002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Kameoka, S.; Tsai, A.-P. Heusler Alloys: A Group of Novel Catalysts. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, T.; Felser, C.; Parkin, S.S.P. Simple rules for the understanding of Heusler compounds. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2011, 39, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziebeck, K.R.A.; Neumann, K.-U. Magnetic Properties of metals. In Landolt-Börnstein, New Series, Group III; Wijn, H.R.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; Volume 32c, pp. 64–414. [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis, I.; Özdoğan, K.; Şaşıoğlu, E. Spin-filter and spin-gapless semiconductors: The case of Heusler compounds. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 055606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, M.; Dronskowski, R. A combinatorial study of full Heusler alloys by first-principles computational methods. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, M.; Herper, H.C. Exploration of all-3d Heusler alloys for permanent magnets: An ab initio based high-throughput study. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 107, 174402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, S.; Khenchoul, S.; Lefkaier, I.K.; Lagoun, B. DFT-based investigation of the structural, magnetic, electronic, half-metallicity and elastic properties in the all-d heusler compounds: The case of Co2VZn and CoVZn. Eur. Phys. J. B 2021, 94, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurmehl, S.; Fecher, G.H.; Kandpal, H.C.; Ksenofontov, V.; Felser, C.; Lin, H.J.; Morais, J. Geometric, Electronic, and Magnetic Structure of Co2FeSi: Curie Temperature and Magnetic Moment Measurements and Calculations. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. Mater. Phys. 2005, 72, 184434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, M.C.; Nain, H.; Yusoff, N.H.N.; Manap, A.R.A.; Slamatt, R.; Anuar, M.H. An Overview of Ship Magnetic Signature and Silencing Technologies. Def. ST Tech. Bull. 2019, 12, 176–192. [Google Scholar]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Garcia-Gomez, A.; Ipatov, M.; Corte-Leon, P.; Zhukova, V.; Blanco, J.M.; Zhukov, A. Fabrication and Magneto-Structural Properties of Co2-Based Heusler Alloy Glass-Coated Microwires with High Curie Temperature. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnawski, J.; Buszman, K.; Woloszyn, M.; Rutkowski, T.A.; Cichocki, A.; Józwiak, R. Measurement Campaign and Mathematical Model Construction for the Ship Zodiak Magnetic Signature Reproduction. Measurement 2021, 186, 110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rauf, A.M.; Mohd Hambali, A.; Mahdi Che, I.; Mohd Hazri, R.; Roslan, S.; Mohd Yusri, O.; Hasril, N.; Zuraini, A.M.; Muhammad Syauqat, A.K. Magnetic Assessment of Newly Installed Onboard Degaussing System. Def. ST Tech. Bull. 2018, 11, 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Koo, J.; Ning, W.; Li, J.; Miao, L.; Min, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Alem, N.; Liu, C.X.; et al. Giant Room Temperature Anomalous Hall Effect and Tunable Topology in a Ferromagnetic Topological Semimetal Co2MnAl. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belopolski, I.; Manna, K.; Sanchez, D.S.; Chang, G.; Ernst, B.; Yin, J.; Zhang, S.S.; Cochran, T.; Shumiya, N.; Zheng, H.; et al. Discovery of Topological Weyl Fermion Lines and Drumhead Surface States in a Room Temperature Magnet. Science 2019, 365, 1278–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemard, C.; Petit-Watelot, S.; Pasquier, L.; Pierre, D.; Ghanbaja, J.; RojasSánchez, J.C.; Bataille, A.; Rault, J.; le Fèvre, P.; Bertran, F.; et al. Ultralow Magnetic Damping in Co2Mn-Based Heusler Compounds: Promising Materials for Spintronics. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 11, 064009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohata, A.; Sagar, J.; Lari, L.; Fleet, L.R.; Lazarov, V.K. Heusler-alloy films for spintronic devices. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 111, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, M.; Minár, J.; Braun, J.; Kronenberg, A.; Chadov, S.; Balke, B.; Gloskovskii, A.; Kolbe, M.; Elmers, H.J.; Schönhense, G.; et al. Direct Observation of Half-Metallicity in the Heusler Compound Co2MnSi. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, N.; Prajapat, C.L.; Babu, P.D.; Rai, S.; Kumar, S.; Jha, S.N.; Bhattacharyya, D. Pulsed Laser Deposited Co2FeSi Heusler Alloy Thin Films: Effect of Different Thermal Growth Processes. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 804, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; García-Gomez, A.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. Preparation and magnetic properties of Co2-based Heusler alloy glass-coated microwires with high Curie temperature. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 025325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, K.R.; Gyawali, P.; Forbes, A.; Pegg, I.L.; Philip, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Co2FeAl Nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 123906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.; Wolf, D.; Wang, C.; Levin, A.A.; Lubk, A.; Sturm, S.; Lichte, H.; Fecher, G.H.; Felser, C. Synthesis and Three-Dimensional Magnetic Field Mapping of Co2FeGa Heusler Nanowires at 5 Nm Resolution. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Garcia, A.; Corte-Leon, P.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A. Unveiling the Effect of Annealing on Magnetic Properties of Nanocrystalline Half-Metallic Heusler Co2FeSi Alloy Glass-Coated Microwires. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 4161–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Khan, U.; Irfan, M.; Javed, K.; Liu, P.; Ban, S.L.; Han, X.F. Fabrication and Magnetic Investigations of Highly Uniform CoNiGa Alloy Nanowires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 432, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Ipatov, M.; Corte-Leon, P.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A. Effect of Annealing on the Magnetic Properties of Co2MnSi-Based Heusler Alloy Glass-Coated Microwires. Metals 2023, 13, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khovaylo, V.V.; Rodionova, V.V.; Shevyrtalov, S.N.; Novosad, V. Magnetocaloric Effect in “Reduced” Dimensions: Thin Films, Ribbons, and Microwires of Heusler Alloys and Related Compounds. Phys. Status Solidi 2014, 251, 2104–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmeguenai, M.; Tuzcuoglu, H.; Gabor, M.S.; Petrisor, T.; Tiusan, C.; Zighem, F.; Chérif, S.M.; Moch, P. Co2FeAl Heusler Thin Films Grown on Si and MgO Substrates: Annealing Temperature Effect. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 043918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Shen, L.E.I.; Han, G.; Feng, Y.P. Data Storage: Review of Heusler Compounds. Spin 2012, 2, 1230006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Modern soft magnets: Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials. Acta Mater. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, K.; Wilens, R.H.; Duwez, P. Non-crystalline structure in solidified Gold-Silicon alloys. Nature 1970, 187, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, A. : Garcia, C.; Ilyn, M.: Varga, R.; del Val, J. J.; Granovsky, A.; Rodionova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V. Magnetic and transport properties of granular and Heusler-type glass-coated microwires, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukova, V.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. Anomalous magnetic behavior in MnFePSi glass-coated microwires. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1002, 175244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, A.; Rodionova, V.; Ilyn, M.; Aliev, A.M.; Varga, R.; Michalik, S.; Aronin, A.; Abrosimova, G.; Kiselev, A.; Ipatov, M.; et al. Magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in Heusler-type glass-coated NiMnGa microwires. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 575, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, V.; Cobeño, A.F.; Zhukov, A.; de Arellano Lopez, A.R.; López-Pombero, S.; Blanco, J.M.; Larin, V.; Gonzalez, J. Correlation between magnetic and mechanical properties of devitrified glass-coated Fe71.8Cu1Nb3.1Si15B9.1 microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 249, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHenry, M.; Willard, M.; Laughlin, D. Amorphous and Nanocrystalline Materials for Applications as Soft Magnets. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1999, 44, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Masumoto, K. T. Masumoto, K. Hashimoto. Corrosion properties of amorphous metals, J. Phys. Colloques, 1980, 41 (C8), pp.C8-894-C8-900. [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukova, V.; Lopez Anton, R.; Zhukov, A. Dependence of Magnetic Properties of As-Prepared Nanocrystalline Ni2MnGa Glass-Coated Microwires on the Geometrical Aspect Ratio. Sensors 2024, 24, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Antón, R.; Andrés, J.P.; González, J.A.; García-Gómez, A.; Zhukova, V.; Chizhik, A.; Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukov, A. Tuning of magnetic properties and Giant Magnetoimpedance effect in multilayered microwires. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2024, 100821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Peng, H.X. Ferromagnetic microwires enabled multifunctional composite materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 183–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Óvári, T.A.; Pop, G. Internal stress distribution in glass-covered amorphous magnetic wires. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 10104–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T. Fe-B and Fe-Si-B system alloy filaments produced by glass-coated melt spinning. Trans. JIM 1980, 21, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A.; Hufnagel, T.C.; Ramamurty, U. Mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4067–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, M.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Mechanical properties of Fe–Si–B amorphous wires produced by in-rotating-water spinning method. Metall. Trans. A 1982, 13, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Nagano, M.; Wehara, N. Mechanical properties of amorphous Fe80P16C3B1 filament produced by glass-coated melt spinning. Trans. JIM 1977, 18, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, S.A.; Larin, V.S.; Torcunov, A.V. Technology, Preparation and Properties of the Cast Glass-Coated Magnetic Microwires. Crystals 2017, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozejova, D.; Fecova, L.; Klein, P.; Sabol, R.; Hudak, R.; Sulla, I.; Mudronova, D.; Galik, J.; Varga, R. Biomedical Applications of Glass-Coated Microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 470, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulitovsky, A.V.; Maianski, I.M.; Avramenco, A.I. 1960 Method of Continuous Casting of Glass Coated Microwire. USSR Patent 128427, 6 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Garcia-Gomez, A.; Corte-León, P.; Gonzalez, A.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Gonzalez, J.M.; López Antón, R.; Zhukov, A. Manipulation of Magnetic and Structure Properties of Ni2FeSi Glass-Coated Microwires by Annealing. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 942, 169026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte-Leon, P.; Zhukova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Blanco, J.M.; González, J. Churyukanova, M.; Taskaev, S.; Zhukov, A. The effect of annealing on magnetic properties of “Thick” microwires. J. Alloys Compd, 1509. [Google Scholar]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Wederni, A.; Ipatov, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A. Elucidation of the Strong Effect of the Annealing and the Magnetic Field on the Magnetic Properties of Ni2-Based Heusler Microwires. Crystals 2022, 12, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Wederni, A.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Lopez Anton, R.; Zhukov, A. Enhancing the Squareness and Bi-Phase Magnetic Switching of Co2FeSi Microwires for Sensing Application. Sensors 2023, 23, 5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennel, M.; Varga, M.; Frolova, L.; Nalevanko, S.; Ibarra-Gaytán, P.; Vidyasagar, R.; Sarkar, P.; Dzubinska, A.; Galdun, L.; Ryba, T.; et al. Heusler-Based Cylindrical Micro- and Nanowires. Phys. Status Solidi A 2022, 219, 2100657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennel, M.; Galdun, L.; Džubinská, A.; Reiffers, M.; Varga, R. High efficiency direct magnetocaloric effect in Heusler Ni2MnGa microwire at low magnetic fields. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Lupu, N.; Stoian, G.; Ababei, G.; Corodeanu, S.; Óvári, T.A. Ultrathin Nanocrystalline Magnetic Wires. Crystals 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Ovari, T.-A. Amorphous glass-covered magnetic wires: Preparation, properties, applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1996, 40, 333–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, J.; Nematov, M.; Yudanov, N.; Podgornaya, S.; Panina, L. High-Frequency Magnetoimpedance (MI) and Stress-MI in Amorphous Microwires with Different Anisotropies. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.; Varga, R.; Badini-Confalonieri, G.A.; Vazquez, M. Domain Wall Dynamics in Amorphous and Nanocrystalline FeCoMoB Microwires. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 7464–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torcunov, A.V.; Baranov, S.A.; Larin, V.S. The internal stresses dependence of the magnetic properties of cast amorphous microwires covered with glass insulation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater.
- Corodeanu, S.; Hlenschi, C.; Chiriac, H.; Óvári, T.-A.; Lupu, N. Comparative Study of the Magnetic Behavior of FINEMET Thin Magnetic Wires: Glass-Coated, Glass-Removed, and Cold-Drawn. Materials 2023, 16, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhukova, V.; Corte-Leon, P.; Blanco, J.M.; Ipatov, M.; Gonzalez-Legarreta, L.; Gonzalez, A.; Zhukov, A. Development of Magnetically Soft Amorphous Microwires for Technological Applications. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematov, M.G.; Baraban, I.; Yudanov, N.A.; Rodionova, V.; Qin, F.X.; Peng, H.X.; Panina, L.V. Evolution of the magnetic anisotropy and magnetostriction in Co-based amorphous alloys microwires due to current annealing and stress-sensory applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 837, 155584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitxelena-Iribarren, O.; Campisi, J.; de Apellániz, I.M.; Lizarbe-Sancha, S.; Arana, S.; Zhukova, V.; Mujika, M.; Zhukov, A. Glass-coated ferromagnetic microwire-induced magnetic hyperthermia for in vitro cancer cell treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 106, 110261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Gómez, C.; Aragon, A.M.; Hernando-Rydings, M.; Marin, P.; Hernando, A. Stress and field contactless sensor based on the scattering of electromagnetic waves by a single ferromagnetic microwire. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 92405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostitsyna, E.V.; Gudoshnikov, S.A.; Popova, A.V.; Petrzhik, M.I.; Tarasov, V.P.; Usov, N.A.; Ignatov, A.S. Mechanical properties and internal quenching stresses in Co-rich amorphous ferromagnetic microwires. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhumazoda, A.; Panina, L.V.; Nematov, M.G.; Ukhasov, A.A.; Yudanov, N.A.; Morchenko, A.T.; Qin, F.X. Temperature-stable magnetoimpedance (MI) of current-annealed Co-based amorphous microwires. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astefanoaei, I.; Radu, D.; Chiriac, H. Internal stress distribution in DC joule-heated amorphous glass-covered microwires. J. Condens. Matter. Phys. 2006, 18, 2689–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, N.N.; Gornakov, V.S.; Aronin, A.S. Role of internal stresses in the formation of magnetic structure and magnetic properties of iron-based glass coated microwires. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 205108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, A.S.; Borisov, V.T.; Borisov, O.V.; Prokoshin, A.F.; Usov, N.A. Residual quenching stresses in glass-coated amorphous ferromagnetic microwires. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiriac, H.; Óvári, T.-A.; Corodeanu, S.; Ababei, G. Interdomain wall in amorphous glass-coated microwires. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 214433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panina, L. V.; Dzhumazoda, A.; Evstigneeva, S. A.; Adam, A. M.; Morchenko, A. T.; Yudanov, N. A.; Kostishyn, V. G. Temperature effects on magnetization processes and magnetoimpedance in low magnetostrictive amorphous microwires, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 459, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukov, A. Unveiling the Magnetic and Structural Properties of (X2YZ; X = Co and Ni, Y = Fe and Mn, and Z = Si) Full-Heusler Alloy Microwires with Fixed Geometrical Parameters. Crystals 2023, 13, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigoli, F.A.; Kawano, Y.; Davolos, M.R.; Jafelicci, M., Jr. Phase separation in pyrex glass by hydrothermal treatment: Evidence from micro-Raman spectroscopy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 284, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.F.; Andritschky, M.; Rebouta, L.; Ferreira, J.A.; da Silva, M.F. Macrocrystalline silicon thin films prepared by RF reactive magnetron sputter deposition. Vacuum 1995, 46, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, N.; Prajapat, C.L.; Babu, P.D.; Rai, S.; Kumar, S.; Jha, S.N.; et al. Effect of growth temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of the pulsed laser deposited Co₂FeAl thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 779, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidov, E.S.; Sdobnyakov, V.V.; Vazenmiller, G.V.; Chigirinskii, Y.I.; Dudin, Y.A.; Lesnikov, V.P.; et al. Manufacturing of sputtering composite targets containing phases of Co₂FeSi or Co₂MnSi Heusler alloy. Tech. Phys. 2018, 63, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, V.; Cobeño, A.F.; Zhukov, A.; Blanco, J.M.; Larin, V.; Gonzalez, J. Coercivity of glass-coated Fe73.4-xCu1Nb3.1Si13.4+xB9.1 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1.6) microwires. Nanostruct. Mater.
- Herzer, G. Grain size dependence of coercivity and permeability in nanocrystalline ferromagnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1990, 26, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, T. Nanocrystallization of metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 287, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L. Crystallization of amorphous alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1996, 27, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, A.; Del Val, J.J.; Zhukova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Klein, P.; Varga, R.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhdanova, M.; Churyukanova, M. and Zhukov, A. Effect of annealing on magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Hitperm-type glass-coated microwires, J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurmehl, S.; Fecher, G.H.; Ksenofontov, V.; Casper, F.; Stumm, U.; Felser, C.; Lin, H.J.; Hwu, Y. Half-Metallic Ferromagnetism with High Magnetic Moment and High Curie Temperature in Co2FeSi. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08J103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehnke, A.; Martens, U.; Sterwerf, C.; Niesen, A.; Huebner, T.; Von Der Ehe, M.; Meinert, M.; Kuschel, T.; Thomas, A.; Heiliger, C.; et al. Large Magneto-Seebeck Effect in Magnetic Tunnel Junctions with Half-Metallic Heusler Electrodes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdun, L.; Ryba, T.; Prida, V.M.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A.; Diko, P.; Kavečanský, V.; Vargova, Z.; Varga, R. Monocrystalline Heusler Co2FeSi Alloy Glass-Coated Microwires: Fabrication and Magneto-Structural Characterization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 453, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.B.; Zuo, Y.L.; Cui, B.S.; Li, D.; Yun, J.J.; Wu, K.; et al. Post annealing induced magnetic anisotropy in CoFeSi thin films on MgO(0 0 1). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 085006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Óvári, T.-A.; Lupu, N.; Chiriac, H. Rapidly Solidified Magnetic Nanowires and Submicron Wires. In Advanced Magnetic Materials; Malkinski, L., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1–32. ISBN 978-953-51-0637-1. [Google Scholar]
- Aronin, A.S.; Abrosimova, G.E.; Kiselev, A.P.; Zhukova, V.; Varga, R.; Zhukov, A. The effect of mechanical stress on Ni63.8Mn11.1Ga25.1 microwire crystalline structure and properties, Intermetallics, 2013, 4360-64. [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, K.; Manivel Raja, M.; Sridhara Rao, D.V.; Kamat, S.V. Effect of Sputtering Pressure and Power on Composition, Surface Roughness, Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of as-Deposited Co2FeSi Thin Films. Thin Solid Film. 2014, 558, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, K.; Svedlindh, P.; Andersson, J.O.; Nordblad, P.; Lundgren, L.; Aruga Katori, H.; Ito, A. Magnetic Behavior of a Reentrant Ising Spin Glass. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 46, 8227–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Ilyn, M.; Zhukova, V.; Perov, N.; Gonzalez, J.; et al. Design of magnetic properties of arrays of magnetostatically coupled glass-covered magnetic microwires. Phys. Status Solidi Appl. Mater. Sci. 2010, 207, 1954–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, A.; García, C.; Zhukova, V.; Larin, V.; González, J.; del Val, J.J.; et al. Fabrication and magnetic properties of Cu50(Fe69Si10B16C5)50 thin microwires. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 922–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Vega, V.; Fernández, A.; Prida, V. Anomalous in-plane coercivity behaviour in hexagonal arrangements of ferromagnetic antidot thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 491, 165572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Zhukova, V.; Blanco, J.M.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. The Impact of High-Temperature Annealing on Magnetic Properties, Structure and Martensitic Transformation of Ni₂MnGa-based Glass-Coated Microwires. Ceram. Int. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Talaat, A.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A. Preparation and Magneto-Structural Investigation of Nanocrystalline CoMn-Based Heusler Alloy Glass-Coated Microwires. Processes 2022, 10, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaheldeen, M.; Wederni, A.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A. Preparation and Magneto-Structural Investigation of High Ordered (L21 Structure) Co2MnGe Microwires. Processes 2023, 11, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionova, V. , Ipatov, M., Ilyn, M. et al. Tailoring of Magnetic Properties of Magnetostatically-Coupled Glass-Covered Magnetic Microwires. J Supercond Nov. Magn. 2011, 24, 541–547. [CrossRef]
- Zagrebin, M.A.; Sokolovskiy, V.V.; Buchelnikov, V.D. Electronic and magnetic properties of the Co₂-based Heusler compounds under pressure: First-principles and Monte Carlo studies. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 355004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernenko, V.A.; L'vov, V.A.; Zagorodnyuk, S.P.; Takagi, T. Ferromagnetism of thermoelastic martensites: Theory and experiment. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 064407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wederni, A.; Salaheldeen, M.; Ipatov, M.; Zhukova, V.; Zhukov, A. Influence of the Geometrical Aspect Ratio on the Magneto-Structural Properties of Co2MnSi Microwires. Metals 2023, 13, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




