Submitted:
21 April 2025
Posted:
22 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. Comparative Literature Review
3.2. System Architecture Evaluation
3.3. Proposed System Design
3.4. Cost Analysis and Implementation Plan
4. Comparative Table of IBM Watson VS Microsoft Azure
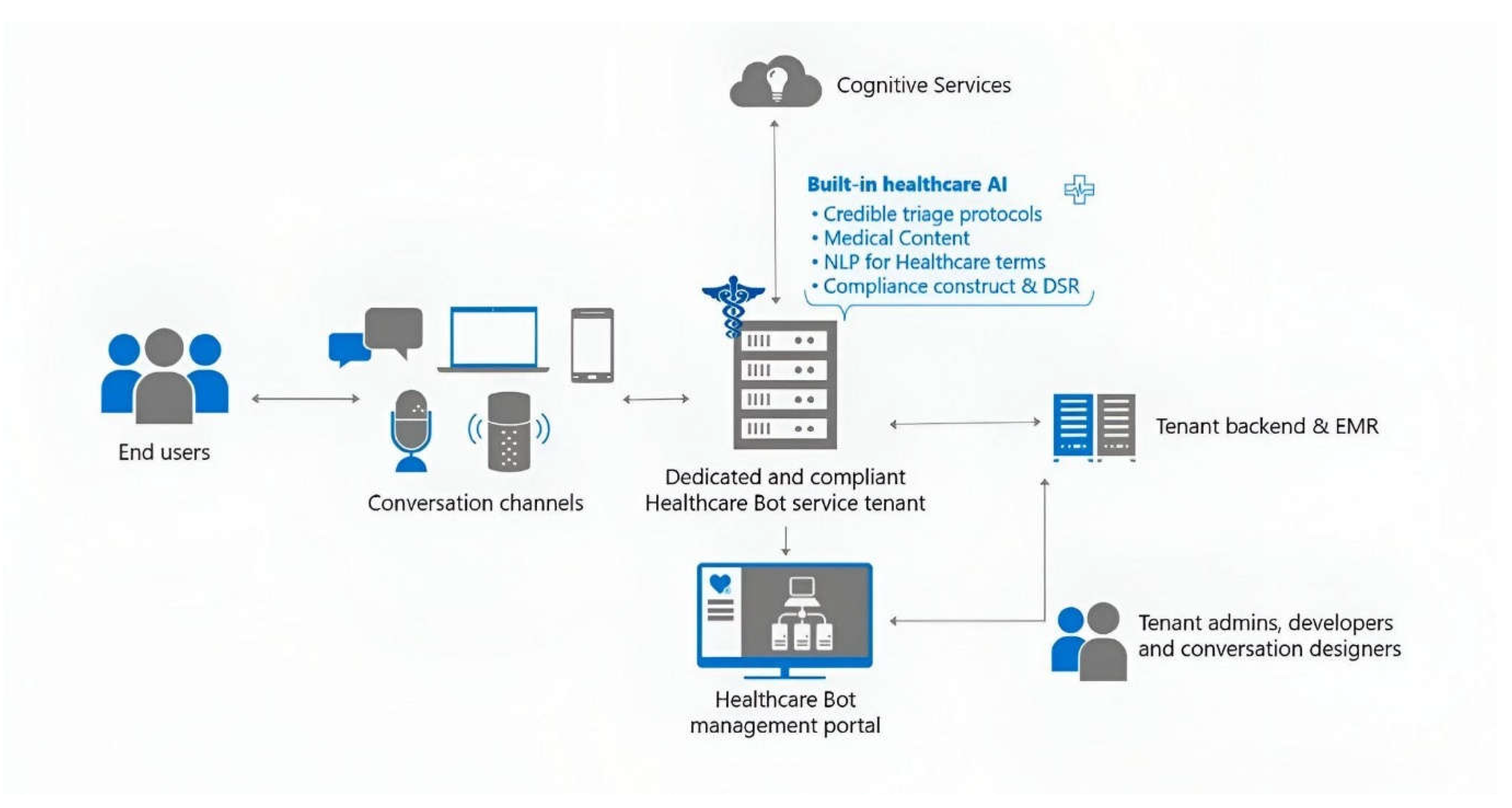
4.1. System Architecture Design
| Comparative Topics |
IBM Watson |
Microsoft Azure |
|
Features |
- Watsonx Assistant AI healthcare chatbot. - Cloud-based system. - Provides API for Automation. - Adaptability across applications. |
- Interoperability and Data Integration - Azure Health Bot - Privacy and Compliance - Data Analytics and AI |
|
Benefits |
- Filter though structured data. - Huge training data. - Provides system integration. - Machine Learning, Deep Learning and traditional rule-based systems. - User-friendly interface. - Accessible to multiple demographics. - Transparent, traceable and explainable responses. - Lengthy track record in business, sales and customer relations. |
- Handle numerous simple processes. - NLP models help communicate with patients in real-time. - Offers constant updates and enhancements. - Multi-domain integration opportunities. - User-friendly interface - Unified data exchange in different departments. - Provides reasoning behind output. - Experienced with healthcare. - Compliance with security requirements. |
|
Limitations |
- Slow to catch up with technological enhancements. - High cost for development and maintenance. - Require significant resources. - Healthcare providers were hesitant to adopt Watson in fear of privacy violation and data exploitation. - Unable to process unstructured data accurately. |
- Learning curve and intricacy. - Pay-as-you-go pricing model. - Vendor locked. - Occasional outages. - Customisation constraints. |
4.2. Current Hospital Information Management System Architecture
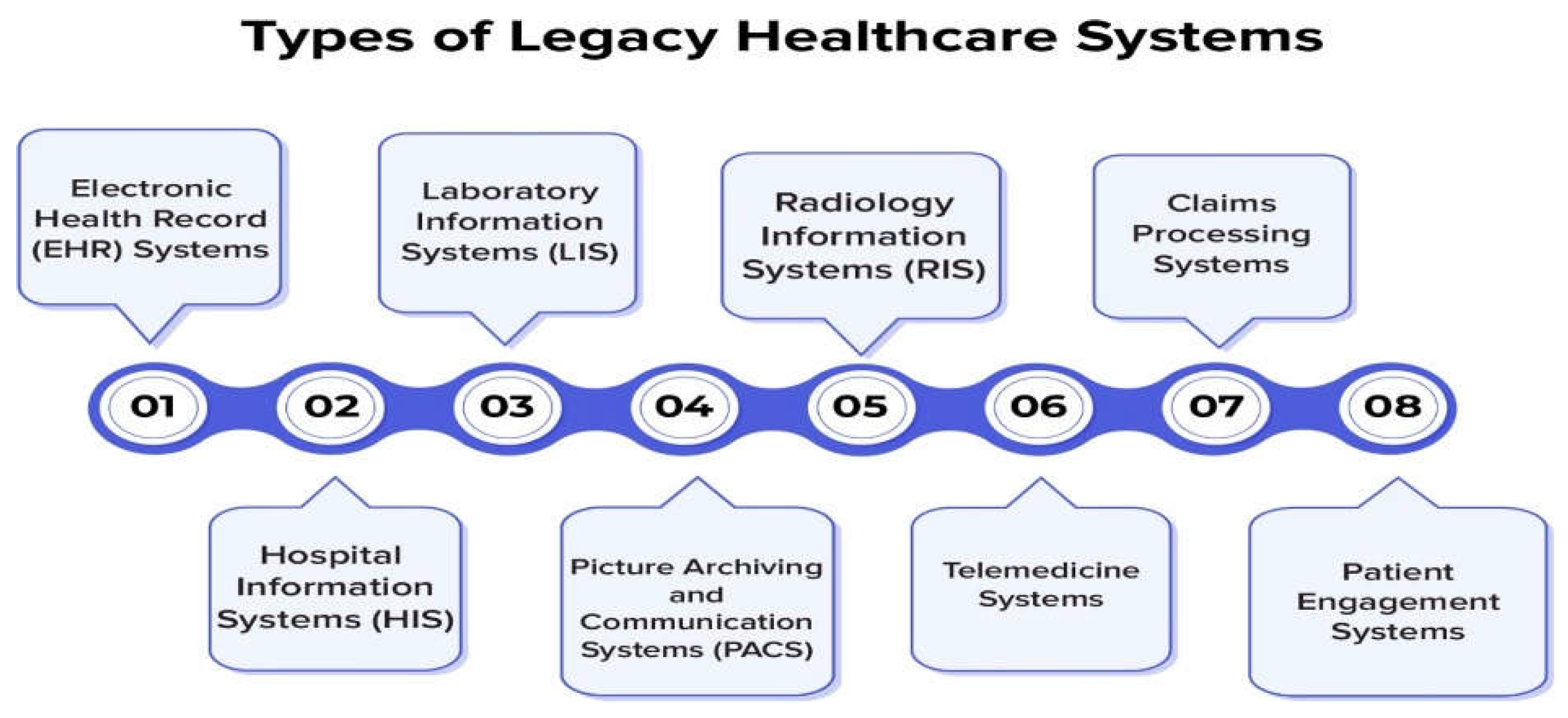
4.2. Meditech
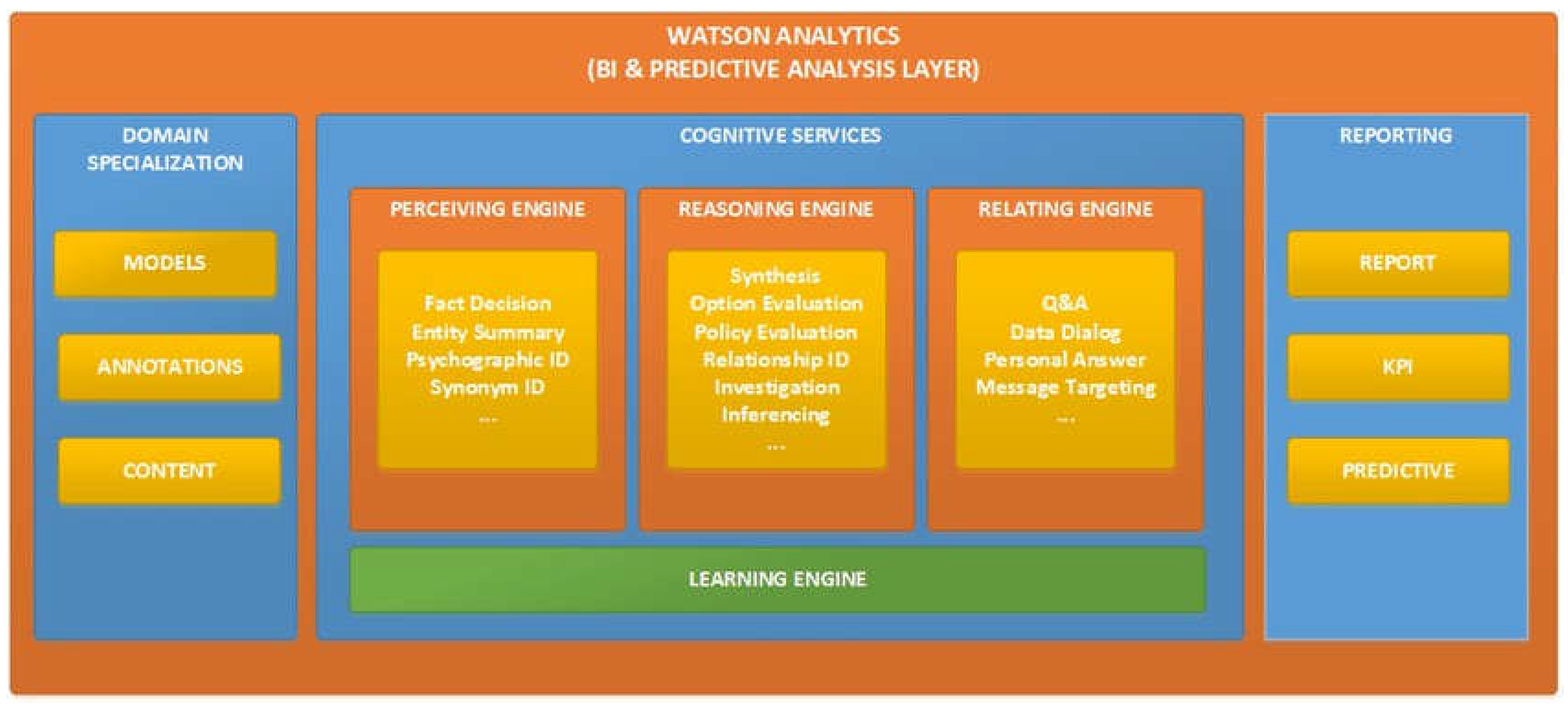
4.2. IBM Watson Architecture Design
4.3. Microsoft Azure Architecture Design
4.2. Data Storage Design
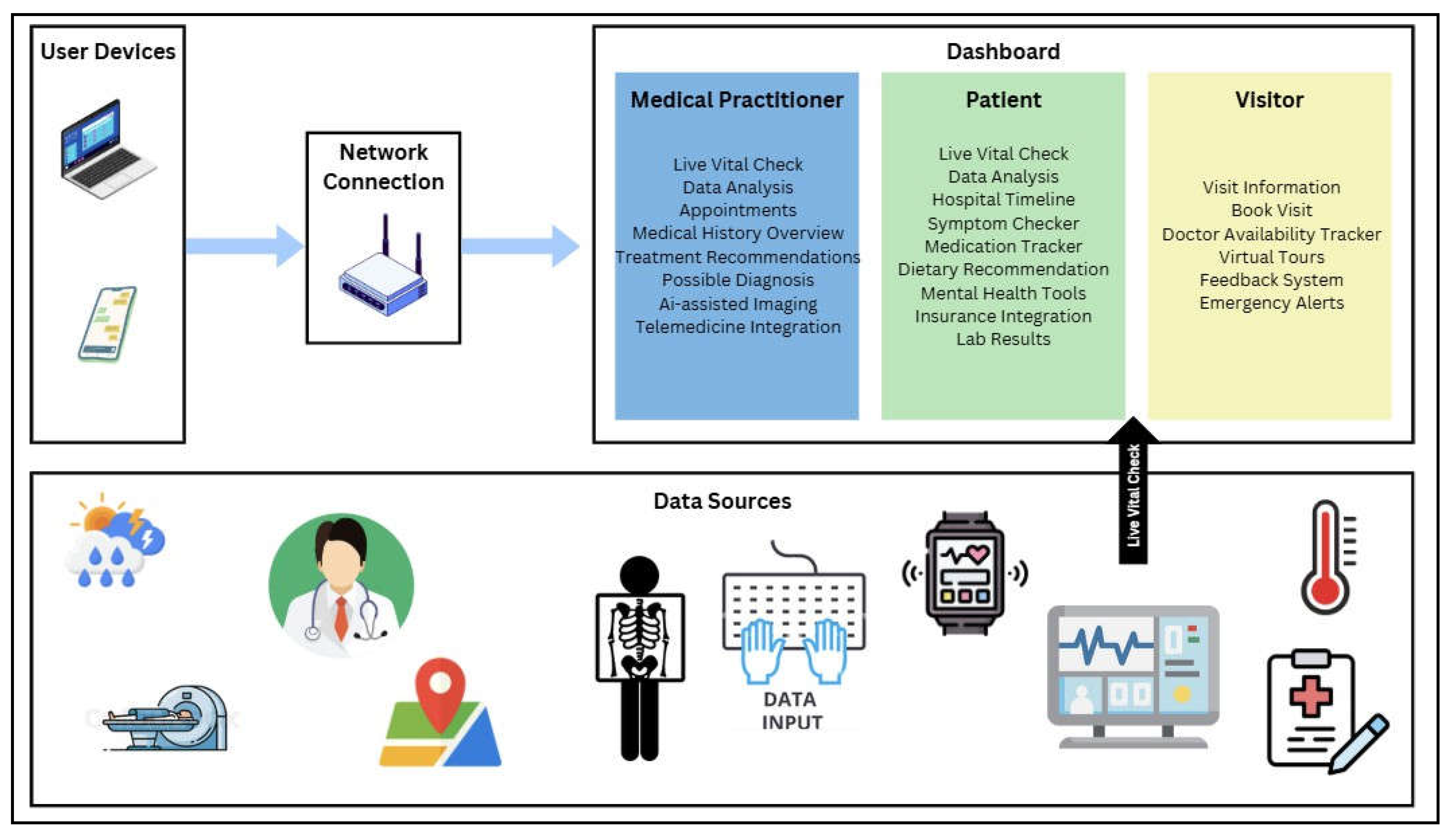
4.2. System Proposal
- Microsoft Azure Architecture for HIMS
- Suggested Design for a Better HIMS
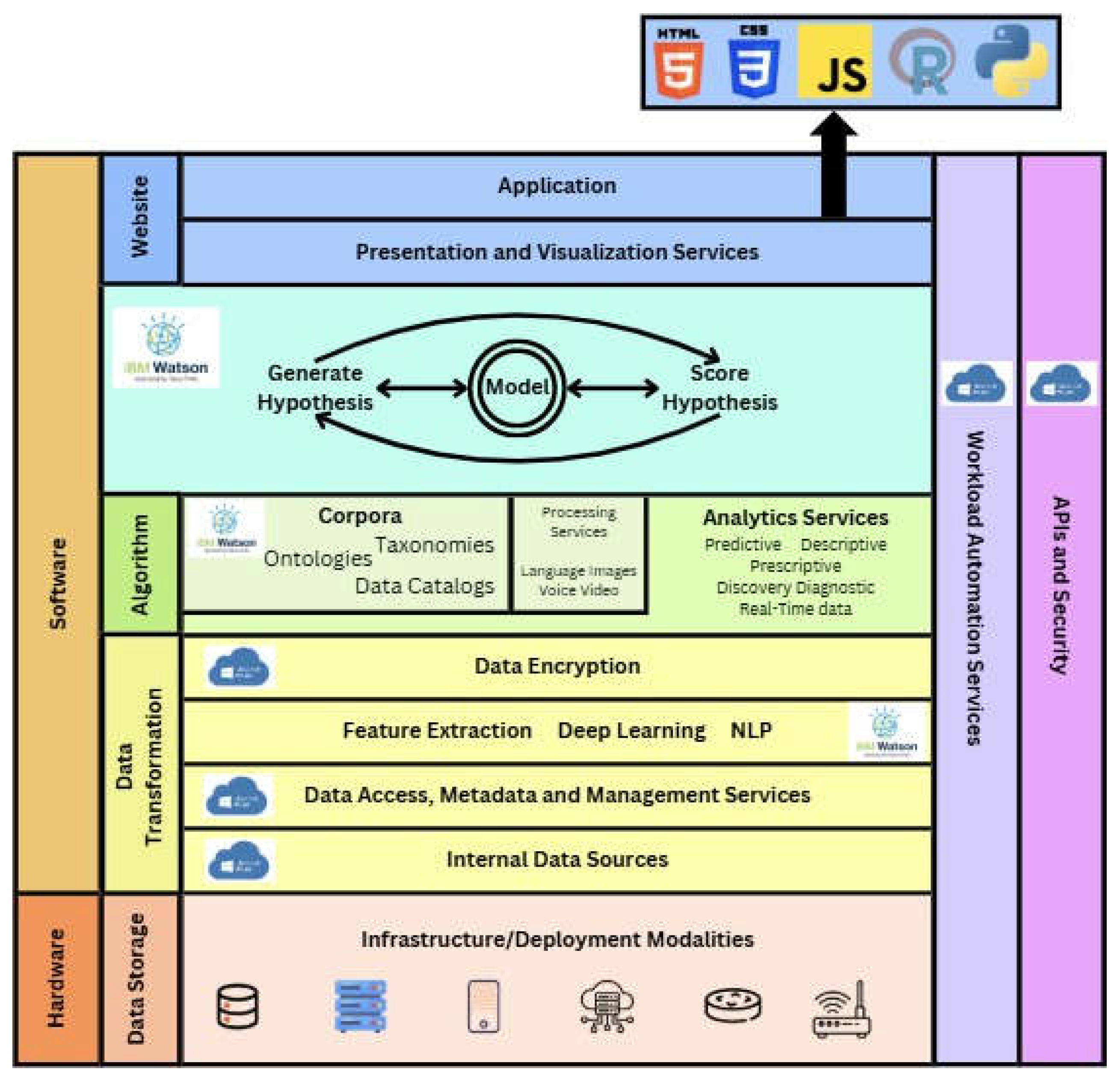
- Proposed SystemArchitecture
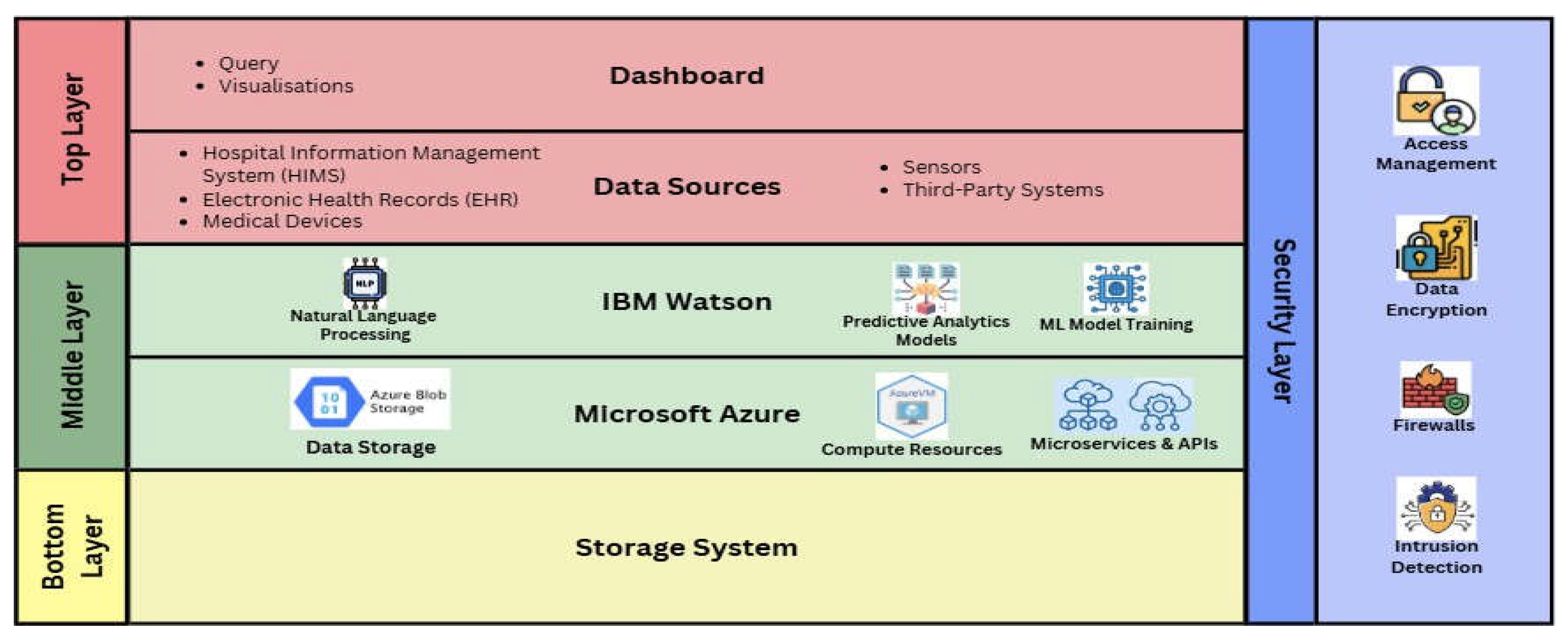
- TopLayer
- Middle Layer
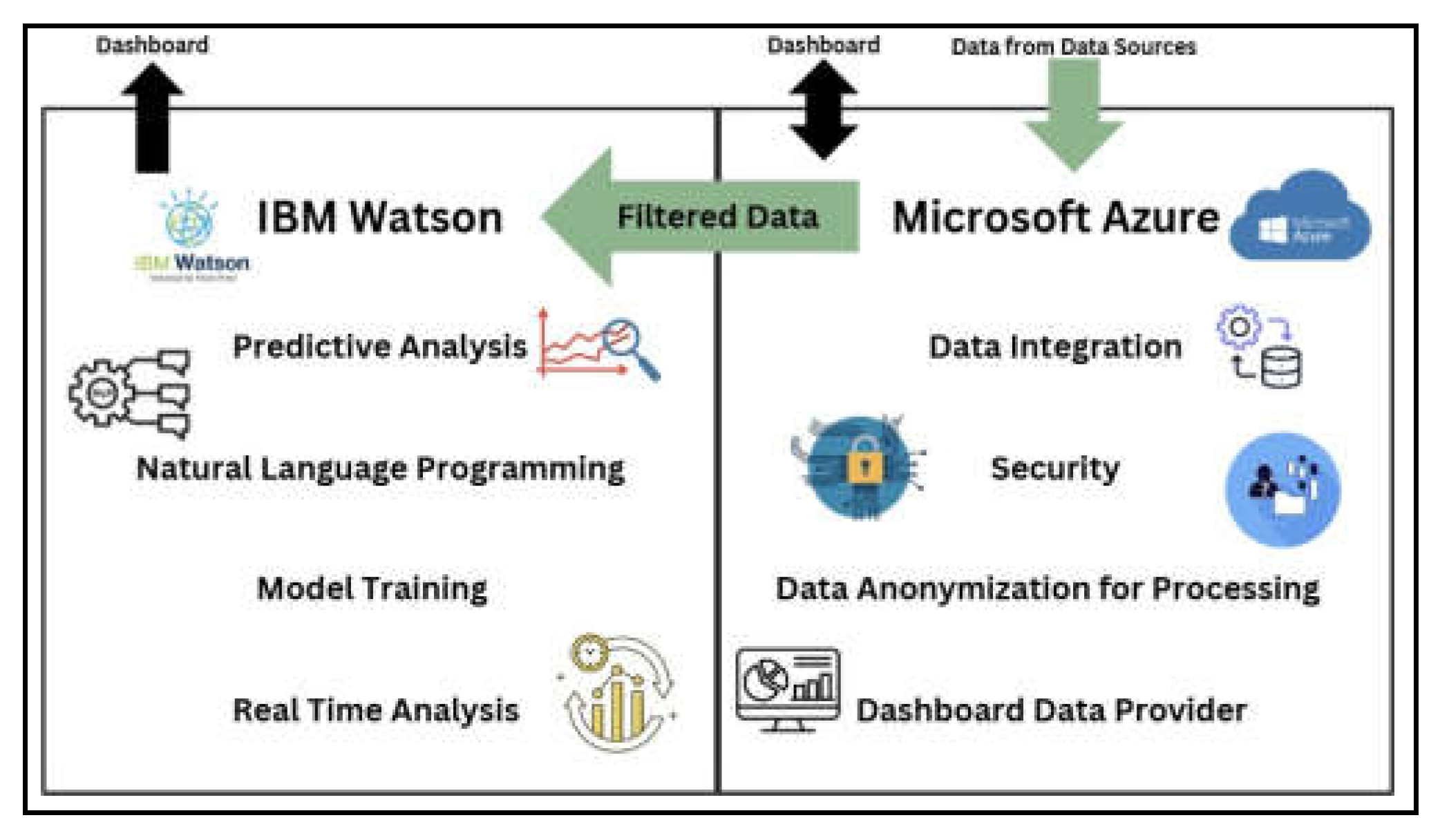
| Component | Microsoft Azure | IBM Watson |
|
Primary Role |
Data Management, Data Integration and Data Security. | AI-driven Analytics, Predictions, Natural Language Processing (NLP). |
|
Data Handling |
Collects, organises, and securely stores data from data Sources. | Processes anonymised data received from Microsoft Azure for analysis and prediction. |
|
Anonymisation |
Removes sensitive patient information before sending it to IBM Watson. |
Operates only on anonymised data and has no access to personally identifiable information (PII). |
|
Security |
Implements encryption, access controls, firewalls and intrusion detection. | Relies on Microsoft Azure;s anonymised data for secure operations. |
| Predictive Analytics | Supports IBM Watson by managing the data for | Performs trend analysis, generates diagnostic |
| analysis. | suggestions and predicts health outcomes. | |
|
Model Training |
Not involved. |
Continuously trains and improves models using filtered real-time data. |
|
Chatbot Integration |
Supports IBM Watson by managing the data for chatbot operations. | Powers the chatbot with its NLP algorithm for booking, symptoms checking and general inquiries. |
|
Real-Time Data |
Supplies live, filtered data from sensors and devices to the dashboard. |
Analyses live data to provide actionable insights and predictions to the dashboard. |
|
Dashboard Interaction |
Feeds real-time data directly to the dashboard for user interactions. |
Provides analytics and chatbot responses to the dashboard for user interaction. |
|
Adaptability |
Uses AI to find patterns in data formatting and security logs. |
Adapts models based on new medical data to improve accuracy and performance. |

- Bottom Layer
- Proposed System Validation
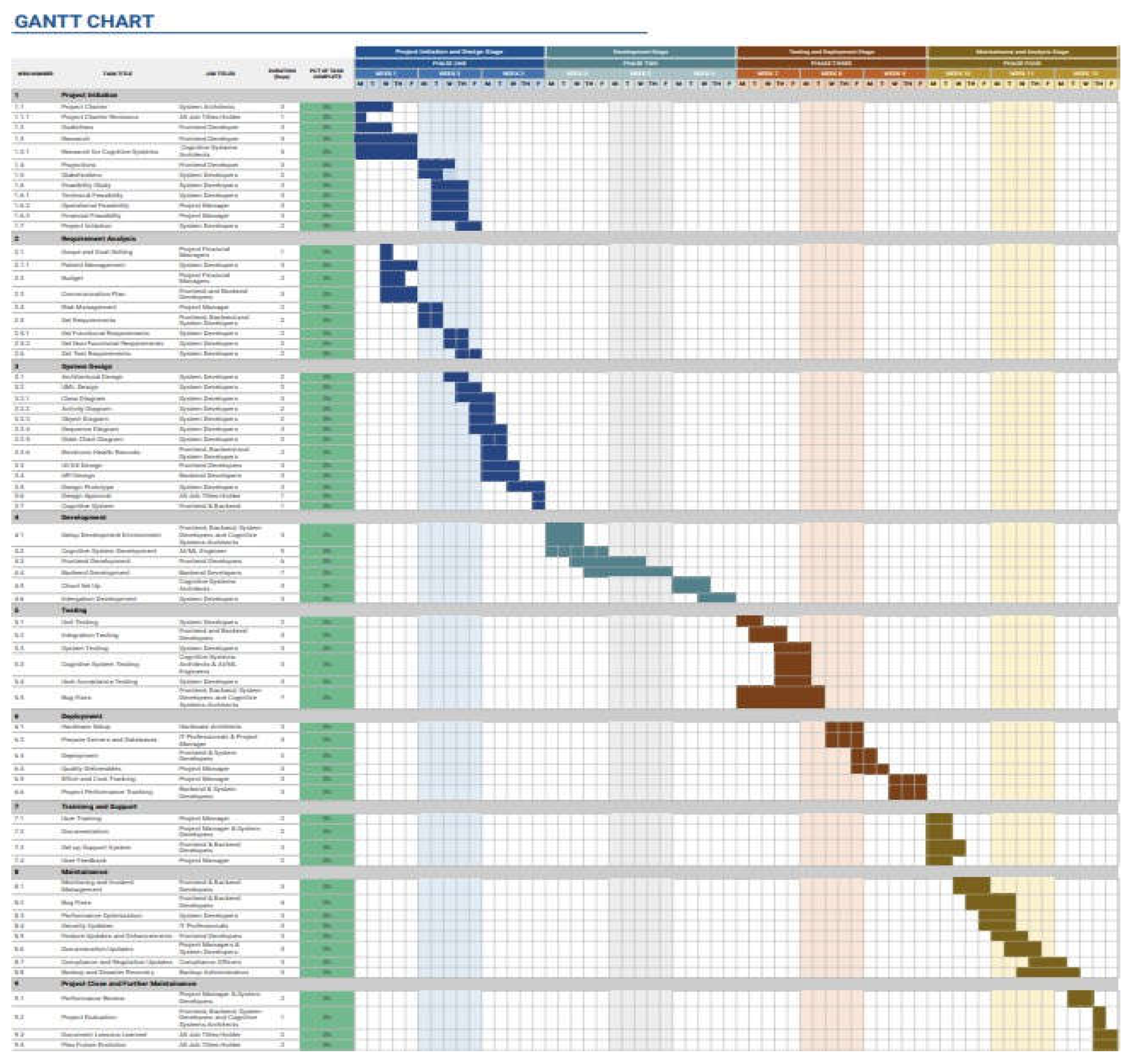
5. Implementation Plan and Challenges
5.2. Implementation Plan
- Challenges and Contingency Plan
- Data Migration
- Lack of Expertise
- System Downtime
- Cost Analysis
- System Maintenance Costs
- Manpower Costs
- Miscellaneous Costs
|
Category |
Details |
Cost for 12 Months |
Sources |
|
Monthly Subscription Costs |
Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines | RM 3,355.15 | Source |
| AWS Cloud-based Servers (PaaS) | RM 643,132 | Source | |
| Azure Blob Storage | RM 47,406 | Source | |
| Microsoft Fabric | RM 275,049.96 | Source | |
| IBM Watson NLP APIs | RM 80,280 | Source | |
| Watson Assistant for Chatbot | RM 7,492.80 | Source | |
| Microsoft Azure Health Bot Services | RM 26,760 | Source | |
| FHIR API | RM 7,163.16 | Source | |
| System Maintenance Costs |
Regular updates for the system |
RM 10,000 |
Source |
|
Manpower Costs |
Developers |
RM 960,000 |
Source |
| Staff Training | Source | ||
| Miscellaneous Costs |
Redundancy Costs |
RM 60,000 |
Source |
| Total | RM 2,120,639.07 | ||
- Ethical and RegulatoryConsiderations
- Data
- ata Privacy and Transparency
- Biases in DiagnosticAlgorithms
Conclusion
References
- Alese, B.K. Elliptic curve cryptography for securing cloud computing applications [PDF]. ResearchGate. 2013. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271851848_Elliptic_Curve_Cryptography_for_Securing_Cloud_Computing_Applications.
- Arslanian-Engoren, C. Gender and age bias in triage decisions. Journal of Emergency Nursing 2000, 26, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, J. Create and deploy a healthcare chatbot with Azure Health Bot: Step-by-step guide. DEV Community. 2024. https://dev.to/john0isaac/create-and-deploy-a-healthcare-chatbot-with-azure-health-bot-step-by-step-guide-414g.
- Barth, S. Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare & hospitals. ForeSee Medical. 2023. https://www.foreseemed.com/artificial-intelligence-in-healthcare.
- Brain, D.; Webb, G. On the effect of data set size on bias and variance in classification learning. 1999. https://i.giwebb.com/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/brainwebb99.
- Ceron, R. AI vs machine learning vs deep learning. IBM. 2019. https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-vs-machine-learning-vs-deep-learning.
- Cordero, D. The downsides of artificial intelligence in healthcare. The Korean Journal of Pain 2023, 37, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielkievych, A. Top 10 data migration challenges in 2023 (Solutions added). Forbytes. 2023. https://forbytes.com/blog/common-data-migration-challenges/.
- Broshkov, D. Why Microsoft Cloud is the best solution for healthcare? ZenBit. 2024. https://zenbit.tech/blog/benefits-microsoft-cloud-for-healthcare.
- Federico, L.; Franco, P.; Minelli, A.; Zumpano, E. 2016 SINSE+. ResearchGate. 2020. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339781629_2016_SINSE.
- FutureLearn. What is AI in healthcare? Pros, cons & applications. 2023. https://www.futurelearn.com/info/blog/what-is-ai-in-healthcare.
- Gianfrancesco, M.A. , Tamang, S., Yazdany, J., & Schmajuk, G. Potential biases in machine learning algorithms using electronic health record data. JAMA Internal Medicine 2018, 178, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alferidah, D.K. , & Jhanjhi, N.Z. Cybersecurity impact over big data and IoT growth. In 2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence (ICCI) (pp. 103–108). IEEE. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Jena, K.K. , Bhoi, S.K., Malik, T.K., Sahoo, K.S., Jhanjhi, N.Z., Bhatia, S., & Amsaad, F. E-learning course recommender system using collaborative filtering models. Electronics 2022, 12, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aherwadi, N.; Mittal, U.; Singla, J.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. , Yassine, A., & Hossain, M.S. Prediction of fruit maturity, quality, and its life using deep learning algorithms. Electronics 2022, 11, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S. , Vimal, S., Jhanjhi, N.Z., Dhanabalan, S.S., & Alhumyani, H.A. Blockchain-based peer-to-peer communication in autonomous drone operation. Energy Reports 2021, 7, 7925–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhanjhi, N.Z. , Humayun, M., & Almuayqil, S.N. Cybersecurity and privacy issues in industrial Internet of Things. Computer Systems Science & Engineering 2021, 37, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Abdullah, A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. A review on honeypot-based botnet detection models for smart factory. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2020, 11, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumaste, P. Top reasons to consider self-service Azure bots. Whizlabs. 2019. https://www.whizlabs.com/blog/top-reasons-to-consider-self-service-azure-bots/.
- Gupta, D. A guide to modernizing legacy systems in healthcare. Appinventiv. 2023. https://appinventiv.com/blog/legacy-systems-in-healthcare/.
- Hammar, M. First, second & third-party audits: The differences. 9001Academy. 2015. https://advisera.com/9001academy/blog/2015/02/24/first-second-third-party-audits-differences/.
- Heyduk, A. Microsoft’s bot to aid global healthcare. Infermedica. 2020. https://infermedica.com/blog/articles/microsoft-health-bot-service-solution-that-enhances-healthcare-organization-globally.
- Hoffman, S.; Podgurski, A. Artificial intelligence and discrimination in health care. Yale Journal of Health Policy, Law, and Ethics. 2021. https://openyls.law.yale.edu/handle/20.500.13051/5964.
- IBM IBM Integration Bus 10.0.0: Security message flow overview. 2023. https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/integration-bus/10.0?topic=security-message-flow-overview.
- IBM IBM Watson. 2023. https://www.ibm.com/watson.
- IBM Healthcare technology solutions & services. 2024. https://www.ibm.com/industries/healthcare.
- IBM IBM watsonx — An AI and data platform built for business. 2024b. https://www.ibm.com/watsonx.
- Joynt Maddox, K.E. , Reidhead, M., Hu, J., Kind, A.J.H., Zaslavsky, A.M., Nagasako, E.M., & Nerenz, D.R. Adjusting for social risk factors impacts performance and penalties in the hospital readmissions reduction program. Health Services Research 2019, 54, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S. Microsoft expands healthcare AI, analytics capabilities. TechTarget. 2024. https://www.techtarget.com/healthtechanalytics/news/366613572/Microsoft-expands-healthcare-AI-analytics-capabilities.
- McGuinness, T. , & CVP Global Healthcare & Life Sciences. Microsoft cloud for healthcare: Reshaping the future of healthcare. Microsoft Industry Blogs. 2022. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/industry/blog/healthcare/2022/03/15/microsoft-cloud-for-healthcare-reshaping-the-future-of-healthcare/.
- McKeon, J. Fix for Azure Health Bot vulnerabilities prevents exploitation. HealthTech Security. 2024. https://www.techtarget.com/healthtechsecurity/news/366603098/Fix-for-Azure-Health-Bot-vulnerabilities-prevents-exploitation.
- Medical Information Technology Inc. Introducing MEDITECH’s electronic health record. https://home.meditech.com/en/d/uk/otherfiles/ehr12uk.pdf.
- Microsoft. Azure Health Bot project – AI at work for your patients. Microsoft Research.2023. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/health-bot/.
- Panch, T.; Mattie, H.; Atun, R. Artificial intelligence and algorithmic bias: Implications for health systems. Journal of Global Health 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.S. AI-enabled hospital management systems for modern healthcare: An analysis of system components and interdependencies. Journal of Advanced Analytics in Healthcare Management 2023, 7, 212–228. [Google Scholar]
- Price, L. IBM’s Watson was once heralded as the future of healthcare – what went wrong? Nelson Advisors Blog. 2023.https://www.healthcare.digital/single-post/ibm-s-watson-was-once-heralded-as-the-future-of-healthcare-what-went-wrong.
- Restack. Explainable AI features in IBM Watson. Restack.io. 2024. https://www.restack.io/p/explainable-ai-answer-ibm-watson-features-cat-ai.
- Adlluru, S.K. The rise and fall of IBM Watson: Lessons from AI’s journey in healthcare. Medium. 2024. https://medium.com/@14asaikiran06/the-rise-and-fall-of-ibm-watson-lessons-from-ais-journey-in-healthcare-8d43bb60cc85.
- Shachar, C.; Gerke, S. Prevention of bias and discrimination in clinical practice algorithms. JAMA. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shacklett, M. IBM Watson: A cheat sheet. TechRepublic. 2018. https://www.techrepublic.com/article/ibm-watson-the-smart-persons-guide/.
- Shah, N.D. , Steyerberg, E.W., & Kent, D.M. Big data and predictive analytics. JAMA 2018, 320, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, A.; Chen, F.; Khan, H.U. , Ming, Z., Ahmad, A., Nazir, S., & Shafiq, M. A systematic review on cloud storage mechanisms concerning e-healthcare systems. Sensors 2020, 20, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajane, K.; Dave, S.; Jahagirdar, P.; Ghadge, A.; Musale, A. AI-based chatbot using Azure cognitive services. IEEE Xplore. [CrossRef]
- Sindiramutty, S.R. , Jhanjhi, N.Z., Tan, C.E., Lau, S.P., Muniandy, L., Gharib, A.H.,... & Murugesan, R.K.Industry 4.0: Future Trends and Research Directions. Convergence of Industry 4.0 and Supply Chain Sustainability 2024, 2018, 342-405.
- Shah, I.A. , Jhanjhi, N.Z., & Ray, S.K. Enabling Explainable AI in Cybersecurity Solutions. In Advances in Explainable AI Applications for Smart Cities (pp. 255–275). IGI Global Scientific Publishing. 2024.
- Gaur, L.; Jhanjhi, N.Z. (Eds.) Metaverse applications for intelligent healthcare. IGI Global. 2023. 2023.
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Verma, S.; Kavita Jhanjhi, N.Z. , & Ghoniem, R.M. Vbswp-CeaH: vigorous buyer-seller watermarking protocol without trusted certificate authority for copyright Protection in cloud environment through additive homomorphism. Symmetry, 14(11) 2022, 2441.
- Gaur, L.; Arora, G.K. , & Jhanjhi, N.Z. Deep learning techniques for creation of deepfakes. In DeepFakes (pp. 23–34). CRC Press. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Humayun, M.; Sujatha, R.; Almuayqil, S.N. , & Jhanjhi, N.Z. A transfer learning approach with a convolutional neural network for the classification of lung carcinoma. In Healthcare (Vol. 10, No. 6, p. 1058). MDPI. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Anandan, R.; Suseendran, G.; Chatterjee, P.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Ghosh, U. How COVID-19 is accelerating the digital revolution. Springer: Cham, Switzerland. 2022. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




