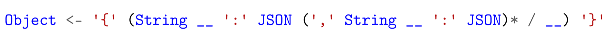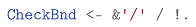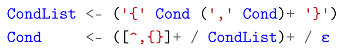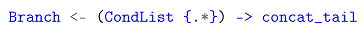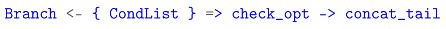1. Introduction
Text parsing and pattern matching are critical in modern software development, underpinning tasks like processing configuration files, interpreting data formats, and crafting domain-specific languages. LPeg, a Lua-based implementation of Parsing Expression Grammars (PEG), combines PEG’s expressive power and predictability with Lua’s simplicity and adaptability in this domain. Academic research, such as Ierusalimschy (2009), delves into LPeg’s internals as a PEG-driven pattern matching tool [
1] while Medeiros (2008) dissects the parsing machine that drives its functionality [
2]. Despite its robust design, LPeg’s advanced capabilities remain underutilized in practice.
This paper seeks to unlock LPeg’s potential through a dual case study approach, highlighting advanced techniques that extend beyond basic pattern matching. By focusing on optimized grammar design, we aim to demonstrate how these methods enhance performance while preserving code clarity and readability. Our exploration centers on two intricate parsing challenges:
High-performance JSON parser: We implement a JSON parser that leverages advanced LPeg optimizations to achieve performance comparable to hand-optimized Lua parsers. This case study showcases techniques including table construction optimization and substitution capture.
Sophisticated Glob-to-LPeg converter: We develop a converter that transforms Glob patterns into equivalent LPeg patterns, showcasing LPeg’s flexibility in handling complex pattern matching scenarios. This study illustrates how clear separation of pattern matching rules and strategic optimization choices can lead to both performant and maintainable code.
These studies illustrate how different LPeg grammar designs, applied to identical parsing goals, yield diverse performance outcomes when the library’s strengths are fully leveraged. We reveal optimization techniques for PEG-based parsers that rely on thoughtful pattern construction rather than altering the core library. Our work offers actionable insights into building efficient parsers without sacrificing code quality.
The paper is organized as follows: We begin with an overview of LPeg’s core concepts to build a basic understanding of LPeg; we also introduce existing JSON parsers and Glob matchers to provide context for our two case studies. Next, we dive into the case studies, detailing their implementation, optimization approaches, and technical hurdles. We then assess the performance and efficacy of our solutions, benchmarking them against existing alternatives. Finally, we distill our findings and explore how these LPeg techniques could apply to other parsing contexts.
Through these detailed, real-world examples, we aim to equip the Lua community with a deeper understanding of LPeg’s capabilities, encouraging developers to harness its full power for complex text processing and parsing challenges. The full source is available at
https://github.com/brynne8/advanced-lpeg.
2. Related Work
To lay the groundwork for exploring advanced LPeg applications, it is important to first review the technical background. This review encompasses not only the development of LPeg but also related parsing techniques, as well as studies on JSON parsers and Glob matchers.
2.1. Overview of LPeg
LPeg (Lua Parsing Expression Grammars) is a pattern matching library for the Lua programming language, offering powerful parsing capabilities. LPeg was first proposed by Roberto Ierusalimschy in 2008 as an efficient way to implement Parsing Expression Grammars (PEGs) in Lua. PEGs, introduced by Ford (2004) [
3], provide an alternative to context-free grammars (CFGs) for specifying the syntax of programming languages and other structured data formats. One advantage of PEGs over CFGs is that a PEG specification not only describes the language syntax but also inherently defines how to parse it, eliminating the need for separate parsing algorithms or disambiguation rules that are often required with CFGs.
LPeg’s design philosophy emphasizes simplicity, expressiveness, and efficiency. It allows developers to define grammars using a combination of pattern matching functions and operators, which can be easily composed to create complex parsing expressions. LPeg’s core features include:
Pattern Matching: LPeg provides a concise and expressive syntax for defining patterns, enabling powerful and flexible pattern matching within Lua.
-
Captures: LPeg allows capturing and extracting specific parts of the input during parsing, enabling the construction of structured representations of the parsed data, such as abstract syntax trees (ASTs) or Lua tables. Among its various capture types:
Group captures let you collect multiple related matches as a single unit
Match-time captures provide dynamic control over the matching process by evaluating a function at runtime that can determine whether and how the match should proceed
Accumulator captures modify previous captured values by applying a function that combines the last capture with the current one.
Grammar Definition: LPeg grammars are defined using a set of rules, each associating a name with a parsing expression. These rules can be recursive, allowing the specification of complex language constructs. However, LPeg does not support left recursion and will detect and report such patterns as errors.
Efficiency: LPeg is designed with performance in mind, featuring a fast pattern matching engine implemented in C. It employs various optimization techniques, such as special purpose instructions, tail call optimization and head-fail optimization, to minimize parsing overhead.
One of LPeg’s key strengths lies in its seamless integration with Lua. LPeg grammars can be defined using Lua’s expressive and dynamic features, such as first-class functions and table constructors. This enables developers to create modular and reusable parsing components that can be easily combined and extended.
LPeg has found widespread adoption in the Lua community for a variety of parsing tasks, including configuration file processing, data format parsing, and the implementation of domain-specific languages (DSLs). Its simple yet powerful API and efficient implementation have made it a go-to choice for many Lua developers.
In the following sections, we will explore advanced LPeg techniques and optimizations through two in-depth case studies: a high-performance JSON parser and a sophisticated Glob-to-LPeg converter. These case studies will demonstrate how LPeg can be leveraged to tackle complex parsing challenges while achieving high performance and strong expressiveness.
2.2. JSON Parsers
JSON parsing efficiency is crucial in modern software development, where applications must handle increasingly data-rich operations. The challenges in implementing an efficient JSON parser extend beyond simple text processing, encompassing the handling of deeply nested structures, dynamic type management, and memory optimization. These challenges have led to various implementation approaches across programming languages.
In various programming languages, there are dedicated JSON parsing libraries, such as JSON.parse in JavaScript, the json library in Python, Jackson and Gson in Java, and RapidJSON in C++. These parsers are usually implemented as handwritten recursive descent parsers or state machines to achieve efficient parsing.
In the Lua ecosystem, common JSON parsing libraries include:
These existing JSON parsing libraries in the Lua ecosystem provide a solid foundation for understanding different approaches to JSON parsing, from pure Lua implementations to high-performance C libraries.
2.3. Glob Matchers
Glob patterns are primarily used for file path matching and are widely used in Unix/Linux systems [
4]. They provide a concise syntax for matching file paths through wildcards and pattern expressions. While conceptually simple, implementing efficient and correct glob matching presents interesting challenges, particularly regarding standardization and performance.
The implementations of glob matchers vary across programming environments, including the built-in glob command in Unix/Linux, Python’s glob module, Node.js libraries like minimatch, and Go’s filepath.Glob function. From analyzing these implementations, two predominant approaches emerge: converting glob patterns to regular expressions, and implementing dedicated parsers.
The Lua ecosystem has limited options for Glob pattern matching. An early attempt, lua-glob-pattern [
5], tried to provide basic file globbing by converting glob patterns to Lua patterns, but its functionality was constrained by the inherent limitations of Lua patterns. Subsequently, lua-glob [
6] emerged as a notable implementation built with LPegLabel (an extension of LPeg). NeoVim also includes its own LPeg-based glob implementation, designed specifically for its environment [
7].
The emergence of Microsoft’s Language Server Protocol (LSP) 3.17 specification [
8] has begun to address the historical lack of formal standardization in glob implementations, with projects like NeoVim adopting this specification as a reference. These existing implementations, with their different approaches and performance characteristics, provide a valuable insights for understanding the challenges and opportunities in glob pattern matching.
3. Notation and Conventions
To make the LPeg patterns in this paper more readable and understandable, we adopt the same syntax used in LPeg.re (except in long strings, forms like
\0 or
\31 are escaped representing specific characters), a Lua module for LPeg that allows patterns to be written in a string format closer to standard PEG syntax. For readers who are more familiar with LPeg’s Lua API functions (such as
lpeg.P,
lpeg.R,
lpeg.S, etc.), please refer to the LPeg.re official documentation
2 for a detailed explanation of the relationship between the two syntaxes.
In this paper, we will use the following notation conventions:
These conventions aim to make it easier for readers to understand and follow the examples and case studies discussed throughout the paper.
3.1. Symbols
Throughout this paper, we use consistent symbols to enhance readability:
p denotes a pattern, which depending on context may refer to a PEG pattern or a Glob pattern
s refers to the starting rule in a grammar, particularly when a grammar has only one rule
denotes the PEG transformation of a Glob pattern p, resulting in an equivalent PEG expression
Note that the transformed could be a grammar with several rules, in which case refers to the call to the starting rule of that grammar, rather than inlining the entire grammar. Additionally, can be used within larger PEG expressions, combining with other PEG syntaxes.
This notation allows us to precisely describe the transformation process from Glob patterns to their equivalent LPeg implementations, which is central to our Glob-to-LPeg converter case study.
4. Case Studies
To showcase the application of advanced LPeg techniques and demonstrate their impact on parsing performance and pattern matching expressiveness, we have selected two representative case studies for in-depth analysis. These case studies, focusing on a high-performance JSON parser and a sophisticated Glob-to-LPeg converter, allow us to explore a range of LPeg optimization strategies and extensions in practical scenarios.
As a widely used data exchange format, the implementation of a JSON parser can effectively demonstrate LPeg’s advantages and potential for optimization when handling structured data. The Glob-to-LPeg conversion, on the other hand, demonstrates LPeg’s flexibility and powerful features in handling complex pattern matching problems. Through these two case studies, we can see not only the practical application of LPeg but also explore how to use LPeg’s features to optimize performance and improve code quality.
Next, let’s analyze these two case studies in detail.
4.1. Case Study: JSON Parser - A Concise Example
This section describes the implementation of a JSON parser using LPeg that complies with the ECMA-404 JSON specification [
9]. The discussion begins by presenting a slightly modified version of the Parsing Expression Grammar (PEG) description of JSON, as outlined by Yedidia [
10].
 |
|
Listing 1. PEG grammar for JSON |
The grammar provided above is a concise representation of how one might typically define a JSON grammar for purposes of understanding and implementation. This string-based grammar can be directly utilized with LPeg’s re.compile to produce a JSON validator. When JSON text conforms to this grammar, the validator returns the length of the JSON string plus one; for non-conforming text, it returns nil. This behavior is consistent with any grammar that does not include LPeg-specific captures.
To transform this validator into a full-fledged JSON parser, captures must be added to retain the JSON data as a Lua table structure. Consider the following examples for Array and Number:
In this extended grammar, the Array rule captures JSON values within an outermost table capture, thereby aggregating them into a single Lua table. The Number rule uses the tonumber function to convert the matched string into a Lua number.
Furthermore, the UnicodeEscape rule cannot remain as currently defined. To correctly identify UTF-16 surrogate pairs, we need to handle two different cases:
Here, the surrogate function handles surrogate pairs, while proc_uesc processes unicode characters in the Basic Multilingual Plane.
After incorporating these captures, the parser becomes capable of generating a usable Lua table structure from JSON data. However, the performance of this parser remains average, with potential risks of exceeding Lua’s maximum stack limit.
4.1.1. Optimizing Whitespace Handling
Regarding the whitespace in this JSON grammar (the __ rule in the PEG), we have some ideas for improvement. One simple approach is to eliminate redundant matching of whitespaces. For the JSON rule, which handles whitespace uniformly at its end, we notice that the String rule also processes whitespace at its conclusion. We therefore consider removing the trailing whitespace part from the String rule, and adding the necessary whitespace after it when the String exists as an Object key. This transforms our Object rule to:
Additionally, we realize that the trailing whitespace in the JSON rule affects the ability of its preceding choices to benefit from tail call optimization. Removing the trailing whitespace from the JSON rule will improve performance and reduce the LPeg VM stack usage for JSON parsing, helping to parse more deeply nested JSON files. The modified JSON rule becomes:
Corresponding locations that use the JSON rule would then supplement it with whitespace calls. Through these modifications, we ensure that the JSON grammar doesn’t sacrifice performance in its formulation. This provides a solid foundation for discussing more advanced optimizations later.
4.1.2. Accumulator vs Function-Based Object Construction
LPeg’s accumulator captures provide an intuitive approach to implementing JSON object parsing by enabling incremental construction of complex data structures. This mechanism effectively implements a fold operation within PEG, allowing us to aggregate captured values into a growing structure. Consider this implementation using accumulator captures:
The add_prop function serves as the accumulator, incrementally constructing the object by adding each property. Here is its implementation, which clearly demonstrates how it processes the key-value pairs:
This implementation initializes an empty table via new_table, which serves as the accumulator’s initial value. As the parser encounters each key-value pair, it invokes add_prop to incorporate the property into the growing table. The anonymous group capture ensures proper aggregation of the matched content, correctly binding both key and value parameters.
Considering LuaJIT’s optimization characteristics, where well-crafted Lua code can potentially outperform C implementations, we can explore an alternative implementation strategy:
This alternative approach employs a single function capture at the pattern’s conclusion. By collecting all pairs first and constructing the object at once, it optimizes C-to-Lua transitions and simplifies group captures. The corresponding make_table implementation requires careful attention:
While this implementation incurs the overhead of creating an argument table (as Lua lacks direct stack manipulation capabilities), it leverages strategic table management to enhance performance. Notably, it pre-allocates the result table with precise hash space dimensioning via
table.new [
11], enabling more efficient memory utilization by the Lua VM. This function-based approach demonstrates particular efficiency when processing JSON objects with numerous key-value pairs, where the benefits of bulk object construction become more pronounced.
4.1.3. Substitution Capture
Substitution capture, while less known, is a powerful feature of LPeg. PEG captures can be categorized into generative and substitutive. Generative captures build larger structures from captured components, while substitutive captures aim to replace parts of a string based on a predefined pattern.
LPeg’s substitution capture falls into the latter category. Within a substitution capture, all captures replace the original matched content rather than generating results directly. This technique is particularly useful in scenarios like handling escapes within strings. Without substitution capture, the rules related to String might look like this:
Due to the presence of
Escape,
StringBody generates multiple string fragments. To merge these fragments efficiently, table capture is used to gather them into a Lua table, which is then merged using the
fast_merge function (actually
table.concat3). This approach is faster than concatenating strings individually, given Lua’s inefficiency with the
.. operator for large-scale string concatenation. Using substitution capture simplifies and accelerates this process:
Substitution capture optimizes the getcaptures phase by reducing memory allocation overhead, which is particularly beneficial for large JSON files. In generative capture, each fragment generates a Lua string, necessitating memory allocation and deallocation. Substitution capture, by contrast, uses luaL_Buffer to merge C strings, significantly reducing the memory burden.
4.2. Case Study: Glob-to-LPeg Converter - An In-Depth Analysis
The JSON parser case study exemplifies a relatively straightforward application of LPeg optimization, providing a foundation for understanding basic concepts. However, the challenge of converting Glob patterns to LPeg representations introduces a more intricate problem, meriting a thorough exploration. This expanded case study enables us to delve into a wider array of LPeg features and optimization strategies within a practical context.
Glob patterns offer a concise yet powerful syntax for file path matching. The
vim.glob.to_lpeg converter in the NeoVim project [
7], which translates Glob patterns into corresponding LPeg patterns, highlights the potential of such conversions, though it leaves room for improvement. In this section, we propose Peglob, a more comprehensive converter from Glob to LPeg, aiming to enhance the functionality and precision of existing tools.
4.2.1. Overview of Glob Grammar
According to the LSP 3.17 specification [
8], Glob patterns incorporate various special characters and syntaxes, including:
* to match one or more characters in a path segment
? to match on one character in a path segment
** to match any number of path segments, including none
{} to group conditions (e.g. *.ts,js matches all TypeScript and JavaScript files)
[] to declare a range of characters to match in a path segment (e.g., example.[0-9] to match on example.0, example.1, …)
[!...] to negate a range of characters to match in a path segment (e.g., example.[!0-9] to match on example.a, example.b, but not example.0)
The LSP specification provides a broad definition of Glob patterns without enforcing a strict grammar. To implement a well-defined PEG version of Glob patterns, we apply the following constraints:
A Glob pattern must match an entire path, with partial matches considered failures.
The pattern only determines success or failure, without specifying which parts correspond to which characters.
A path segment is the portion of a path between two adjacent path separators (/), or between the start/end of the path and the nearest separator.
The ** (globstar) pattern matches zero or more path segments, including intervening separators (/). Within pattern strings, ** must be delimited by path separators (/) or pattern boundaries and cannot be adjacent to any characters other than /. If ** is not the final element, it must be followed by /.
{} (braced conditions) contains valid Glob patterns as branches, separated by commas. Commas are exclusively used for separating branches and cannot appear within a branch for any other purpose. Nested {} structures are allowed, but {} must contain at least two branches—zero or one branch is not permitted.
In [] or [!...], a character range consists of character intervals (e.g., a-z) or individual characters (e.g., w). A range including / won’t match that character.
4.2.2. Pattern Analysis and Implementation Strategy
The key to efficient Glob pattern matching lies in a fundamental architectural decision: strictly separating in-segment pattern matching from segment-crossing behaviors. This separation simplifies both implementation and optimization while maintaining pattern matching correctness.
Within a path segment, patterns operate in a well-defined, constrained environment. Patterns in a segment can be categorized into two types:
Fixed-length patterns: Including string literals, single character wildcards (?), and character classes ([])
Variable-length patterns: Including star (*) and globstar (**)
This classification guides our implementation strategy, particularly in handling path segments efficiently. Within path segments, patterns alternate between fixed-length Word constructs and variable-length Star operators, forming the basis of our matching algorithm.
This controlled scope of segment-level matching allows us to safely apply sophisticated optimizations without risking unintended interactions with segment-crossing patterns. The separation of concerns ensures that our optimization strategies remain effective while maintaining pattern matching correctness.
The handling of segment-crossing patterns, particularly the globstar (**) operator, becomes cleaner through this separation. The globstar operator is treated as a distinct element that operates purely at the segment boundary level. This clarity of purpose makes the implementation both more robust and more maintainable.
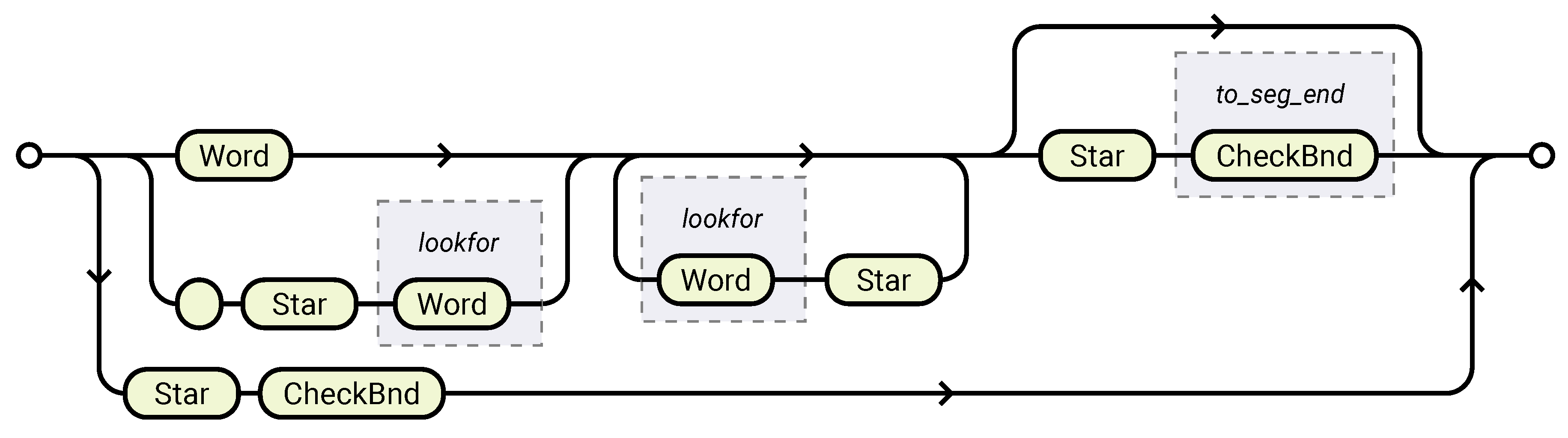
Segment-Level Pattern Matching
In path segment matching, patterns alternate between
Word and
Star, as outlined in the syntax diagram at
Figure 1. Both
lookfor and
to_seg_end operate as accumulator captures, folding over the matched text to incrementally build the result. The
Segment grammar splits into two branches: the first begins with
Word as the initial accumulator value, while the second starts with an empty string (denoted by an empty circle in the railroad diagram).
A constraint in this syntax is CheckBnd, enforced whenever a Star appears at the end of a Segment match:
This rule prevents globstar patterns from erroneously spanning segment boundaries by requiring either a forward slash (/) or the end of input. By doing so, it confines star matching to within a single segment, ensuring precise control over pattern scope.
The foundation of fixed-length pattern matching lies in the Word rule:
Here, Word establishes the basis for matching fixed-length patterns. An optimization comes from the FIRST rule, which extracts a deterministic first character when possible:
Due to LPeg’s limitations, extracting the first character requires match-time capture, as other capture types cannot capture the character without consuming it.
Captured via LPeg’s named group mechanism, this first-character information drives the
lookfor function, which generates tailored LPeg search patterns. When a deterministic first character is identified,
lookfor produces an optimized pattern (
); otherwise, it defaults to a plain pattern (
):
The
lookfor function’s ability to produce
is key to its efficiency. When a deterministic first character is identified,
optimizes the search by skipping positions in the input where the current character doesn’t match the pattern
p’s required starting character. This
skipping false starts technique, adapted from Ierusalimschy’s work [
1], boosts performance by avoiding unnecessary matching attempts, unlike the slower
, which lacks this optimization.
Handling star patterns within segments poses a distinct challenge. Drawing on Cox’s insight into pattern matching structure [
12], we avoid nested matching—which often leads to exponential backtracking—and instead flatten the
lookfor function calls. For instance, a pattern like
a*b?c*x is processed as sequential calls—
a lookfor(b?c) lookfor(x)—rather than a nested structure like
a lookfor(b?c lookfor(x)). This flattening preserves correctness while significantly reducing complexity. The
lookfor function’s accumulator capture maintains state across the matching process, and its use of
ensures that the search for each subsequent pattern benefits from the false-start-skipping optimization tailored to Glob semantics.
For star patterns at segment ends, the to_seg_end function translates them into a greedy match ([⌃/]*), appended to the existing grammar. Since the star is terminal, it consumes all remaining characters within the segment boundary, with CheckBnd ensuring no overreach beyond the slash or input end.
The
Word rule also integrates the
Branch rule to support braced conditions, introducing variable-length elements. While this departs from strict fixed-length matching, it raises complexities addressed later in
Section 4.2.3.
Together, these components—the deterministic character extraction of FIRST, the pattern generation and optimization of lookfor, and Cox’s flattened search strategy—form a robust framework for segment-level pattern matching. By enforcing strict segment boundaries and leveraging these optimizations, the system efficiently handles complex patterns while maintaining semantic accuracy.
Cross-Segment Pattern Matching
With segment-level matching established as a foundation, we can construct higher-level grammatical structures. In our Glob grammar, the topmost layer consists of the Glob and Element rules, as shown in Listing 2. The Glob rule handles both absolute paths (beginning with slash) and local paths (beginning with Element). Consequently, the Glob rule starts with an optional Element.
The rules Glob, Element, and DSeg each incorporate EOF handling to ensure proper termination: EOF functions as a boundary marker for these rules. The first branch of the Element rule ending (slash eof / eof?) is deliberately designed this way to ensure that a slash not followed by EOF is handled by the (slash Element)* portion of the Glob rule. Each rule maintains strict boundary awareness, avoiding consumption of input required by other rules.
 |
|
Listing 2. The topmost rules of our Glob-to-LPeg converter, Peglob. The captures are removed to present a clear grammar. DSeg and DSEnd rules are used to process globstars. |
Element, functioning as a fundamental matching unit, provides an abstraction that can be repeated at the higher level (Glob rule) while integrating globstar patterns with ordinary Segment groups (structured as Segment (slash Segment)*). Regarding the downward functionality, we must first examine how globstar semantics are implemented in our PEG grammar.
We categorize globstars into two types based on their position: globstars appearing at the pattern’s end are processed by the DSEnd (double-star ending) rule, as they do not involve searching for subsequent patterns. For globstars in other positions, we employ the DSeg (double-star segment) rule, which processes the globstar together with the following slash, forming a segment-like structure (though its function is inherently cross-segment).
This differentiation enables simpler handling of straightforward cases. The
DSEnd rule directly translates a terminal globstar into a greedy match (
.*), which consumes all remaining input. The
DSeg processing is more complex, transforming the globstar and its continuation (the
Element or EOF matched in the rule) into a search structure. For a pattern like
**/p, the resulting PEG takes the form:
While this search represents a form of lazy matching for , its second branch efficiently skips in-segment content since we only need to determine whether globstar’s continuation can be matched from a certain segment head. By restricting the globstar’s continuation to a single Element, we mirror the flattened search strategy discussed earlier. By enabling Element to match Segment groups, DSeg’s search need only concern itself with matching this portion, without considering subsequent glob pattern matching.
The use of Segment groups rather than individual Segments addresses an important edge case. Consider a Glob pattern like */b/d/* and a path /a/b/c/b/d/e. If the last Element branch matched only a single Segment, after matching /a/b, the grammar would expect /d, but encountering /c would cause the match to fail since the prior /b cannot be backtracked.
This design allows our glob matcher to avoid backtracking at the cross-segment level. Combined with segment-level optimizations, this establishes a robust foundation for efficient pattern matching across both segment and path levels.
4.2.3. Braced Conditions and Expansion
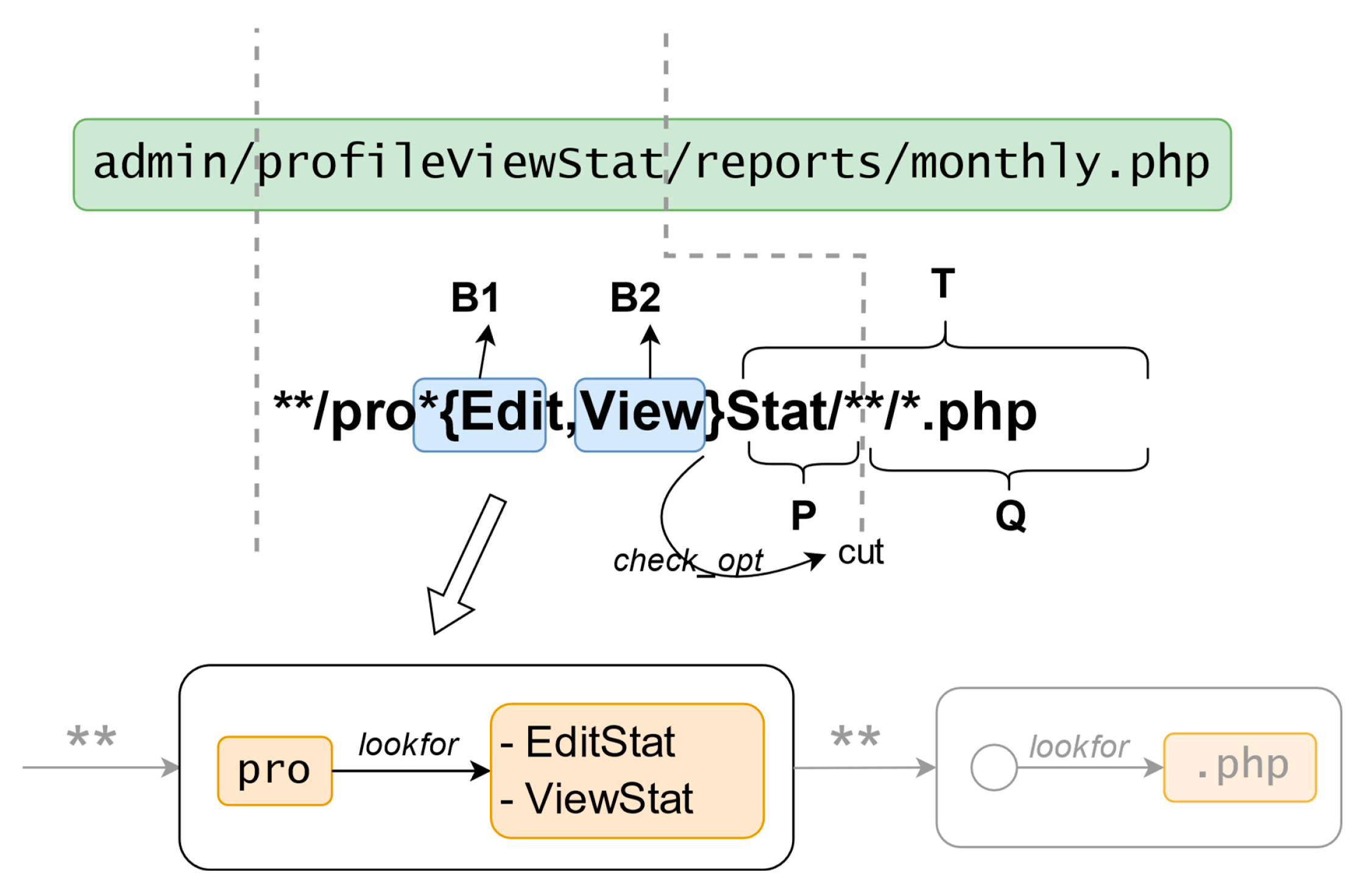
Braced conditions ({}) introduce branching complexity that requires careful handling. While our initial approach aimed to handle complex structures without expansion, practical considerations led us to implement brace expansion as a preprocessing step.
Brace expansion, a Unix shell feature, simplifies input by specifying similar string parameters. For example,
enable_{audio,video} expands to
enable_audio and
enable_video. The expansion rules are as follows: comma-separated segments within braces represent alternatives, generating all possible combinations. These alternatives accumulate in a Cartesian product and expand in left-to-right order. Unmatched braces and special characters are treated as literals [
13].
Before delving deeper, let’s examine how braced conditions are transformed into PEG. Braced conditions in Glob patterns are analogous to alternation in regular expressions. Therefore, our approach to handling braced conditions mirrors Medeiros’s [
14] treatment of alternation. For Glob patterns
R,
S, and
T, the expression
transforms into PEG form following this derivation:
For instance, the glob pattern
{foo,bar}baz transforms into the PEG
’foo’ ’baz’ / ’bar’ ’baz’. To further illustrate this concept, consider a more complex example: the glob pattern
{ab,c{d,e}}fg. We first expand the braced conditions, then combine them with the subsequent pattern:
This means that when we transform braced conditions into PEG, we must consume the full pattern that follows the braced condition, to construct the equivalent ordered choices structure in PEG.
4 We’ve designed a two-level PEG structure to handle braced condition transformations.
At the lower level, the CondList and Cond grammar rules work together to implement true Unix shell-style brace expansion:
Here, denotes an empty string. By folding captures on CondList and Cond, we derive an expanded list of strings in a table format.
At a higher level, these expansion results are concatenated and transformed into LPeg through concat_tail in the Branch rule:
This covers the basic processing logic for braced conditions. In the glob grammar, braced conditions are embedded within the Word rule through the WordAux rule. This design choice is critical because braced conditions can vary in scope—either staying within a single path segment or extending across multiple segments—depending on their internal patterns. By integrating them into WordAux, the grammar accommodates these differences seamlessly, without requiring significant changes to its core structure.
Moreover, this integration ensures that braced conditions are handled consistently with standard Word patterns, even in segments that include the star (*). This consistency allows the lookfor function to operate reliably across all cases. As a result, the grammar correctly parses braced conditions without complicating its structure.
Corner Cases with Star and Globstar
The interaction between brace expansion and star/globstar patterns creates several important corner cases:
Scenario 1: ...*{*/p,...}, where expansion results in a star before and after the brace merging into a globstar.
Scenario 2: ...**{*p,...}, where the globstar takes precedence over the star, converting into three tokens: **, *, and p.
Scenario 3: ...**{**/p}, which, regardless of expansion, results in two globstars followed by /p.
Scenario 4: ...q{/**/p,...}, where q is a Word not ending in a star or globstar. This scenario expands into a valid pattern (q/**/p).
Our handling of these cases ensures consistent behavior while maintaining the system’s overall integrity:
By keeping the content before the first brace unchanged and expanding the content afterward, star merging is prevented. While this approach may differ from some other Glob matchers, such patterns are rare in practice.
Scenarios involving globstar precedence are avoided by our grammar constraints, as they would produce invalid patterns according to our globstar positioning rules.
Double globstar cases, while syntactically valid, are semantically meaningless due to our constraints on globstar behavior. The system correctly identifies and rejects such patterns.
Valid combinations with path separators match correctly, maintaining consistent matching semantics even with variable-length content.
5. Evaluation
To comprehensively evaluate the effectiveness of the LPeg optimization techniques and the Glob-to-LPeg conversion method proposed in this paper, we designed a series of experiments. These experiments aim to test the performance of our JSON parser and Glob-to-LPeg converter from different angles and compare them with existing solutions. All experiments were conducted in a controlled environment using an Intel Core i7-8550U processor, 8GB DDR4 2400MHz RAM, running Alpine Linux v3.18 with LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta3 and LPeg 1.1.0. Each benchmark included 3 warmup runs to account for JIT behavior and was executed 10 times to ensure statistical significance.
5.1. JSON Parser Performance
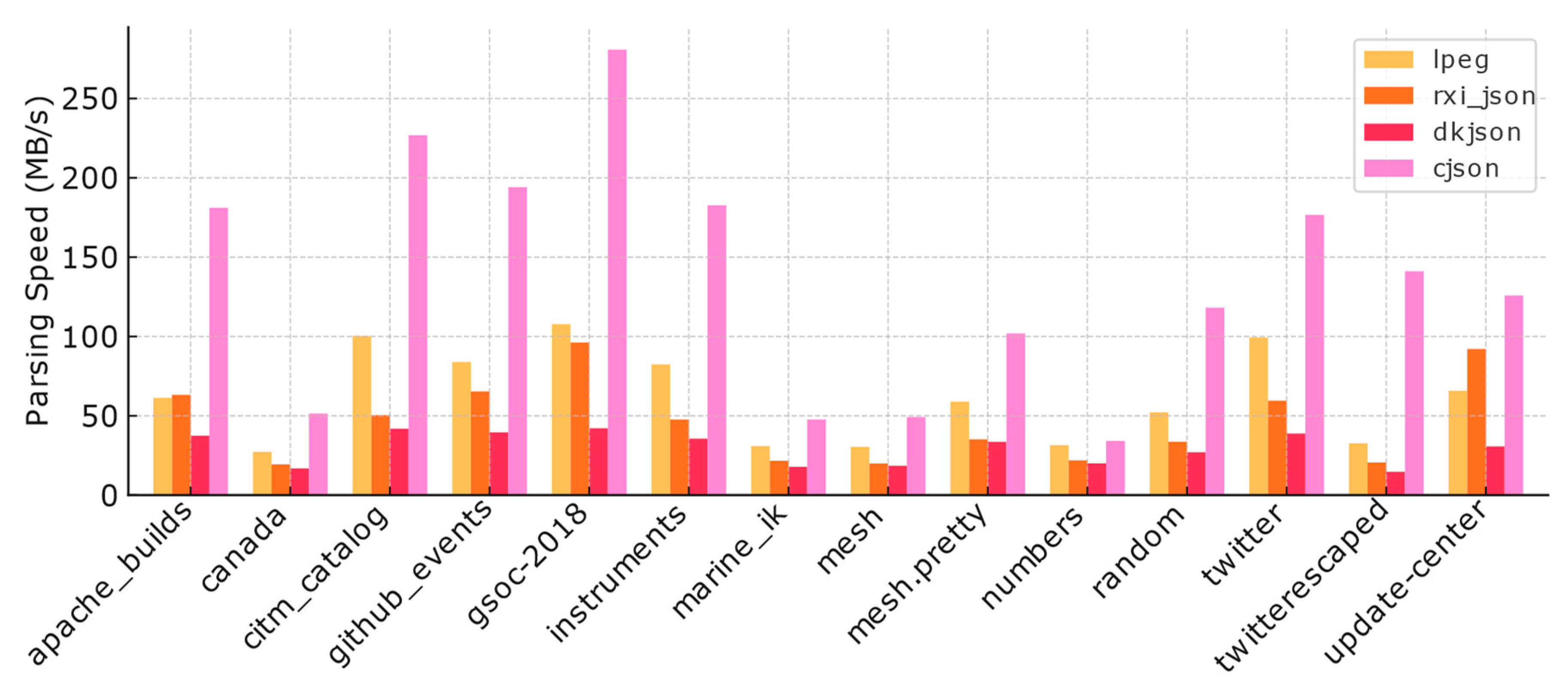
We evaluated our optimized LPeg JSON parser’s performance against existing JSON parsers (cjson, dkjson, and rxi_json) using a diverse set of JSON files ranging from 64KB to 3MB with varying structural complexities from [
15]. As shown in
Figure 3, our implementation demonstrated competitive performance, particularly excelling in processing documents with complex structural patterns and diverse content types.
The parser showed remarkable efficiency in handling documents with high structural density and deep nesting patterns. For string-dominated documents like gsoc-2018.json and instruments.json, our implementation achieved parsing speeds of 107.80 MB/s and 82.41 MB/s respectively, significantly outperforming rxi_json. This advantage extended to documents with mixed content types, as demonstrated in github_events.json (83.94 MB/s) and instruments.json (82.41 MB/s), where our parser efficiently handled varying combinations of strings, numbers, and nested structures.
While the C-based cjson maintained its performance lead due to its lower-level implementation, our LPeg-based parser consistently outperformed dkjson and showed competitive results against rxi_json across most test cases. The only exception was update-center.json, where the relatively uniform structure appeared to favor rxi_json’s parsing approach. These results validate our optimization strategy and demonstrate the viability of LPeg-based parsing for performance-critical JSON processing tasks.
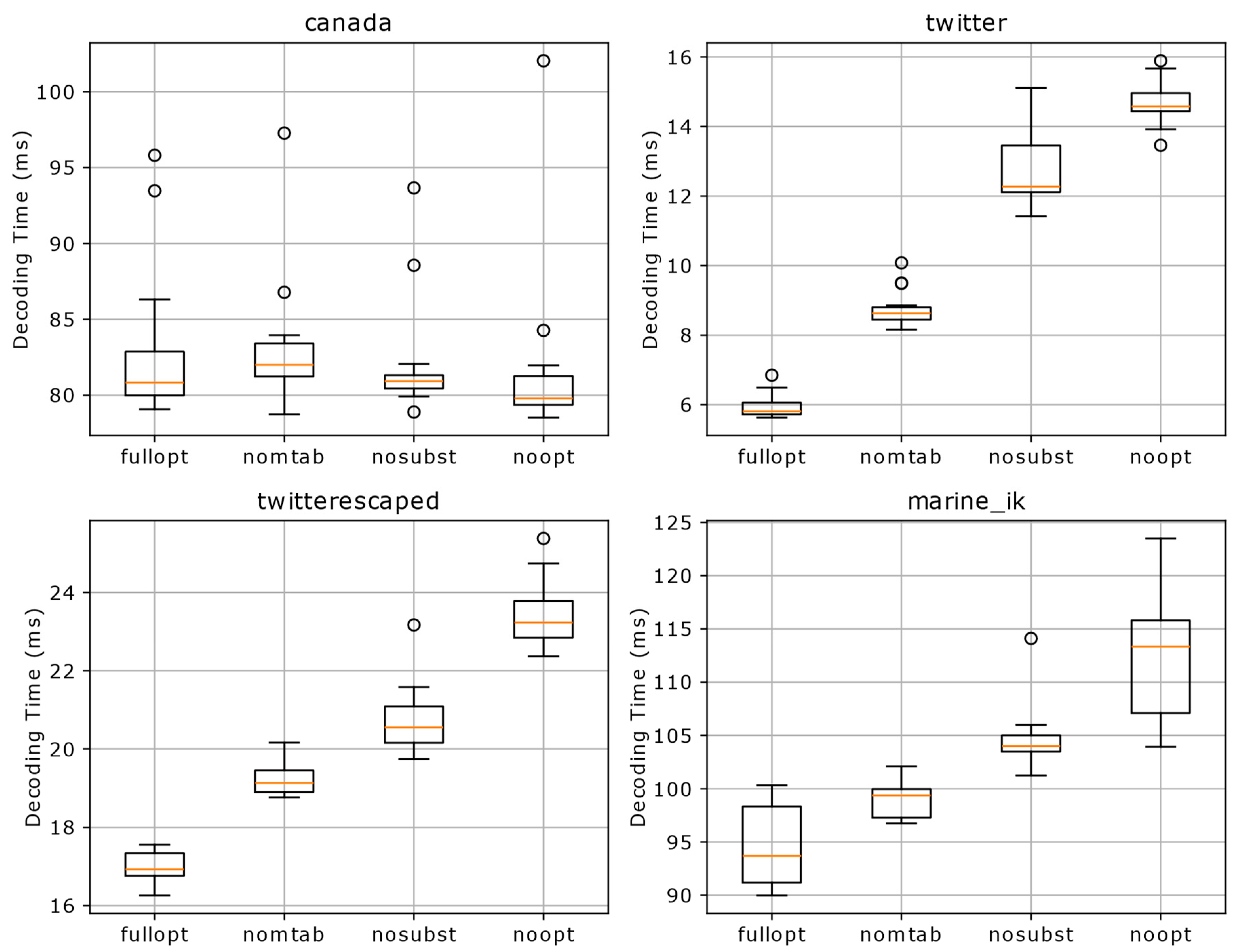
We also analyzed the contribution of different optimization techniques to overall performance by evaluating the impact of two key optimizations: table creation (via
make_table) and substitution capture. Four diverse datasets were considered—canada.json for numerical processing, twitter.json for Unicode handling, twitterescaped.json for escape sequence processing, and marine_ik.json for complex nested structures—with performance measured as the median decoding time under four configurations: fully optimized, without table creation, without substitution capture, and with no optimizations, as depicted in
Figure 4.
For the string-heavy datasets, the benefits of these optimizations were pronounced. In twitter.json, the fully optimized median was 5.81 ms; however, disabling table construction optimization increased this to 8.63 ms (about a 49% slowdown), while omitting substitution capture nearly doubled the time to 12.27 ms (an increase of roughly 111%). Similarly, for twitterescaped.json, the fully optimized median of 16.93 ms rose to 19.14 ms without table construction optimization (a 13% increase) and to 20.55 ms without substitution capture (around a 21% slowdown).
In contrast, canada.json exhibited minimal sensitivity to these optimizations—with median times varying by less than 2.5%—indicating limited benefit for numerical data. The marine_ik.json dataset, while structurally complex, showed moderate performance degradation: its fully optimized median of 93.7 ms increased to 99.38 ms (roughly a 6% slowdown) when table creation was disabled and to 103.99 ms (about an 11% increase) without substitution capture, reaching 113.33 ms when both were removed. These findings underscore that optimization effectiveness is highly data-dependent, with string-heavy JSON benefiting significantly from substitution capture, numerically-dominated content showing negligible response to optimizations, and structurally complex data exhibiting moderate but meaningful improvements.
5.2. Glob-to-LPeg Converter Evaluation
We evaluated the correctness and performance of our Glob-to-LPeg converter, Peglob, focusing on how our architectural decisions affected real-world usage. Using the Bun.js Glob test suite as our foundation, we categorized test cases into six groups: basic patterns, star patterns, globstar patterns, brace expansions, Unicode patterns, and extension patterns. We selected this test suite for its comprehensive coverage of edge cases and complex pattern interactions, including intricate combinations of stars, globstars, character classes, and brace expansions.
We made two specific modifications to the test suite:
Correctness was assessed using accuracy (proportion of correct matches) and precision (proportion of true matches among claimed true matches) for each test case category. These are calculated as:
Here, TP (true positives), TN (true negatives), FP (false positives), and FN (false negatives) are standard evaluation metrics.
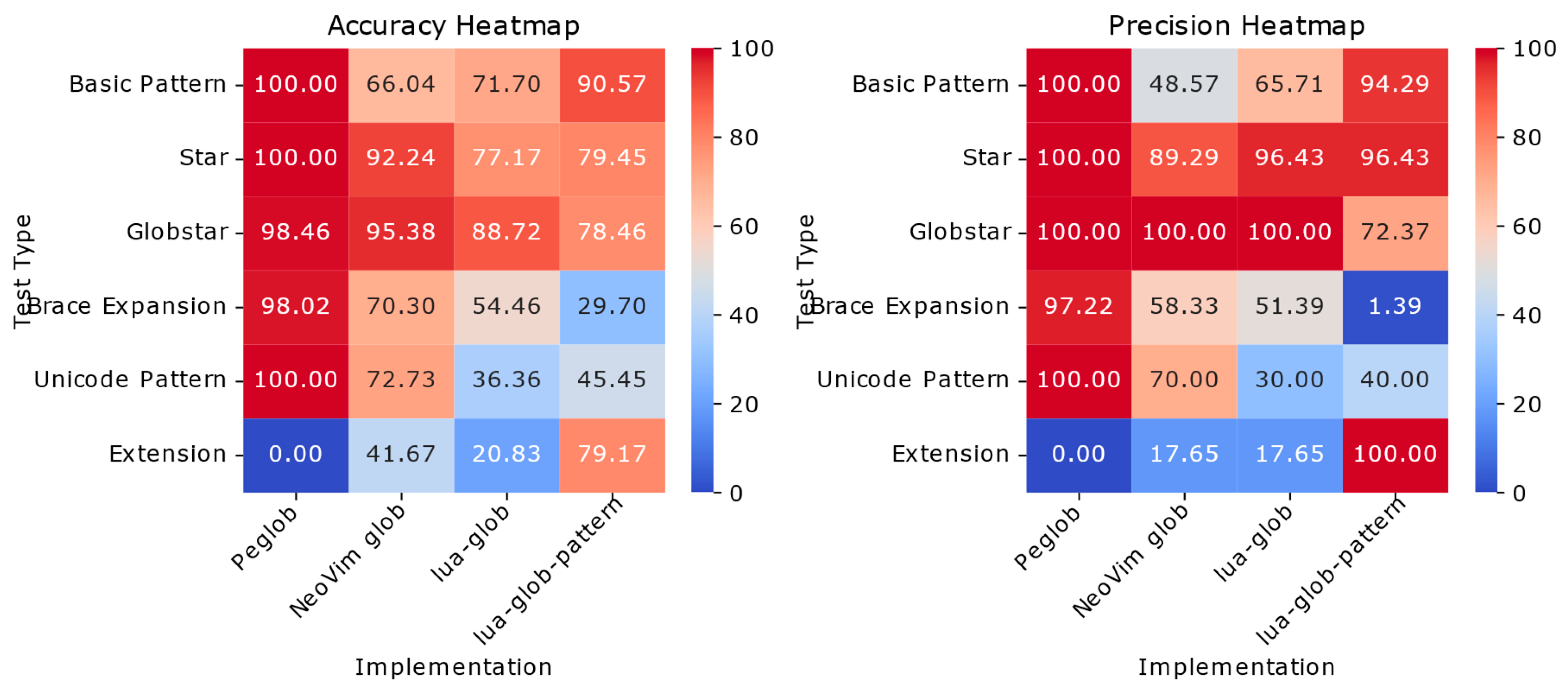
As shown in
Figure 5, Peglob demonstrates exceptional reliability across standard glob patterns, achieving perfect 100% accuracy and precision in basic patterns, star patterns, and Unicode handling. Its robustness extends to complex cases with impressive results in globstar patterns (98.46% accuracy, 100% precision) and brace expansions (98.02% accuracy, 97.22% precision). These results validate our architectural decisions, particularly our strict grammar specification which deliberately rejects all extension patterns—ensuring predictable behavior for standard glob patterns at the expense of specialized extensions that allow
** within path segments.
Comparative analysis reveals distinct trade-offs among existing implementations. Lua-glob-pattern excels with extension patterns (100% precision, 79.17% accuracy) but significantly underperforms with brace expansions (1.39% precision), revealing fundamental limitations in Lua’s pattern matching. The LPeg-based implementations show varying specializations: NeoVim’s matcher handles globstar patterns well (95.38% accuracy, 100% precision) but struggles with basic patterns (66.04% accuracy), while lua-glob achieves perfect precision in globstar matching (100%) but falls short in overall consistency, particularly with Unicode (36.36% accuracy). This performance landscape highlights the challenge of balancing comprehensive glob feature support with reliable pattern interpretation—a balance where Peglob’s grammar-driven approach demonstrates clear advantages for standard use cases.
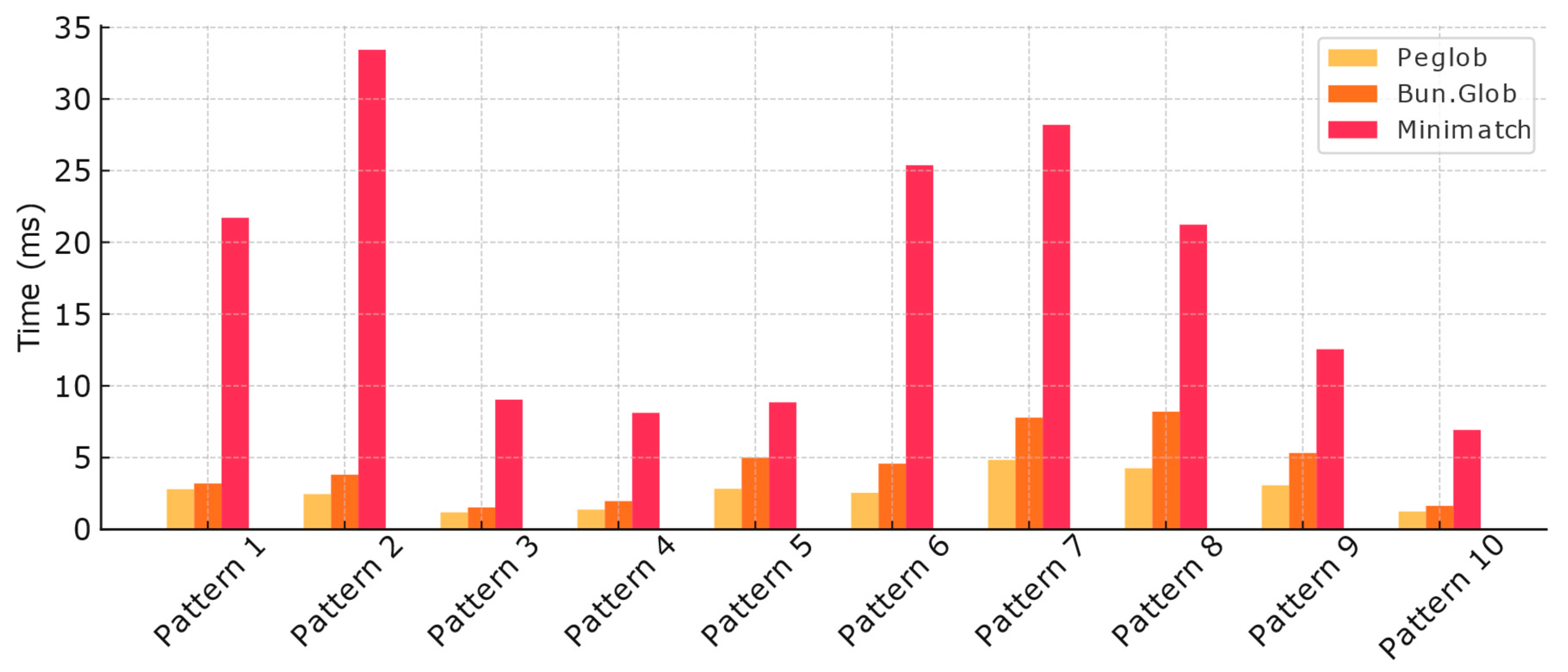
For performance testing, we used VSCode 1.97.0’s source code repository, comprising 7,894 file paths. We designed 10 challenging patterns (shown in Listing 3) to test real-world performance scenarios. We believe real-world performance is the most valuable metric as it involves a mix of matching and non-matching paths. We deliberately created high-difficulty test cases because performance differences in glob matching typically emerge from stars, globstars, and braced conditions, so our examples extensively combine these syntaxes while remaining practical.
 |
|
Listing 3. Patterns used to benchmark Glob matchers |
We compared Peglob with Bun.Glob
5 and Minimatch
6, excluding other Lua glob libraries that couldn’t correctly handle most of our test patterns. We chose Bun.Glob partly because it met our correctness requirements, thanks in part to our feedback to the Bun team.
7 Minimatch, a JavaScript library that excels in correctness, represents a typical approach of converting globs to equivalent regular expressions. Importantly, our benchmark measured only the final matching speed, not including time spent converting globs to LPeg objects or regular expressions.
The results demonstrate that our optimized Peglob implementation consistently outperformed both competitors across all test patterns. Peglob is 14% to 92% faster than Bun.Glob and 3 to 14 times as fast as Minimatch. The performance gap between Peglob and its competitors widens as pattern complexity increases, with Bun.Glob struggling with specific patterns (e.g. Pattern 7 and Pattern 8) and Minimatch showing high computational overhead across all scenarios.
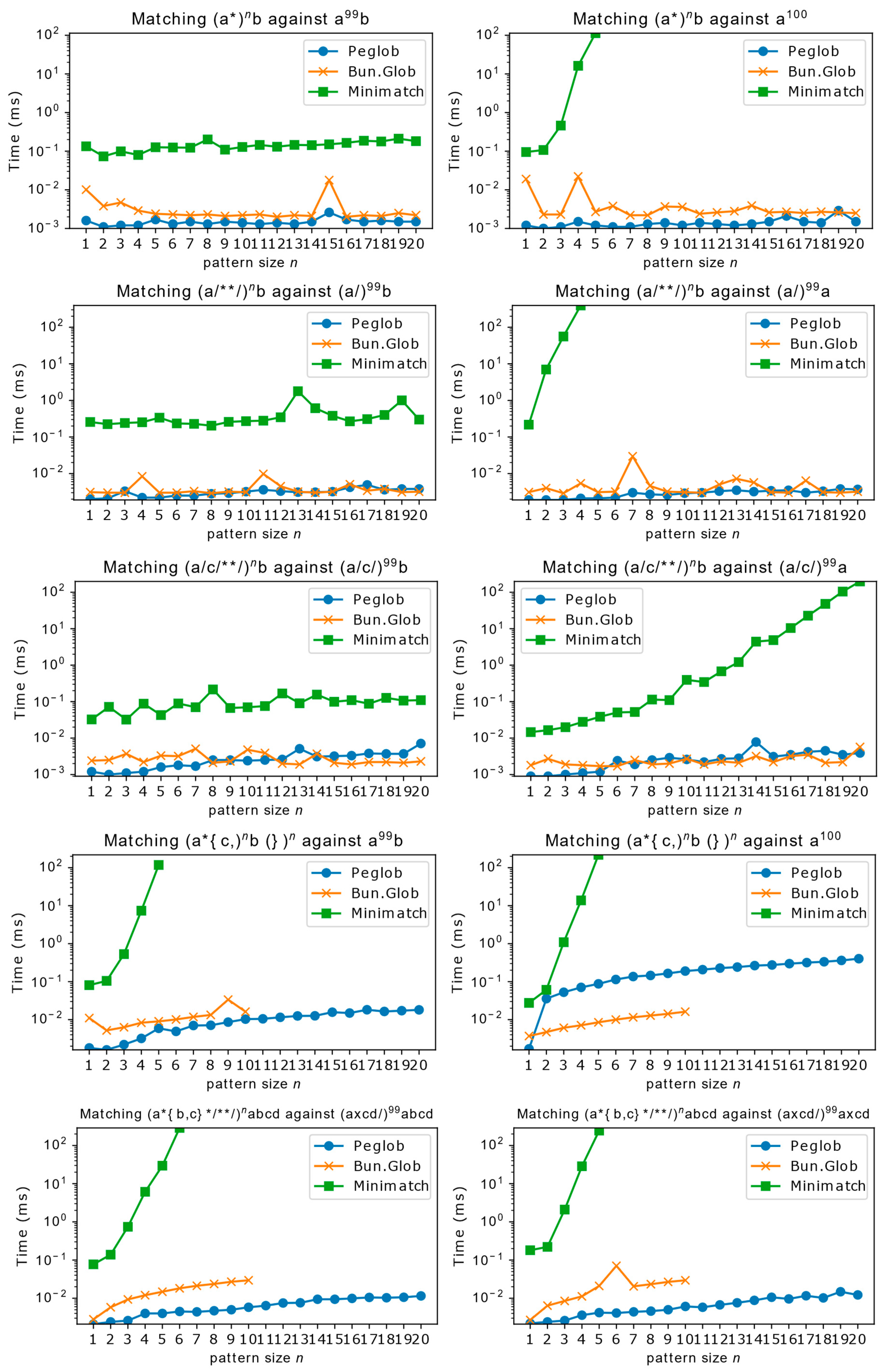
Beyond real-world scenarios, we also evaluated Peglob’s performance in extreme cases prone to backtracking. We designed five test groups to measure processing speed when gradually increasing variable-length elements for large inputs, inspired by Cox’s work [
12]. Each test group contains two scenarios: one where the pattern is expected to match the input (requiring less backtracking), and another where the pattern is expected not to match (potentially triggering extensive backtracking in unoptimized implementations).
The results in
Figure 7 show Minimatch lacks optimizations for these situations, demonstrating what performance would look like without relevant optimizations. Both Peglob and Bun.Glob performed excellently, avoiding excessive backtracking. For the last test group, specifically designed to test braced condition optimization effectiveness, Peglob’s performance remained remarkably stable. Without our braced condition optimization, Peglob would exhibit exponential time complexity due to numerous branches after brace expansion.
These consistent results across correctness and performance metrics demonstrate that our formal grammar specification and architectural decisions successfully balance robustness with efficiency, while our optimization strategies deliver significant performance improvements without compromising reliability.
6. Conclusion
This paper has explored advanced techniques for leveraging LPeg’s capabilities through two case studies: a high-performance JSON parser and a sophisticated Glob-to-LPeg pattern converter.
Our JSON parser analysis revealed that substitution capture significantly improves efficiency by reducing memory allocation overhead, particularly for string-heavy JSON documents. The table construction optimization demonstrated measurable performance improvements for object-intensive documents by pre-allocating hash space and optimizing C-to-Lua transitions. These optimizations enabled our parser to outperform other pure Lua implementations while highlighting areas where native C implementations still maintain advantages.
The Glob-to-LPeg converter case study demonstrated how a comprehensive approach to pattern matching can lead to effective results. By establishing a formal grammar specification, implementing Cox’s flattened search strategy, optimizing braced conditions, and carefully handling edge cases, we developed a solution that consistently performed well in both real-world and stress-test scenarios. Our evaluation against the VSCode repository showed Peglob performing 14% to 92% faster than Bun.Glob and 3 to 14 times faster than Minimatch across diverse pattern matching challenges. The architectural decision to separate in-segment pattern matching from segment-crossing behaviors proved particularly effective, enabling targeted optimizations while maintaining pattern matching correctness.
These case studies illustrate that PEG-based parsers can be substantially optimized through technique selection and grammar construction without modifying the underlying library. They also demonstrate that systematic analysis of pattern matching problems can lead to implementations that excel in both performance and maintainability.
Future research could explore enhancing LPeg’s memory management efficiency and extending these optimization techniques to other complex parsing domains. Our work provides practical insights for implementing efficient parsers while maintaining code clarity and reliability, contributing to the advancement of text processing capabilities in the Lua ecosystem.
7. Acknowledgement
We express our deepest gratitude to Professor Roberto Ierusalimschy and all contributors to the LPeg library for their exceptional work in creating a highly optimized PEG implementation that forms the cornerstone of our research. We are equally indebted to Dylan Conway of the Bun Team, whose prompt resolution of issues in Bun.Glob enabled us to successfully present a comprehensive benchmark for Glob matchers with all tests accurately executed.
We also extend our sincere appreciation to the reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback, which significantly enhanced the quality of this paper.
Lastly, we are grateful to the readers of this work. Your interest and engagement give our efforts purpose. We hope this paper serves as a valuable resource and source of inspiration in your exploration of LPeg and PEG, and we invite you to join us in advancing the growth and vitality of the LPeg community.
Declaration of Generative AI in Scientific Writing
During the preparation of this work the author used Anthropic Claude in order to translate the manuscript into English and improve the writing. After using this tool/service, the author reviewed and edited the content as needed and takes full responsibility for the content of the published article.
References
- Ierusalimschy, R. A text pattern-matching tool based on Parsing Expression Grammars. Software: Practice and Experience 2009, 39, 221–258. [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros, S.; Ierusalimschy, R. A parsing machine for PEGs. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2008 symposium on Dynamic languages, 2008, pp. 1–12.
- Ford, B. Parsing expression grammars: a recognition-based syntactic foundation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 31st ACM SIGPLAN-SIGACT symposium on Principles of programming languages, 2004, pp. 111–122.
- Linux man-pages project. glob - globbing pathnames. The Linux Documentation Project, 2023. Accessed: 2023-10-05.
- Manura, D. lua-glob-pattern: Converts file glob string to Lua pattern string. Available online: https://github.com/davidm/lua-glob-pattern.
- Sumneko. lua-glob. Available online: https://github.com/sumneko/lua-glob.
- NeoVim Contributors. NeoVim’s Glob Implementation. Available online: https://github.com/neovim/neovim/blob/f8cbdbb/runtime/lua/vim/glob.lua.
- Microsoft Language Server Protocol. Language Server Protocol Specification. Available online: https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/specifications/lsp/3.17/specification/#documentFilter.
- Ecma International. The JSON Data Interchange Syntax. Available online: https://ecma-international.org/publications-and-standards/standards/ecma-404/. 2nd edition, December 2017.
- Yedidia, Z. Incremental PEG Parsing. Bachelor’s thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2021.
- Pall, M. LuaJIT Extensions: table.new. Available online: https://luajit.org/extensions.html#table_new.
- Cox, R. Glob Matching Can Be Simple And Fast Too. Available online: https://research.swtch.com/glob.
- Rosetta Code. Brace Expansion. Available online: https://rosettacode.org/wiki/Brace_expansion?oldid=366904.
- Medeiros, S.; Mascarenhas, F.; Ierusalimschy, R. From regular expressions to parsing expression grammars. In Proceedings of the Brazilian Symposium on Programming Languages; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Langdale, G.; Lemire, D. Parsing gigabytes of JSON per second. The VLDB Journal 2019, 28, 941–960. [Google Scholar]
- Bun Team. bun.Glob class | API reference. Available online: https://bun.sh/reference/bun/Glob.
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
The fast_merge alias is used to better emphasizing the intention of using this function. |
| 4 |
Even with Section 4.2.3.2 optimizations, we consume at least to the segment’s end |
| 5 |
Using Bun v1.2.4-canary.13+6aa62fe4b which includes the skip_brace bugfix after Bun 1.2.3 that ported the Rust crate fast-glob. |
| 6 |
Using Minimatch 10.0.1, run in Bun environment for consistent comparison. |
| 7 |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).