Submitted:
23 April 2025
Posted:
24 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retroviral Expression Constructs and Cloning of the GBAC Vector System
2.2. Golden Gate Cloning
2.3. Surveyor Nuclease Assay
2.4. Cut-Point-Analysis by Deep Sequencing
2.5. Multiplex Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (M-FISH)
2.6. Western Blotting and Immunodetection
2.7. Data Analysis and Presentation
2.8. Culturing of Cell Lines
2.9. Retrovirus Production and Infection
2.10. Flow Cytometry
2.11. Cell Sorting
2.12. IL-3-Deprivation of Ba/F3 Cells
3. Results
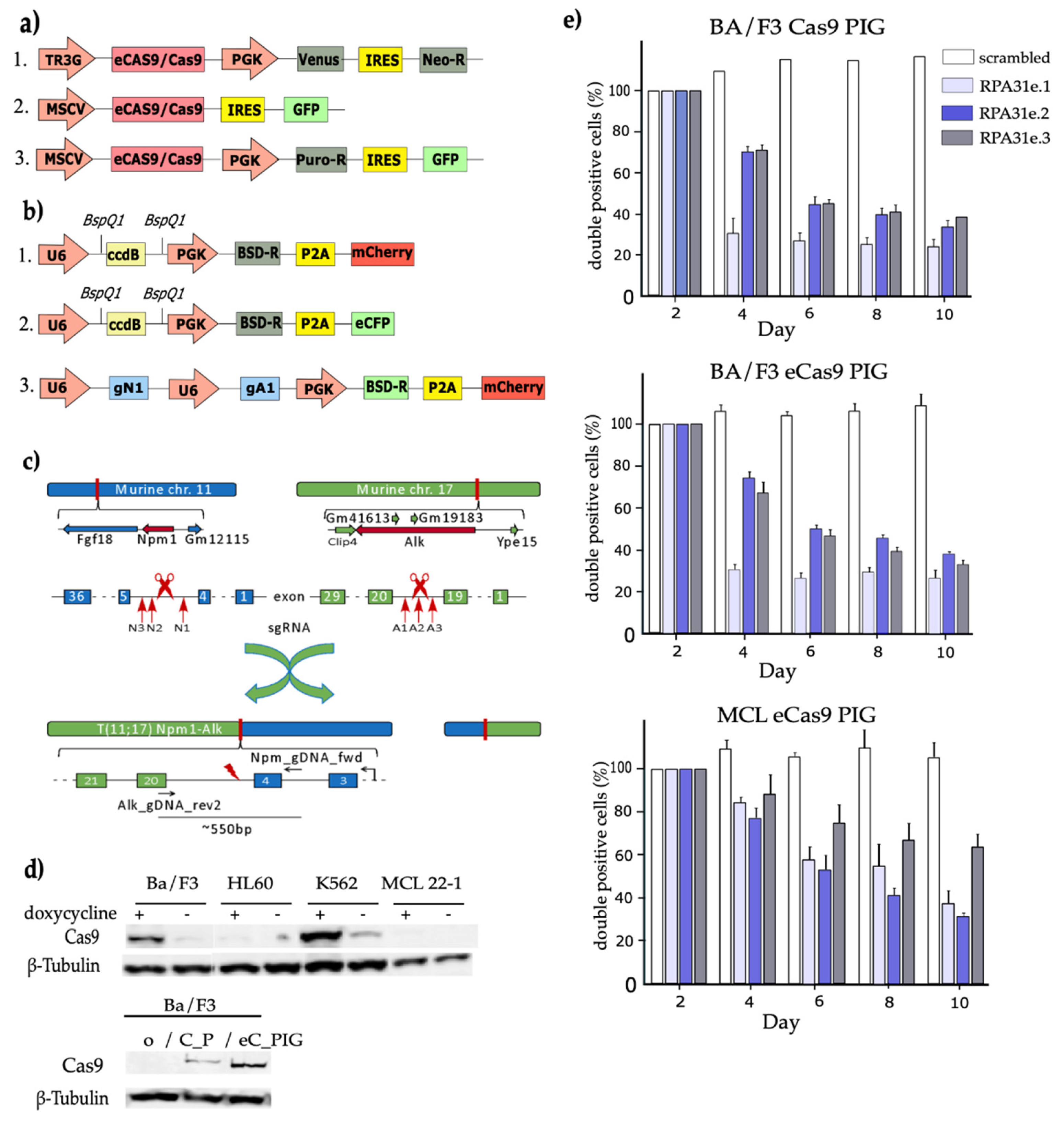
3.1. Establishment of a CRISPR/Cas9-Based Vector System
3.2. Functional Validation of Cas9 Expression Vectors After Retroviral Infection of Target Cells
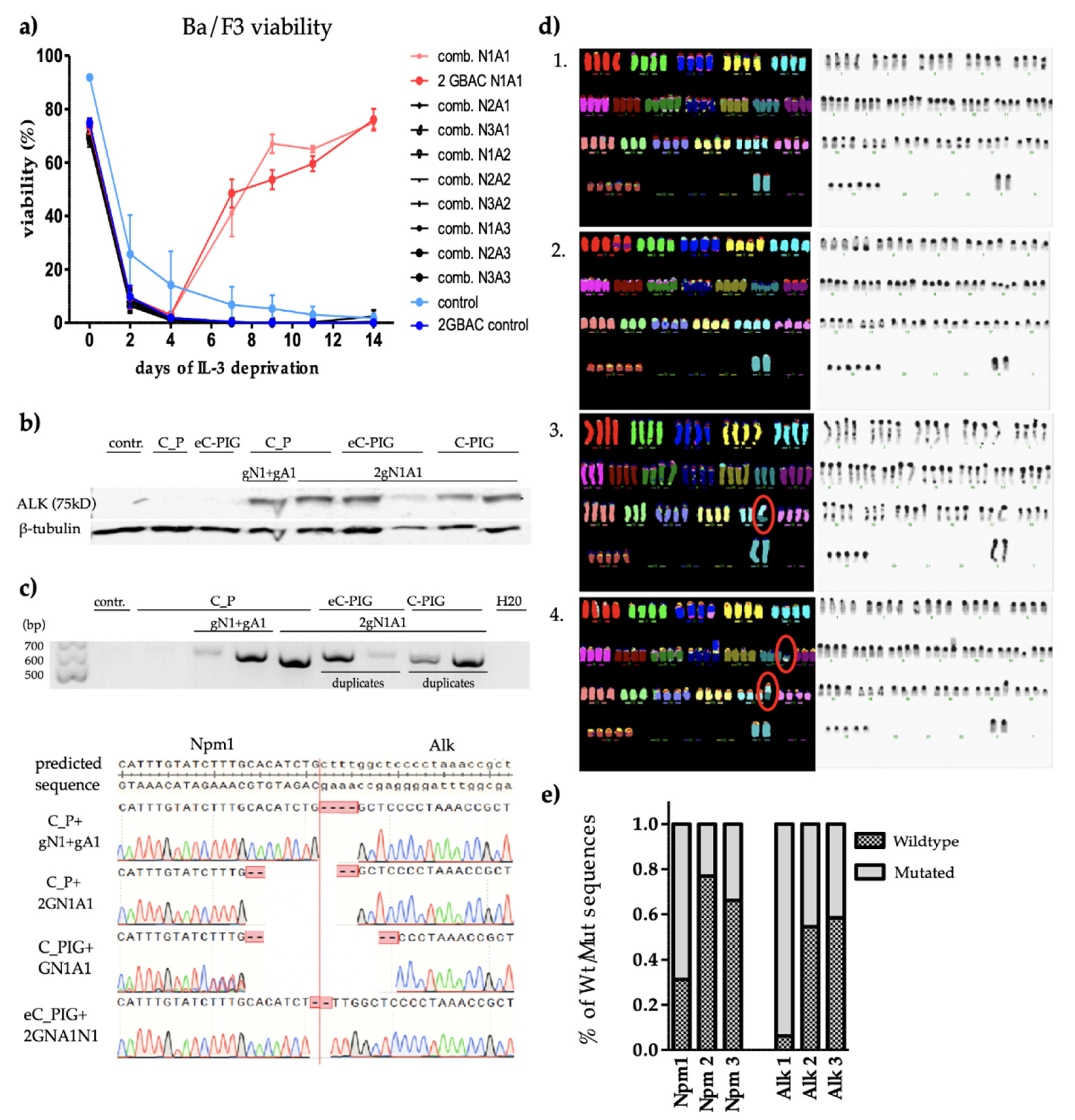
3.3. CRISPR/Cas9 Induced Npm1-Alk Translocation
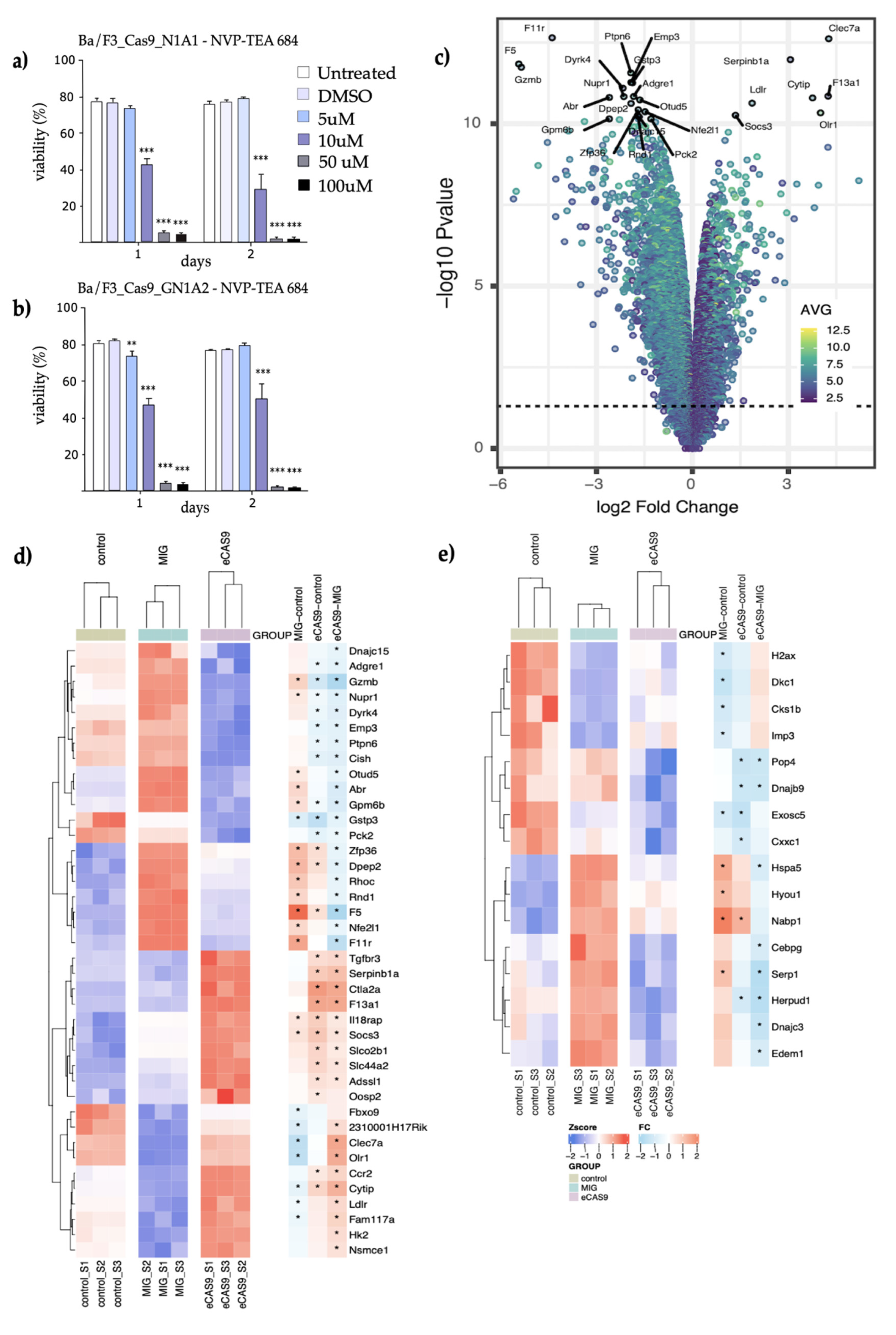
3.4. CRISPR-Cas9-Induced Npm-Alk Fusions Respond to Alk-Inhibition and Show a Distinct mRNA Expression Pattern
3.5. Cells Carrying an Endogenous Npm-Alk Translocation Demonstrate a Different mRNA Expression Pattern than Ba/F3 Cells Transformed by the Overexpressed Fusion Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAVs | adeno-associated viruses |
| ALCL | anaplastic large cell lymphoma |
| ALK | anaplastic lymphoma kinase domain |
| BIA-ALCL | breast implant-associated ALCL |
| CRISPR | clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats |
| CPPs | cell penetrating peptides |
| DBS | double-strand breaks |
| FACS | fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| GFP | green fluorescent protein |
| GOI | gene of interest |
| GSEA | gene set enrichment analysis |
| MCL | mantle cell lymphoma |
| M-FISH | multiplex fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| mHSC | murine hematopoietic stem cells |
| NHL | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| NHEJ | non-homologous end joining |
| NPM | nucleophosmin domain |
| Npm-Alk | Nucleophosmin-Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase |
| PLC-γ | phospholipase C-γ |
| SIN | self-inactivating |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| sgRNAs | single guide RNAs |
| UPR | Unfolded Protein Response |
References
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a Kinase Gene, ALK, to a Nucleolar Protein Gene, NPM, in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B. de O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boi, M.; Zucca, E.; Inghirami, G.; Bertoni, F. Advances in Understanding the Pathogenesis of Systemic Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphomas. British Journal of Haematology 2015, 168, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, B.; Pileri, S.; Zinzani, P.L.; Carbone, A.; Zagonel, V.; Wolf-Peeters, C.; Verhoef, G.; Menestrina, F.; Todeschini, G.; Paulli, M.; et al. ALK+ Lymphoma: Clinico-Pathological Findings and Outcome. Blood 1999, 93, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascoyne, R.D.; Aoun, P.; Wu, D.; Chhanabhai, M.; Skinnider, B.F.; Greiner, T.C.; Morris, S.W.; Connors, J.M.; Vose, J.M.; Viswanatha, D.S.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Protein Expression in Adults With Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Blood 1999, 93, 3913–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, C.; Jasin, M. Frequent Chromosomal Translocations Induced by DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Nature 2000, 405, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, R.T.; Saccardo, M.B.; Ardini, E.; Menichincheri, M.; Rusconi, L.; Magnaghi, P.; Orsini, P.; Avanzi, N.; Borgia, A.L.; Nesi, M.; et al. Crystal Structures of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in Complex with ATP Competitive Inhibitors. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6813–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamo, A.; Chiarle, R.; Piva, R.; Howes, J.; Fan, Y.; Chilosi, M.; Levy, D.E.; Inghirami, G. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Activates Stat3 and Protects Hematopoietic Cells from Cell Death. Oncogene 2002, 21, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slupianek, A.; Nieborowska-Skorska, M.; Hoser, G.; Morrione, A.; Majewski, M.; Xue, L.; Morris, S.W.; Wasik, M.A.; Skorski, T. Role of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase-Akt Pathway in Nucleophosmin/Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Mediated Lymphomagenesis1. Cancer Research 2001, 61, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, L.; Gundry, M.C.; Goodell, M.A. New Insights into the Biology of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Mutated NPM1. Int J Hematol 2019, 110, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, J.K.; Paquet, N.; Adams, M.N.; Boucher, D.; Bolderson, E.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Nucleophosmin: From Structure and Function to Disease Development. BMC Molecular Biol 2016, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischof, D.; Pulford, K.; Mason, D.Y.; Morris, S.W. Role of the Nucleophosmin (NPM) Portion of the Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma-Associated NPM-Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Fusion Protein in Oncogenesis. Molecular and Cellular Biology 1997, 17, 2312–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Viscardi, G.; Di Liello, R.; Fasano, M.; Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; Ciardiello, F.; Morgillo, F. Role and Targeting of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in Cancer. Molecular Cancer 2018, 17, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoumariyeh, K.; Schneider, N.; Poggio, T.; Veratti, P.; Ehrenfeld, S.; Redhaber, D.M.; Khan, R.; Pfeifer, D.; Klingeberg, C.; Kreutmair, S.; et al. A Novel Conditional NPM-ALK-Driven Model of CD30+ T-Cell Lymphoma Mediated by a Translational Stop Cassette. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, A.F.; Martin, L.J.; Minder, J.L.; Roe, J.-S.; Shi, J.; Steurer, S.; Bader, G.; McConnell, D.; Pearson, M.; Gerstberger, T.; et al. Sensitivity and Engineered Resistance of Myeloid Leukemia Cells to BRD9 Inhibition. Nat Chem Biol 2016, 12, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, E.; Milazzo, J.P.; Wang, Z.; Kinney, J.B.; Vakoc, C.R. Discovery of Cancer Drug Targets by CRISPR-Cas9 Screening of Protein Domains. Nature Biotechnology 2015, 33, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaymaker, I.M.; Gao, L.; Zetsche, B.; Scott, D.A.; Yan, W.X.; Zhang, F. Rationally Engineered Cas9 Nucleases with Improved Specificity. Science 2016, 351, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Marraffini, L.A.; et al. Multiplex Genome Engineering Using CRISPR/Cas Systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1α-Responsive Genes Involved in Oxidative Phosphorylation Are Coordinately Downregulated in Human Diabetes. Nat Genet 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Hallmark Gene Set Collection. Cell Syst 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, S.; Kojima, T.; Kitamura, T. Plat-E: An Efficient and Stable System for Transient Packaging of Retroviruses. Gene Ther 2000, 7, 1063–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, C.; Marillonnet, S. Golden Gate Cloning. Methods Mol Biol 2014, 1116, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossen, M.; Bujard, H. Tight Control of Gene Expression in Mammalian Cells by Tetracycline-Responsive Promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992, 89, 5547–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftode, C.; Daniely, Y.; Borowiec, J.A. Replication Protein A (RPA): The Eukaryotic SSB. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 1999, 34, 141–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A Tool to Design Target-Specific Primers for Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Bioinformatics 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkin, A.V.; Melnick, J.S.; Kim, S.; Hood, T.L.; Li, N.; Li, L.; Xia, G.; Steensma, R.; Chopiuk, G.; Jiang, J.; et al. Identification of NVP-TAE684, a Potent, Selective, and Efficacious Inhibitor of NPM-ALK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harewood, L.; Fraser, P. The Impact of Chromosomal Rearrangements on Regulation of Gene Expression. Human Molecular Genetics 2014, 23, R76–R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, M.S. Replication Protein A: A Heterotrimeric, Single-Stranded DNA-Binding Protein Required for Eukaryotic DNA Metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem 1997, 66, 61–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemmer, M.; Thumberger, T.; Keyer, M. del S.; Wittbrodt, J.; Mateo, J.L. CCTop: An Intuitive, Flexible and Reliable CRISPR/Cas9 Target Prediction Tool. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0124633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harewood, L.; Schütz, F.; Boyle, S.; Perry, P.; Delorenzi, M.; Bickmore, W.A.; Reymond, A. The Effect of Translocation-Induced Nuclear Reorganization on Gene Expression. Genome Research 2010, 20, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapaniemi, E.; Botla, S.; Persson, J.; Schmierer, B.; Taipale, J. CRISPR–Cas9 Genome Editing Induces a P53-Mediated DNA Damage Response. Nature Medicine 2018, 24, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




