Submitted:
25 April 2025
Posted:
25 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Physiological α-Synuclein: A Necessary Disordered Protein
2.1. Structure of α-Synuclein
2.2. Function and Subcellular Localization of α-Synuclein
2.3. α-Synuclein Interactome Further Complexes Its Understanding
2.4. Mechanisms of α-Synuclein Clearance
3. Mechanisms of Aggregation and Pathology
3.1. Mechanisms of Aggregation
3.2. Role of Post-Translational Modifications and Metals in α-Synuclein Pathology
3.3. Lewy Bodies and Pathological Inclusions
3.4. Genetic and Phenotypic Diversity in Synucleinopathies
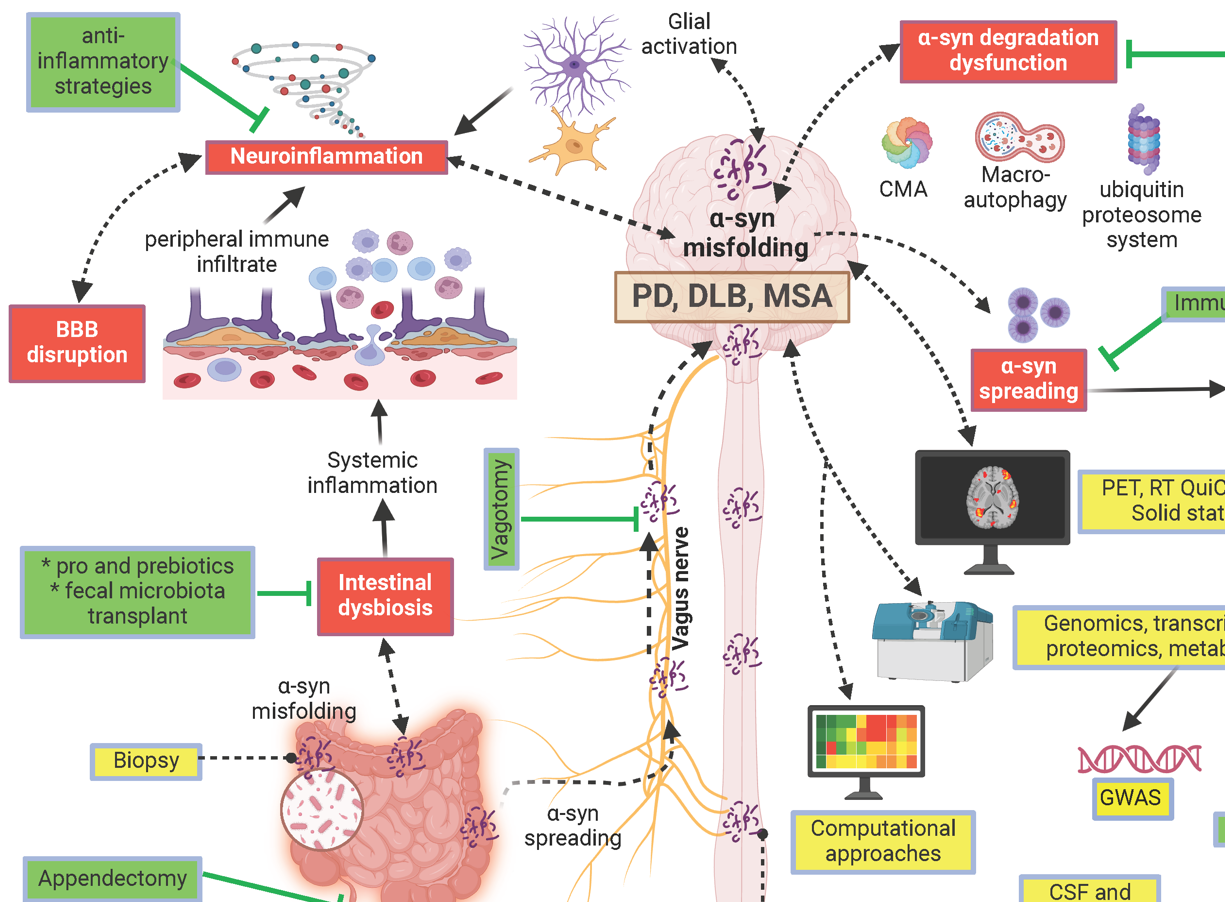
4. Propagation and Spreading
4.1. The Role of α-Synuclein Spreading in Pathology
4.2. Immune Responses and the Microbiome in Parkinson's Disease Pathogenesis
5. Models of Synucleinopathies
5.1. Animal Models of Synucleinopathies Through α-Synuclein Expression
5.2. Cellular Models of α-Synuclein Toxicity and Aggregation
6. Towards Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies
6.1. Biomarkers for Diagnosis
6.2. Therapeutic Strategies
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | Blood-Brain Barrier |
| CMA | Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CRISPR | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| DLB | Dementia with Lewy Bodies |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| GBA1 | Glucosylceramidase Beta 1 |
| GCIs | Glial Cytoplasmic Inclusions |
| GWAS | Genome-Wide Association Study |
| IDP | Intrinsically Disordered Protein |
| LB | Lewy Body |
| LRRK2 | Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 |
| MAMs | Mitochondria-Associated Membranes |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MSA | Multiple System Atrophy |
| NAC | Non-Amyloid Component |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| PD | Parkinson's Disease |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| PMCA | Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification |
| PrPC | Cellular Prion Protein |
| RT-QuiC | Real-Time Quaking-Induced Conversion |
| SAA | Seed Amplification Assay |
| SN | Substantia Nigra |
| UPS | Ubiquitin-Proteasome System |
References
- Fanciulli, A.; Wenning, G.K. Multiple-system atrophy. N Engl J Med 2015, 372, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poewe, W.; Stankovic, I.; Halliday, G.; Meissner, W.G.; Wenning, G.K.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Seppi, K.; Palma, J.A.; Kaufmann, H. Multiple system atrophy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2022, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, C.H.; Levine, T.; Adler, C.; Bellaire, B.; Wang, N.; Stohl, J.; Agarwal, P.; Aldridge, G.M.; Barboi, A.; Evidente, V.G.H.; et al. Skin Biopsy Detection of Phosphorylated alpha-Synuclein in Patients With Synucleinopathies. JAMA 2024, 331, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, L.V.; Berg, D.; Kordower, J.H.; Shannon, K.M.; Taylor, J.P.; Cardoso, F.; Goldman, J.G.; Jeon, B.; Meissner, W.G.; Tijssen, M.A.J.; et al. International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society Viewpoint on Biological Frameworks of Parkinson's Disease: Current Status and Future Directions. Mov Disord 2024, 39, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroteaux, L.; Campanelli, J.T.; Scheller, R.H. Synuclein: a neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J Neurosci 1988, 8, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulopoulos, M.; Levy, O.A.; Alcalay, R.N. The neuropathology of genetic Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2012, 27, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson's disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Yoshimoto, M.; Tsuji, S.; Takahashi, H. Alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in multiple system atrophy. Neurosci Lett 1998, 249, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.; So, R.W.L.; Lau, H.H.C.; Sang, J.C.; Ruiz-Riquelme, A.; Fleck, S.C.; Stuart, E.; Menon, S.; Visanji, N.P.; Meisl, G.; et al. alpha-Synuclein strains target distinct brain regions and cell types. Nat Neurosci 2020, 23, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Pritzkow, S.; Mendez, N.; Rabadia, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Schmeichel, A.; Singer, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Discriminating alpha-synuclein strains in Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. Nature 2020, 578, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Woerman, A.L.; Mordes, D.A.; Watts, J.C.; Rampersaud, R.; Berry, D.B.; Patel, S.; Oehler, A.; Lowe, J.K.; Kravitz, S.N.; et al. Evidence for alpha-synuclein prions causing multiple system atrophy in humans with parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, E5308–E5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espay, A.J.; Vizcarra, J.A.; Marsili, L.; Lang, A.E.; Simon, D.K.; Merola, A.; Josephs, K.A.; Fasano, A.; Morgante, F.; Savica, R.; et al. Revisiting protein aggregation as pathogenic in sporadic Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases. Neurology 2019, 92, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.H.; Rhim, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Sung, Y.M.; Lee, M.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Wolozin, B.; Chang, J.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Kwon, T.K.; et al. alpha-Synuclein interacts with phospholipase D isozymes and inhibits pervanadate-induced phospholipase D activation in human embryonic kidney-293 cells. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 12334–12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamzadeh, F.N. Alpha-synuclein structure, functions, and interactions. J Res Med Sci 2016, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasson, B.I.; Murray, I.V.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliezer, D.; Kutluay, E.; Bussell, R., Jr.; Browne, G. Conformational properties of alpha-synuclein in its free and lipid-associated states. J Mol Biol 2001, 307, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, C.R.; Dobson, C.M.; Bax, A. Multiple tight phospholipid-binding modes of alpha-synuclein revealed by solution NMR spectroscopy. J Mol Biol 2009, 390, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. A protein-chameleon: conformational plasticity of alpha-synuclein, a disordered protein involved in neurodegenerative disorders. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2003, 21, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, R.M.; Fairlie, D.P.; Mason, J.M. Alpha-synuclein structure and Parkinson's disease - lessons and emerging principles. Mol Neurodegener 2019, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantsyzov, A.B.; Maltsev, A.S.; Ying, J.; Shen, Y.; Hummer, G.; Bax, A. A maximum entropy approach to the study of residue-specific backbone angle distributions in alpha-synuclein, an intrinsically disordered protein. Protein Sci 2014, 23, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theillet, F.X.; Binolfi, A.; Bekei, B.; Martorana, A.; Rose, H.M.; Stuiver, M.; Verzini, S.; Lorenz, D.; van Rossum, M.; Goldfarb, D.; et al. Structural disorder of monomeric alpha-synuclein persists in mammalian cells. Nature 2016, 530, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltsev, A.S.; Ying, J.; Bax, A. Impact of N-terminal acetylation of alpha-synuclein on its random coil and lipid binding properties. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 5004–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergaard, M.; Brander, S.; Poulsen, F.M. Random coil chemical shift for intrinsically disordered proteins: effects of temperature and pH. J Biomol NMR 2011, 49, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvagnion, C.; Brown, J.W.; Ouberai, M.M.; Flagmeier, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Buell, A.K.; Sparr, E.; Dobson, C.M. Chemical properties of lipids strongly affect the kinetics of the membrane-induced aggregation of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvagnion, C. The Role of Lipids Interacting with alpha-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease. J Parkinsons Dis 2017, 7, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musteikyte, G.; Jayaram, A.K.; Xu, C.K.; Vendruscolo, M.; Krainer, G.; Knowles, T.P.J. Interactions of alpha-synuclein oligomers with lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 2021, 1863, 183536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurouski, D. Elucidating the Role of Lipids in the Aggregation of Amyloidogenic Proteins. Acc Chem Res 2023, 56, 2898–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, P.; Pincet, F. Freezing and piercing of in vitro asymmetric plasma membrane by alpha-synuclein. Commun Biol 2020, 3, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Claessens, M. Disruptive membrane interactions of alpha-synuclein aggregates. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 2019, 1867, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.; Pancoe, S.X.; Rhoades, E.; Petersson, E.J. The Effects of Lipids on alpha-Synuclein Aggregation In Vitro. Biomolecules 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boni, L.; Wallis, A.; Hays Watson, A.; Ruiz-Riquelme, A.; Leyland, L.A.; Bourinaris, T.; Hannaway, N.; Wullner, U.; Peters, O.; Priller, J.; et al. Aggregation-resistant alpha-synuclein tetramers are reduced in the blood of Parkinson's patients. EMBO Mol Med 2024, 16, 1657–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, T.; Bendor, J.; Toupin, C.; Thorn, K.; Edwards, R.H. alpha-Synuclein promotes dilation of the exocytotic fusion pore. Nat Neurosci 2017, 20, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabresi, P.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Marino, G.; Campanelli, F.; Ghiglieri, V. Advances in understanding the function of alpha-synuclein: implications for Parkinson's disease. Brain 2023, 146, 3587–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Burre, J. alpha-Synuclein in synaptic function and dysfunction. Trends Neurosci 2023, 46, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Rivas, L.A.; Madhivanan, K.; Aulston, B.D.; Wang, L.; Prakashchand, D.D.; Boyer, N.P.; Saia-Cereda, V.M.; Branes-Guerrero, K.; Pizzo, D.P.; Bagchi, P.; et al. Serine-129 phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein is an activity-dependent trigger for physiologic protein-protein interactions and synaptic function. Neuron 2023, 111, 4006–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, N.; Jin, S.X.; Moors, T.E.; Fonseca-Ornelas, L.; Shimanaka, K.; Lei, S.; Cam, H.P.; Watson, A.H.; Brontesi, L.; Ding, L.; et al. Dynamic physiological alpha-synuclein S129 phosphorylation is driven by neuronal activity. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2023, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, T.; Choi, J.G.; Selkoe, D.J. alpha-Synuclein occurs physiologically as a helically folded tetramer that resists aggregation. Nature 2011, 477, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Chen, X.; Rizo, J.; Jahn, R.; Sudhof, T.C. A broken alpha -helix in folded alpha -Synuclein. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 15313–15318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kam, T.I.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. alpha-Synuclein pathology as a target in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurol 2025, 21, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Conde, L.D.; Ramos-Acevedo, R.; Reyes-Hernandez, M.A.; Balbuena-Olvera, A.J.; Morales-Moreno, I.D.; Arguero-Sanchez, R.; Schule, B.; Guerra-Crespo, M. Alpha-Synuclein Physiology and Pathology: A Perspective on Cellular Structures and Organelles. Front Neurosci 2019, 13, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin, D.L.; Troyer, M.D.; Nakamura, K.; Kubo, S.; Anthony, M.D.; Edwards, R.H. Lipid rafts mediate the synaptic localization of alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 2004, 24, 6715–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, W.K.; Tahirbegi, B.; Vrettas, M.D.; Preet, S.; Ying, L.; Vendruscolo, M.; De Simone, A.; Fusco, G. The docking of synaptic vesicles on the presynaptic membrane induced by alpha-synuclein is modulated by lipid composition. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burre, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Sudhof, T.C. Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghio, S.; Kamp, F.; Cauchi, R.; Giese, A.; Vassallo, N. Interaction of alpha-synuclein with biomembranes in Parkinson's disease--role of cardiolipin. Prog Lipid Res 2016, 61, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maio, R.; Barrett, P.J.; Hoffman, E.K.; Barrett, C.W.; Zharikov, A.; Borah, A.; Hu, X.; McCoy, J.; Chu, C.T.; Burton, E.A.; et al. alpha-Synuclein binds to TOM20 and inhibits mitochondrial protein import in Parkinson's disease. Sci Transl Med 2016, 8, 342ra378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, E.; Coune, P.; Liu, Y.; Pletnikova, O.; Troncoso, J.C.; Iwatsubo, T.; Schneider, B.L.; Lee, M.K. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is important for the manifestations of alpha-synucleinopathy in vivo. J Neurosci 2012, 32, 3306–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzulli, J.R.; Zunke, F.; Isacson, O.; Studer, L.; Krainc, D. alpha-Synuclein-induced lysosomal dysfunction occurs through disruptions in protein trafficking in human midbrain synucleinopathy models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, 1931–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, D.; Howard, S.; Zhou, M.; Diaz-Perez, N.; Urban, N.T.; Guerrero-Given, D.; Kamasawa, N.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; LoGrasso, P.; Lasmezas, C.I. Identification of a highly neurotoxic alpha-synuclein species inducing mitochondrial damage and mitophagy in Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, E2634–E2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, S.; Outeiro, T.F. Assessing the subcellular dynamics of alpha-synuclein using photoactivation microscopy. Mol Neurobiol 2013, 47, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaser, A.J.; Osterberg, V.R.; Dent, S.E.; Stackhouse, T.L.; Wakeham, C.M.; Boutros, S.W.; Weston, L.J.; Owen, N.; Weissman, T.A.; Luna, E.; et al. Alpha-synuclein is a DNA binding protein that modulates DNA repair with implications for Lewy body disorders. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, R.; Kling, K.; Anderson, J.P.; Banducci, K.; Cole, T.; Diep, L.; Fox, M.; Goldstein, J.M.; Soriano, F.; Seubert, P.; et al. Red blood cells are the major source of alpha-synuclein in blood. Neurodegener Dis 2008, 5, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan-Montojo, F.; Anichtchik, O.; Dening, Y.; Knels, L.; Pursche, S.; Jung, R.; Jackson, S.; Gille, G.; Spillantini, M.G.; Reichmann, H.; et al. Progression of Parkinson's disease pathology is reproduced by intragastric administration of rotenone in mice. PLoS One 2010, 5, e8762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan-Montojo, F.; Schwarz, M.; Winkler, C.; Arnhold, M.; O'Sullivan, G.A.; Pal, A.; Said, J.; Marsico, G.; Verbavatz, J.M.; Rodrigo-Angulo, M.; et al. Environmental toxins trigger PD-like progression via increased alpha-synuclein release from enteric neurons in mice. Sci Rep 2012, 2, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelender, S.; Kaminsky, Z.; Guo, X.; Sharp, A.H.; Amaravi, R.K.; Kleiderlein, J.J.; Margolis, R.L.; Troncoso, J.C.; Lanahan, A.A.; Worley, P.F.; et al. Synphilin-1 associates with alpha-synuclein and promotes the formation of cytosolic inclusions. Nat Genet 1999, 22, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, P.S.; Huang, Y.; Gysbers, A.; Cheng, D.; Gai, W.P.; Outeiro, T.F.; Halliday, G.M. LRRK2 interactions with alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease brains and in cell models. J Mol Med (Berl) 2013, 91, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, H.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; McGeer, E.G.; McGeer, P.L. Lrrk2 interaction with alpha-synuclein in diffuse Lewy body disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009, 390, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejlerskov, P.; Rasmussen, I.; Nielsen, T.T.; Bergstrom, A.L.; Tohyama, Y.; Jensen, P.H.; Vilhardt, F. Tubulin polymerization-promoting protein (TPPP/p25alpha) promotes unconventional secretion of alpha-synuclein through exophagy by impairing autophagosome-lysosome fusion. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 17313–17335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zondler, L.; Miller-Fleming, L.; Repici, M.; Goncalves, S.; Tenreiro, S.; Rosado-Ramos, R.; Betzer, C.; Straatman, K.R.; Jensen, P.H.; Giorgini, F.; et al. DJ-1 interactions with alpha-synuclein attenuate aggregation and cellular toxicity in models of Parkinson's disease. Cell Death Dis 2014, 5, e1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitler, A.D.; Chesi, A.; Geddie, M.L.; Strathearn, K.E.; Hamamichi, S.; Hill, K.J.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A.; Cooper, A.A.; Rochet, J.C.; et al. Alpha-synuclein is part of a diverse and highly conserved interaction network that includes PARK9 and manganese toxicity. Nat Genet 2009, 41, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes da Fonseca, T.; Pinho, R.; Outeiro, T.F. A familial ATP13A2 mutation enhances alpha-synuclein aggregation and promotes cell death. Hum Mol Genet 2016, 25, 2959–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhjavani, M.; Morteza, A.; Khajeali, L.; Esteghamati, A.; Khalilzadeh, O.; Asgarani, F.; Outeiro, T.F. Increased serum HSP70 levels are associated with the duration of diabetes. Cell Stress Chaperones 2010, 15, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outeiro, T.F.; Klucken, J.; Strathearn, K.E.; Liu, F.; Nguyen, P.; Rochet, J.C.; Hyman, B.T.; McLean, P.J. Small heat shock proteins protect against alpha-synuclein-induced toxicity and aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 351, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breda, C.; Nugent, M.L.; Estranero, J.G.; Kyriacou, C.P.; Outeiro, T.F.; Steinert, J.R.; Giorgini, F. Rab11 modulates alpha-synuclein-mediated defects in synaptic transmission and behaviour. Hum Mol Genet 2015, 24, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutna, O.; Goncalves, S.; Villar-Pique, A.; Guerreiro, P.; Marijanovic, Z.; Mendes, T.; Ramalho, J.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Ventura, S.; Klucken, J.; et al. The small GTPase Rab11 co-localizes with alpha-synuclein in intracellular inclusions and modulates its aggregation, secretion and toxicity. Hum Mol Genet 2014, 23, 6732–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihse, E.; Yamakado, H.; van Wijk, X.M.; Lawrence, R.; Esko, J.D.; Masliah, E. Cellular internalization of alpha-synuclein aggregates by cell surface heparan sulfate depends on aggregate conformation and cell type. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, R.; Paiva, I.; Jercic, K.G.; Fonseca-Ornelas, L.; Gerhardt, E.; Fahlbusch, C.; Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Kerimoglu, C.; Pavlou, M.A.S.; Villar-Pique, A.; et al. Nuclear localization and phosphorylation modulate pathological effects of alpha-synuclein. Hum Mol Genet 2019, 28, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; McLaurin, J.; Yip, C.M.; St George-Hyslop, P.; Fraser, P.E. alpha-Synuclein membrane interactions and lipid specificity. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 34328–34334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.H.C.; Wislet-Gendebien, S.; Samuel, F.; Visanji, N.P.; Zhang, G.; Marsilio, D.; Langman, T.; Fraser, P.E.; Tandon, A. alpha-Synuclein membrane association is regulated by the Rab3a recycling machinery and presynaptic activity. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 7438–7449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltieri, M.; Grigoletto, J.; Longhena, F.; Navarria, L.; Favero, G.; Castrezzati, S.; Colivicchi, M.A.; Della Corte, L.; Rezzani, R.; Pizzi, M.; et al. alpha-synuclein and synapsin III cooperatively regulate synaptic function in dopamine neurons. J Cell Sci 2015, 128, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, B.; Saha, K.; Rana, T.; Becker, J.P.; Sambo, D.; Davari, P.; Goodwin, J.S.; Khoshbouei, H. Dopamine Transporter Activity Is Modulated by alpha-Synuclein. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 29542–29554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, M.J.; O'Farrell, C.; Daya, S.; Ahmad, R.; Miller, D.W.; Hardy, J.; Farrer, M.J.; Cookson, M.R. Co-ordinate transcriptional regulation of dopamine synthesis genes by alpha-synuclein in human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Neurochem 2003, 85, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.H.; Fuentes, F.; Vanasco, V.; Alvarez, S.; Alaimo, A.; Cassina, A.; Coluccio Leskow, F.; Velazquez, F. Alpha-synuclein mitochondrial interaction leads to irreversible translocation and complex I impairment. Arch Biochem Biophys 2018, 651, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, L.; Raghavendran, V.; Prabhu, B.M.; Avadhani, N.G.; Anandatheerthavarada, H.K. Mitochondrial import and accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 9089–9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.L.; Chappard, A.; Singh, B.P.; Maclachlan, C.; Rodrigues, M.; Fedotova, E.I.; Berezhnov, A.V.; De, S.; Peddie, C.J.; Athauda, D.; et al. Pathological structural conversion of alpha-synuclein at the mitochondria induces neuronal toxicity. Nat Neurosci 2022, 25, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.; Khurana, N.; Duggal, N. The misfolding mystery: alpha-synuclein and the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Int 2024, 177, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Su, C.; Pieper, A.A.; Zhu, X.; Leverenz, J.B.; Wang, F.; Cummings, J.; Cheng, F. A network-based systems genetics framework identifies pathobiology and drug repurposing in Parkinson's disease. Res Sq 2024, 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4869009/v1. [CrossRef]
- van Diggelen, F.; Frank, S.A.; Somavarapu, A.K.; Scavenius, C.; Apetri, M.M.; Nielsen, J.; Tepper, A.; Enghild, J.J.; Otzen, D.E. The interactome of stabilized alpha-synuclein oligomers and neuronal proteins. FEBS J 2020, 287, 2037–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaun-Panzano, J.; Arotcarena, M.L.; Bezard, E. Monitoring alpha-synuclein aggregation. Neurobiol Dis 2023, 176, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzer, D.; Edwards, R.H. The physiological role of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to Parkinson's Disease. J Neurochem 2019, 150, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balupuri, A.; Choi, K.E.; Kang, N.S. Computational insights into the role of alpha-strand/sheet in aggregation of alpha-synuclein. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahur, P.; Sharma, A.; Jahan, G.; S, G.A.; Kumar Singh, A.; Muthukumaran, J.; Jain, M. Understanding Genetic Risks: Computational Exploration of Human beta-Synuclein nsSNPs and their Potential Impact on Structural Alteration. Neurosci Lett 2024, 833, 137826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, J.C.; Hidari, E.; Meisl, G.; Ranasinghe, R.T.; Spillantini, M.G.; Klenerman, D. Super-resolution imaging reveals alpha-synuclein seeded aggregation in SH-SY5Y cells. Commun Biol 2021, 4, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.; Mao, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, M.; Dai, W.; Gan, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Lin, H.; Liu, Q.; et al. alpha-Synuclein seeding amplification assays for diagnosing synucleinopathies: an innovative tool in clinical implementation. Transl Neurodegener 2024, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogiatzi, T.; Xilouri, M.; Vekrellis, K.; Stefanis, L. Wild type alpha-synuclein is degraded by chaperone-mediated autophagy and macroautophagy in neuronal cells. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 23542–23556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, G.; Marinig, D.; Arosio, A.; Ferrarese, C. Role of Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy Dysfunctions in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease. Front Mol Neurosci 2016, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Vicente, M.; Talloczy, Z.; Kaushik, S.; Massey, A.C.; Mazzulli, J.; Mosharov, E.V.; Hodara, R.; Fredenburg, R.; Wu, D.C.; Follenzi, A.; et al. Dopamine-modified alpha-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Clin Invest 2008, 118, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, N.; Aguado, C.; Horst, M.; Knecht, E. Import of a cytosolic protein into lysosomes by chaperone-mediated autophagy depends on its folding state. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 27447–27456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.L.; Hassel, B.A. Proteasomes modulate conjugation to the ubiquitin-like protein, ISG15. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanouilidou, E.; Melachroinou, K.; Roumeliotis, T.; Garbis, S.D.; Ntzouni, M.; Margaritis, L.H.; Stefanis, L.; Vekrellis, K. Cell-produced alpha-synuclein is secreted in a calcium-dependent manner by exosomes and impacts neuronal survival. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 6838–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmene, M.; Berard, M.; Oueslati, A. Dissecting the Molecular Pathway Involved in PLK2 Kinase-mediated alpha-Synuclein-selective Autophagic Degradation. J Biol Chem 2017, 292, 3919–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, M.B.; Ait-Bouziad, N.; Dikiy, I.; Mbefo, M.K.; Jovicic, A.; Kiely, A.; Holton, J.L.; Lee, S.J.; Gitler, A.D.; Eliezer, D.; et al. The novel Parkinson's disease linked mutation G51D attenuates in vitro aggregation and membrane binding of alpha-synuclein, and enhances its secretion and nuclear localization in cells. Hum Mol Genet 2014, 23, 4491–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalaf, O.; Fauvet, B.; Oueslati, A.; Dikiy, I.; Mahul-Mellier, A.L.; Ruggeri, F.S.; Mbefo, M.K.; Vercruysse, F.; Dietler, G.; Lee, S.J.; et al. The H50Q mutation enhances alpha-synuclein aggregation, secretion, and toxicity. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 21856–21876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loria, F.; Vargas, J.Y.; Bousset, L.; Syan, S.; Salles, A.; Melki, R.; Zurzolo, C. alpha-Synuclein transfer between neurons and astrocytes indicates that astrocytes play a role in degradation rather than in spreading. Acta Neuropathol 2017, 134, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpowicz, R.J., Jr.; Haney, C.M.; Mihaila, T.S.; Sandler, R.M.; Petersson, E.J.; Lee, V.M. Selective imaging of internalized proteopathic alpha-synuclein seeds in primary neurons reveals mechanistic insight into transmission of synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 2017, 292, 13482–13497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Suk, J.E.; Bae, E.J.; Lee, S.J. Clearance and deposition of extracellular alpha-synuclein aggregates in microglia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008, 372, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, J.A.; Kim, H.T.; Ting, L.; Gygi, S.P.; Goldberg, A.L. Why do cellular proteins linked to K63-polyubiquitin chains not associate with proteasomes? EMBO J 2013, 32, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, R.; Szargel, R.; Haskin, J.; Shani, V.; Shainskaya, A.; Manov, I.; Liani, E.; Avraham, E.; Engelender, S. Monoubiquitylation of alpha-synuclein by seven in absentia homolog (SIAH) promotes its aggregation in dopaminergic cells. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 3316–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente Miranda, H.; Cassio, R.; Correia-Guedes, L.; Gomes, M.A.; Chegao, A.; Miranda, E.; Soares, T.; Coelho, M.; Rosa, M.M.; Ferreira, J.J.; et al. Posttranslational modifications of blood-derived alpha-synuclein as biochemical markers for Parkinson's disease. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 13713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueslati, A. Implication of Alpha-Synuclein Phosphorylation at S129 in Synucleinopathies: What Have We Learned in the Last Decade? J Parkinsons Dis 2016, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, V.; Lindfors, M.; Ng, J.; Paetau, A.; Swinton, E.; Kolodziej, P.; Boston, H.; Saftig, P.; Woulfe, J.; Feany, M.B.; et al. Cathepsin D expression level affects alpha-synuclein processing, aggregation, and toxicity in vivo. Mol Brain 2009, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Cantuti-Castelvetri, I.; Fan, Z.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T.; McLean, P.J.; Unni, V.K. Distinct roles in vivo for the ubiquitin-proteasome system and the autophagy-lysosomal pathway in the degradation of alpha-synuclein. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 14508–14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.G.; Lachenmayer, M.L.; Wang, J.; He, L.; Poulose, S.M.; Komatsu, M.; Holstein, G.R.; Yue, Z. Disrupted autophagy leads to dopaminergic axon and dendrite degeneration and promotes presynaptic accumulation of alpha-synuclein and LRRK2 in the brain. J Neurosci 2012, 32, 7585–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gathings, A.; Zaman, V.; Banik, N.L.; Haque, A. Insights into Calpain Activation and Rho-ROCK Signaling in Parkinson's Disease and Aging. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absalyamova, M.; Traktirov, D.; Burdinskaya, V.; Artemova, V.; Muruzheva, Z.; Karpenko, M. Molecular basis of the development of Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience 2025, 565, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, G.; Sehgal, A.; Bhardwaj, S.; Singh, S.; Buhas, C.; Judea-Pusta, C.; Uivarosan, D.; Munteanu, M.A.; Bungau, S. Multifaceted Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xilouri, M.; Brekk, O.R.; Stefanis, L. alpha-Synuclein and protein degradation systems: a reciprocal relationship. Mol Neurobiol 2013, 47, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes da Fonseca, T.; Villar-Pique, A.; Outeiro, T.F. The Interplay between Alpha-Synuclein Clearance and Spreading. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 435–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, Z.A.; Giasson, B.I.; Chakrabarty, P. alpha-Synuclein and astrocytes: tracing the pathways from homeostasis to neurodegeneration in Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 2019, 138, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroeidi, P.; Xilouri, M. Neurons and Glia Interplay in alpha-Synucleinopathies. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.A.; Gasser, T.; Edwards, R.; Zweckstetter, M.; Melki, R.; Stefanis, L.; Lashuel, H.A.; Sulzer, D.; Vekrellis, K.; Halliday, G.M.; et al. Alpha-synuclein research: defining strategic moves in the battle against Parkinson's disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2021, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Padhy, A.A.; Kumari, V.; Mishra, P. Role of Ubiquitin-Proteasome and Autophagy-Lysosome Pathways in alpha-Synuclein Aggregate Clearance. Mol Neurobiol 2022, 59, 5379–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Nonaka, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Oikawa, T.; Arai, T.; Akiyama, H.; Mann, D.M.; Hasegawa, M. Prion-like spreading of pathological alpha-synuclein in brain. Brain 2013, 136, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R.J.; Covell, D.J.; Medellin, C.; Stieber, A.; Robinson, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Pitkin, R.M.; Olufemi, M.F.; Luk, K.C.; et al. Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological alpha-synuclein strains in alpha-synucleinopathies. Nature 2018, 557, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurry, T.; Ullman, O.; Fisher, C.K.; Perovic, I.; Pochapsky, T.; Stultz, C.M. The dynamic structure of alpha-synuclein multimers. J Am Chem Soc 2013, 135, 3865–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caughey, B.; Lansbury, P.T. Protofibrils, pores, fibrils, and neurodegeneration: separating the responsible protein aggregates from the innocent bystanders. Annu Rev Neurosci 2003, 26, 267–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Pallares, I.; Ventura, S. A glimpse into the structural properties of alpha-synuclein oligomers. Biofactors 2024, 50, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Garen, C.R.; Cortez, L.M.; Petersen, N.O.; Woodside, M.T. Early stages of aggregation of engineered alpha-synuclein monomers and oligomers in solution. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousset, L.; Pieri, L.; Ruiz-Arlandis, G.; Gath, J.; Jensen, P.H.; Habenstein, B.; Madiona, K.; Olieric, V.; Bockmann, A.; Meier, B.H.; et al. Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains. Nat Commun 2013, 4, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.L.; Covell, D.J.; Daniels, J.P.; Iba, M.; Stieber, A.; Zhang, B.; Riddle, D.M.; Kwong, L.K.; Xu, Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Distinct alpha-synuclein strains differentially promote tau inclusions in neurons. Cell 2013, 154, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dening, Y.; Strassl, T.; Ruf, V.; Dirscherl, P.; Chovsepian, A.; Stievenard, A.; Khairnar, A.; Schmidt, F.; Giesert, F.; Herms, J.; et al. Toxicity of extracellular alpha-synuclein is independent of intracellular alpha-synuclein. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 21951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lv, G.; Lee, J.S.; Jung, B.C.; Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Hong, C.S.; Valera, E.; Lee, H.J.; Paik, S.R.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Exposure to bacterial endotoxin generates a distinct strain of alpha-synuclein fibril. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 30891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal-Conde, L.D.; Pena-Martinez, V.; Morato-Torres, C.A.; Ramos-Acevedo, R.; Arias-Carrion, O.; Padilla-Godinez, F.J.; Delgado-Gonzalez, A.; Palomero-Rivero, M.; Collazo-Navarrete, O.; Soto-Rojas, L.O.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Gene Alterations Modulate Tyrosine Hydroxylase in Human iPSC-Derived Neurons in a Parkinson's Disease Animal Model. Life (Basel) 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanudjojo, B.; Shaikh, S.S.; Fenyi, A.; Bousset, L.; Agarwal, D.; Marsh, J.; Zois, C.; Heman-Ackah, S.; Fischer, R.; Sims, D.; et al. Phenotypic manifestation of alpha-synuclein strains derived from Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy in human dopaminergic neurons. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancoe, S.X.; Wang, Y.J.; Shimogawa, M.; Perez, R.M.; Giannakoulias, S.; Petersson, E.J. Effects of Mutations and Post-Translational Modifications on alpha-Synuclein In Vitro Aggregation. J Mol Biol 2022, 434, 167859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S.K.; Lee, S.Y. Truncation or proteolysis of alpha-synuclein in Parkinsonism. Ageing Res Rev 2023, 90, 101978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, J.; Loser, T.; Behl, C. Lipids and alpha-Synuclein: adding further variables to the equation. Front Mol Biosci 2024, 11, 1455817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moors, T.E.; Maat, C.A.; Niedieker, D.; Mona, D.; Petersen, D.; Timmermans-Huisman, E.; Kole, J.; El-Mashtoly, S.F.; Spycher, L.; Zago, W.; et al. The subcellular arrangement of alpha-synuclein proteoforms in the Parkinson's disease brain as revealed by multicolor STED microscopy. Acta Neuropathol 2021, 142, 423–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmoradian, S.H.; Lewis, A.J.; Genoud, C.; Hench, J.; Moors, T.E.; Navarro, P.P.; Castano-Diez, D.; Schweighauser, G.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Goldie, K.N.; et al. Lewy pathology in Parkinson's disease consists of crowded organelles and lipid membranes. Nat Neurosci 2019, 22, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihofen, A.; Liu, Y.; Arndt, J.W.; Huy, C.; Quan, C.; Smith, B.A.; Baeriswyl, J.L.; Cavegn, N.; Senn, L.; Su, L.; et al. Development of an aggregate-selective, human-derived alpha-synuclein antibody BIIB054 that ameliorates disease phenotypes in Parkinson's disease models. Neurobiol Dis 2019, 124, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.; Taylor, N.M.; Mona, D.; Ringler, P.; Lauer, M.E.; Riek, R.; Britschgi, M.; Stahlberg, H. Cryo-EM structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils. Elife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.D.; Comellas, G.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Covell, D.J.; Berthold, D.A.; Kloepper, K.D.; Courtney, J.M.; Kim, J.K.; Barclay, A.M.; Kendall, A.; et al. Solid-state NMR structure of a pathogenic fibril of full-length human alpha-synuclein. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2016, 23, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostou, D.; Sfakianaki, G.; Melachroinou, K.; Soutos, M.; Constantinides, V.; Vaikath, N.; Tsantzali, I.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Agnaf, O.E.; Vekrellis, K.; et al. Assessment of Aggregated and Exosome-Associated alpha-Synuclein in Brain Tissue and Cerebrospinal Fluid Using Specific Immunoassays. Diagnostics (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsali, I.; Brinia, M.E.; Constantinides, V.C. Cerebrospinal Fluid Total, Phosphorylated and Oligomeric A-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalon, A.J.; Quiriconi, D.J.; Pitcairn, C.; Mazzulli, J.R. alpha-Synuclein: Multiple pathogenic roles in trafficking and proteostasis pathways in Parkinson's disease. Neuroscientist 2024, 30, 612–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadukul, D.M.; Papp, M.; Thrush, R.J.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y.; Arosio, P.; Aprile, F.A. alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Is Triggered by Oligomeric Amyloid-beta 42 via Heterogeneous Primary Nucleation. J Am Chem Soc 2023, 145, 18276–18285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, E.; Kim, J.R. alpha-synuclein-assisted oligomerization of beta-amyloid (1-42). Arch Biochem Biophys 2022, 717, 109120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Covelo, A.; Martell-Martinez, H.; Nanclares, C.; Sherman, M.A.; Okematti, E.; Meints, J.; Teravskis, P.J.; Gallardo, C.; Savonenko, A.V.; et al. Tau is required for progressive synaptic and memory deficits in a transgenic mouse model of alpha-synucleinopathy. Acta Neuropathol 2019, 138, 551–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, M.; Goldbaum, O.; Richter-Landsberg, C. alpha-Synuclein promotes the recruitment of tau to protein inclusions in oligodendroglial cells: effects of oxidative and proteolytic stress. J Mol Neurosci 2009, 39, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, C.; Meng, L.; Tian, Y.; He, M.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, J.; Chen, G.; et al. Tau accelerates alpha-synuclein aggregation and spreading in Parkinson's disease. Brain 2022, 145, 3454–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, P.; Lashuel, H.A. Opportunities and challenges of alpha-synuclein as a potential biomarker for Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2022, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.G.; Temido-Ferreira, M.; Vicente Miranda, H.; Batalha, V.L.; Coelho, J.E.; Szego, E.M.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Vaz, S.H.; Rhee, J.S.; Schmitz, M.; et al. alpha-synuclein interacts with PrP(C) to induce cognitive impairment through mGluR5 and NMDAR2B. Nat Neurosci 2017, 20, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Ou, M.T.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Kam, T.I.; Yin, X.; Xiong, Y.; Ge, P.; Umanah, G.E.; Brahmachari, S.; Shin, J.H.; et al. Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiated by binding lymphocyte-activation gene 3. Science 2016, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, N.; Arcos-Lopez, T.; Konig, A.; Quintanar, L.; Menacho Marquez, M.; Outeiro, T.F.; Fernandez, C.O. Effects of alpha-synuclein post-translational modifications on metal binding. J Neurochem 2019, 150, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moons, R.; Konijnenberg, A.; Mensch, C.; Van Elzen, R.; Johannessen, C.; Maudsley, S.; Lambeir, A.M.; Sobott, F. Metal ions shape alpha-synuclein. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 16293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, L.; Zheng, J.; Petersen, R.B.; Zheng, L.; et al. Copper and iron ions accelerate the prion-like propagation of alpha-synuclein: A vicious cycle in Parkinson's disease. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 163, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisaglia, M.; Tessari, I.; Mammi, S.; Bubacco, L. Interaction between alpha-synuclein and metal ions, still looking for a role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Neuromolecular Med 2009, 11, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binolfi, A.; Rasia, R.M.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Ceolin, M.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Jovin, T.M.; Fernandez, C.O. Interaction of alpha-synuclein with divalent metal ions reveals key differences: a link between structure, binding specificity and fibrillation enhancement. J Am Chem Soc 2006, 128, 9893–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasia, R.M.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Marsh, D.; Hoyer, W.; Cherny, D.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Jovin, T.M.; Fernandez, C.O. Structural characterization of copper(II) binding to alpha-synuclein: Insights into the bioinorganic chemistry of Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 4294–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, R.; Pountney, D.L.; Jensen, P.H.; Gai, W.P.; Voelcker, N.H. Calcium(II) selectively induces alpha-synuclein annular oligomers via interaction with the C-terminal domain. Protein Sci 2004, 13, 3245–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bras, I.C.; Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Gerhardt, E.; Koss, D.; Lazaro, D.F.; Santos, P.I.; Vasili, E.; Xylaki, M.; Outeiro, T.F. Synucleinopathies: Where we are and where we need to go. J Neurochem 2020, 153, 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, S.S.; Majbour, N.K.; Vaikath, N.N.; Ardah, M.T.; Erskine, D.; Jensen, N.M.; Fayyad, M.; Sudhakaran, I.P.; Vasili, E.; Melachroinou, K.; et al. alpha-Synuclein phosphorylation at serine 129 occurs after initial protein deposition and inhibits seeded fibril formation and toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022, 119, e2109617119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paleologou, K.E.; Oueslati, A.; Shakked, G.; Rospigliosi, C.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Lamberto, G.R.; Fernandez, C.O.; Schmid, A.; Chegini, F.; Gai, W.P.; et al. Phosphorylation at S87 is enhanced in synucleinopathies, inhibits alpha-synuclein oligomerization, and influences synuclein-membrane interactions. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 3184–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Yu, J. Modeling Parkinson's Disease in Drosophila: What Have We Learned for Dominant Traits? Front Neurol 2018, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyawardhane, D.L.; Fernandez, R.D.; Heitger, D.R.; Crozier, M.K.; Wolver, J.C.; Lucas, H.R. Copper Induced Radical Dimerization of alpha-Synuclein Requires Histidine. J Am Chem Soc 2018, 140, 17086–17094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, R.M.; Vicente Miranda, H.; Francelle, L.; Pinho, R.; Szego, E.M.; Martinho, R.; Munari, F.; Lazaro, D.F.; Moniot, S.; Guerreiro, P.; et al. The mechanism of sirtuin 2-mediated exacerbation of alpha-synuclein toxicity in models of Parkinson disease. PLoS Biol 2017, 15, e2000374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, K.; Liu, J.; Maddila, S.; Mouradian, M.M. Posttranslational Modifications of alpha-Synuclein, Their Therapeutic Potential, and Crosstalk in Health and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmacol Rev 2024, 76, 1254–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.R. Metal binding to alpha-synuclein peptides and its contribution to toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009, 380, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorentzon, E.; Kumar, R.; Horvath, I.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Differential effects of Cu(2+) and Fe(3+) ions on in vitro amyloid formation of biologically-relevant alpha-synuclein variants. Biometals 2020, 33, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothian, A.; Lago, L.; Mukherjee, S.; Connor, A.R.; Fowler, C.; McLean, C.A.; Horne, M.; Masters, C.L.; Cappai, R.; Roberts, B.R. Characterization of the metal status of natively purified alpha-synuclein from human blood, brain tissue, or recombinant sources using size exclusion ICP-MS reveals no significant binding of Cu, Fe or Zn. Metallomics 2019, 11, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.W.; Fauvet, B.; Moniatte, M.; Lashuel, H.A. Alpha-synuclein post-translational modifications as potential biomarkers for Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies. Mol Cell Proteomics 2013, 12, 3543–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, A.D.; Zacharopoulou, M.; Kaminski Schierle, G.S. The Cellular Environment Affects Monomeric alpha-Synuclein Structure. Trends Biochem Sci 2019, 44, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, D.M.; Fields, S. Deep mutational scanning: a new style of protein science. Nat Methods 2014, 11, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newberry, R.W.; Leong, J.T.; Chow, E.D.; Kampmann, M.; DeGrado, W.F. Deep mutational scanning reveals the structural basis for alpha-synuclein activity. Nat Chem Biol 2020, 16, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, T.B.; Betarbet, R.; Stout, A.K.; Lund, S.; Baptista, M.; Panov, A.V.; Cookson, M.R.; Greenamyre, J.T. An in vitro model of Parkinson's disease: linking mitochondrial impairment to altered alpha-synuclein metabolism and oxidative damage. J Neurosci 2002, 22, 7006–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S. Emerging Trends in Cryo-EM-based Structural Studies of Neuropathological Amyloids. J Mol Biol 2023, 435, 168361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Sekiya, H.; Kondru, N.; Ross, O.A.; Dickson, D.W. Neuropathology and molecular diagnosis of Synucleinopathies. Mol Neurodegener 2021, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, T.W.; Islam, N.N.; Cook, C.N.; Caulfield, T.R.; Petrucelli, L. Cryo-EM structures of pathogenic fibrils and their impact on neurodegenerative disease research. Neuron 2024, 112, 2269–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Wolman, L. Ultrastructural observations in Parkinsonism. J Pathol 1969, 99, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarutani, A.; Adachi, T.; Akatsu, H.; Hashizume, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Saito, Y.; Robinson, A.C.; Mann, D.M.A.; Yoshida, M.; Murayama, S.; et al. Ultrastructural and biochemical classification of pathogenic tau, alpha-synuclein and TDP-43. Acta Neuropathol 2022, 143, 613–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzuhara, S.; Mori, H.; Izumiyama, N.; Yoshimura, M.; Ihara, Y. Lewy bodies are ubiquitinated. A light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study. Acta Neuropathol 1988, 75, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, J.; Blanchard, A.; Morrell, K.; Lennox, G.; Reynolds, L.; Billett, M.; Landon, M.; Mayer, R.J. Ubiquitin is a common factor in intermediate filament inclusion bodies of diverse type in man, including those of Parkinson's disease, Pick's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, as well as Rosenthal fibres in cerebellar astrocytomas, cytoplasmic bodies in muscle, and mallory bodies in alcoholic liver disease. J Pathol 1988, 155, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.P.; Walker, D.E.; Goldstein, J.M.; de Laat, R.; Banducci, K.; Caccavello, R.J.; Barbour, R.; Huang, J.; Kling, K.; Lee, M.; et al. Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of alpha-synuclein in familial and sporadic Lewy body disease. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 29739–29752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Engelender, S.; Yoshimoto, M.; Tsuji, S.; Ross, C.A.; Takahashi, H. Synphilin-1 is present in Lewy bodies in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 2000, 47, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlossmacher, M.G.; Frosch, M.P.; Gai, W.P.; Medina, M.; Sharma, N.; Forno, L.; Ochiishi, T.; Shimura, H.; Sharon, R.; Hattori, N.; et al. Parkin localizes to the Lewy bodies of Parkinson disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am J Pathol 2002, 160, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, T.; Mattila, P.; Davies, P.; Wang, D.; Dickson, D.W. Colocalization of tau and alpha-synuclein epitopes in Lewy bodies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2003, 62, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Babar, A.; Siedlak, S.L.; Yang, Q.; Ito, G.; Iwatsubo, T.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G.; Chen, S.G. LRRK2 in Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Mol Neurodegener 2006, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Tanji, K.; Mori, F.; Takahashi, H. The Lewy body in Parkinson's disease: molecules implicated in the formation and degradation of alpha-synuclein aggregates. Neuropathology 2007, 27, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, J.E. Lewy Body Dementia. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2024, 30, 1673–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Rub, U.; Bratzke, H.; Del Tredici, K. Stages in the development of Parkinson's disease-related pathology. Cell Tissue Res 2004, 318, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, G.M.; Li, Y.W.; Blumbergs, P.C.; Joh, T.H.; Cotton, R.G.; Howe, P.R.; Blessing, W.W.; Geffen, L.B. Neuropathology of immunohistochemically identified brainstem neurons in Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 1990, 27, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, H.G.; Johnson, M.; Perry, R.H.; LeBeau, F.E.; Dobrowolny, H.; Bogerts, B.; Perry, E.K. Partial loss of parvalbumin-containing hippocampal interneurons in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neuropathology 2011, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugger, B.N.; Dickson, D.W. Cell type specific sequestration of choline acetyltransferase and tyrosine hydroxylase within Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol 2010, 120, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marui, W.; Iseki, E.; Kato, M.; Kosaka, K. Degeneration of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci Lett 2003, 340, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Lue, L.; Sue, L.I.; Bachalakuri, J.; Henry-Watson, J.; Sasse, J.; Boyer, S.; Shirohi, S.; Brooks, R.; et al. Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol 2009, 117, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, A.J.; Stimson, E.; Henderson, J.M.; Halliday, G.M. Clinical correlates of selective pathology in the amygdala of patients with Parkinson's disease. Brain 2002, 125, 2431–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, P.M.; Rinne, J.O.; Helenius, H.; Dickson, D.W.; Roytta, M. Alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive cortical Lewy bodies are associated with cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol 2000, 100, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Presynaptic alpha-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurosci 2007, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E.; Hazrati, L.N.; Fujioka, S.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Dickson, D.W.; Ross, O.A.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Hurtig, H.I.; et al. Clinical correlations with Lewy body pathology in LRRK2-related Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol 2015, 72, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahul-Mellier, A.L.; Burtscher, J.; Maharjan, N.; Weerens, L.; Croisier, M.; Kuttler, F.; Leleu, M.; Knott, G.W.; Lashuel, H.A. The process of Lewy body formation, rather than simply alpha-synuclein fibrillization, is one of the major drivers of neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 4971–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzer, C.; Lassen, L.B.; Olsen, A.; Kofoed, R.H.; Reimer, L.; Gregersen, E.; Zheng, J.; Cali, T.; Gai, W.P.; Chen, T.; et al. Alpha-synuclein aggregates activate calcium pump SERCA leading to calcium dysregulation. EMBO Rep 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaud, S.; Jones, D.R.; Moussaud-Lamodiere, E.L.; Delenclos, M.; Ross, O.A.; McLean, P.J. Alpha-synuclein and tau: teammates in neurodegeneration? Mol Neurodegener 2014, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, A.; Naser, D.; Siebeneichler, B.; Tarasca, M.V.; Meiering, E.M. Methodological advances and strategies for high resolution structure determination of cellular protein aggregates. J Biol Chem 2022, 298, 102197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altay, M.F.; Kumar, S.T.; Burtscher, J.; Jagannath, S.; Strand, C.; Miki, Y.; Parkkinen, L.; Holton, J.L.; Lashuel, H.A. Development and validation of an expanded antibody toolset that captures alpha-synuclein pathological diversity in Lewy body diseases. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2023, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdurand, M.; Levigoureux, E.; Zeinyeh, W.; Berthier, L.; Mendjel-Herda, M.; Cadarossanesaib, F.; Bouillot, C.; Iecker, T.; Terreux, R.; Lancelot, S.; et al. In Silico, in Vitro, and in Vivo Evaluation of New Candidates for alpha-Synuclein PET Imaging. Mol Pharm 2018, 15, 3153–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlovskaya, V.V.; Fedorova, O.S.; Viktorov, N.B.; Vaulina, D.D.; Krasikova, R.N. One-Pot Radiosynthesis of [(18)F]Anle138b-5-(3-Bromophenyl)-3-(6-[(18)F]fluorobenzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazole-A Potential PET Radiotracer Targeting alpha-Synuclein Aggregates. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.H.; Tan, L.Y.; Ng, S.Y. Patient-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Organoids for Modeling Alpha Synuclein Propagation in Parkinson's Disease. Front Cell Neurosci 2018, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Perren, A.; Gelders, G.; Fenyi, A.; Bousset, L.; Brito, F.; Peelaerts, W.; Van den Haute, C.; Gentleman, S.; Melki, R.; Baekelandt, V. The structural differences between patient-derived alpha-synuclein strains dictate characteristics of Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol 2020, 139, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.; Candelise, N.; Canaslan, S.; Altmeppen, H.C.; Matschke, J.; Glatzel, M.; Younas, N.; Zafar, S.; Hermann, P.; Zerr, I. alpha-Synuclein conformers reveal link to clinical heterogeneity of alpha-synucleinopathies. Transl Neurodegener 2023, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, E.M.; Houser, M.C.; Herrick, M.K.; Seibler, P.; Klein, C.; West, A.; Tansey, M.G. Genetic and Environmental Factors in Parkinson's Disease Converge on Immune Function and Inflammation. Mov Disord 2021, 36, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabresi, P.; Mechelli, A.; Natale, G.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Ghiglieri, V. Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease and other synucleinopathies: from overt neurodegeneration back to early synaptic dysfunction. Cell Death Dis 2023, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T. Link between the SNCA gene and parkinsonism. Neurobiol Aging 2015, 36, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauwendraat, C.; Nalls, M.A.; Singleton, A.B. The genetic architecture of Parkinson's disease. Lancet Neurol 2020, 19, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orme, T.; Guerreiro, R.; Bras, J. The Genetics of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2018, 18, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzeff, J.S.; Phan, K.; Purushothuman, S.; Halliday, G.M.; Kim, W.S. Cross-examining candidate genes implicated in multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2019, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardien, S.; Lesage, S.; Brice, A.; Carr, J. Genetic characteristics of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) associated Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2011, 17, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, J.C.C.; Mano, G.B.C.; da Cunha Barreto-Vianna, A.R.; Garcia, T.F.M.; de Vasconcelos, A.V.; Sa, C.S.G.; de Souza Santana, S.L.; Farias, A.G.P.; Seimaru, B.; Lima, M.P.P.; et al. The Molecular Impact of Glucosylceramidase Beta 1 (Gba1) in Parkinson's Disease: a New Genetic State of the Art. Mol Neurobiol 2024, 61, 6754–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granek, Z.; Barczuk, J.; Siwecka, N.; Rozpedek-Kaminska, W.; Kucharska, E.; Majsterek, I. GBA1 Gene Mutations in alpha-Synucleinopathies-Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Pathology and Their Clinical Significance. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwin, A.; Orvisky, E.; Goker-Alpan, O.; LaMarca, M.E.; Sidransky, E. Glucocerebrosidase mutations in subjects with parkinsonism. Mol Genet Metab 2004, 81, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidransky, E.; Nalls, M.A.; Aasly, J.O.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; Annesi, G.; Barbosa, E.R.; Bar-Shira, A.; Berg, D.; Bras, J.; Brice, A.; et al. Multicenter analysis of glucocerebrosidase mutations in Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med 2009, 361, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, R.L. Genetics of Synucleinopathies. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Outeiro, T.F. Aggregation and beyond: alpha-synuclein-based biomarkers in synucleinopathies. Brain 2024, 147, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba-Falek, O. Structural variants in SNCA gene and the implication to synucleinopathies. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2017, 44, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Book, A.; Guella, I.; Candido, T.; Brice, A.; Hattori, N.; Jeon, B.; Farrer, M.J.; Consortium, S.M.I.o.t.G. A Meta-Analysis of alpha-Synuclein Multiplication in Familial Parkinsonism. Front Neurol 2018, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsalenchuk, M.; Gentleman, S.M.; Marzi, S.J. Linking environmental risk factors with epigenetic mechanisms in Parkinson's disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2023, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guhathakurta, S.; Bok, E.; Evangelista, B.A.; Kim, Y.S. Deregulation of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: Insight from epigenetic structure and transcriptional regulation of SNCA. Prog Neurobiol 2017, 154, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Morales, E.; Meier, K.; Sandoval-Carrillo, A.; Salas-Pacheco, J.; Vazquez-Cardenas, P.; Arias-Carrion, O. Implications of DNA Methylation in Parkinson's Disease. Front Mol Neurosci 2017, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, T.; Okuzumi, A.; Matsumoto, G.; Tsunemi, T.; Hattori, N. alpha-Synuclein: A Promising Biomarker for Parkinson's Disease and Related Disorders. J Mov Disord 2024, 17, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, K.; Stefanova, N.; Heras-Garvin, A. The Concept of alpha-Synuclein Strains and How Different Conformations May Explain Distinct Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front Neurol 2021, 12, 737195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Menozzi, E.; Schapira, A.H.V. Genetic variations in GBA1 and LRRK2 genes: Biochemical and clinical consequences in Parkinson disease. Front Neurol 2022, 13, 971252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redensek, S.; Dolzan, V.; Kunej, T. From Genomics to Omics Landscapes of Parkinson's Disease: Revealing the Molecular Mechanisms. OMICS 2018, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordower, J.H.; Chu, Y.; Hauser, R.A.; Freeman, T.B.; Olanow, C.W. Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson's disease. Nat Med 2008, 14, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killinger, B.A.; Kordower, J.H. Spreading of alpha-synuclein - relevant or epiphenomenon? J Neurochem 2019, 150, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bras, I.C.; Outeiro, T.F. Alpha-Synuclein: Mechanisms of Release and Pathology Progression in Synucleinopathies. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijaz, B.A.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A. Initiation and propagation of alpha-synuclein aggregation in the nervous system. Mol Neurodegener 2020, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grozdanov, V.; Danzer, K.M. Release and uptake of pathologic alpha-synuclein. Cell Tissue Res 2018, 373, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, B.B.; DeVos, S.L.; Kfoury, N.; Li, M.; Jacks, R.; Yanamandra, K.; Ouidja, M.O.; Brodsky, F.M.; Marasa, J.; Bagchi, D.P.; et al. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate internalization and propagation of specific proteopathic seeds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, E3138–E3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.; Marano, M.M.; Tandon, A. Import and Export of Misfolded alpha-Synuclein. Front Neurosci 2018, 12, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, R.; Sant'Anna, R.; da Fonseca, A.C.C.; Robbs, B.K.; Foguel, D.; Outeiro, T.F. Extracellular alpha-synuclein: Sensors, receptors, and responses. Neurobiol Dis 2022, 168, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.; Xia, D.; Yu, H.; Meng, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Tian, Y.; Yuan, X.; Niu, X.; Nie, S.; et al. Microglia Process alpha-Synuclein Fibrils and Enhance their Pathogenicity in a TREM2-Dependent Manner. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2024, 10.1002/advs.202413451, e2413451. [CrossRef]
- Uemura, N.; Ueda, J.; Yoshihara, T.; Ikuno, M.; Uemura, M.T.; Yamakado, H.; Asano, M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Takahashi, R. alpha-Synuclein Spread from Olfactory Bulb Causes Hyposmia, Anxiety, and Memory Loss in BAC-SNCA Mice. Mov Disord 2021, 36, 2036–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.; Moon, H.; Jeong, H.; Lee, K.; Song, W.J.; Hur, J.K.; Oh, Y. Role of post-translational modifications on the alpha-synuclein aggregation-related pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. BMB Rep 2022, 55, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashuel, H.A.; Mahul-Mellier, A.L.; Novello, S.; Hegde, R.N.; Jasiqi, Y.; Altay, M.F.; Donzelli, S.; DeGuire, S.M.; Burai, R.; Magalhaes, P.; et al. Revisiting the specificity and ability of phospho-S129 antibodies to capture alpha-synuclein biochemical and pathological diversity. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2022, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angot, E.; Steiner, J.A.; Hansen, C.; Li, J.Y.; Brundin, P. Are synucleinopathies prion-like disorders? Lancet Neurol 2010, 9, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampar, S.; Di Gregorio, S.E.; Grimmer, G.; Watts, J.C.; Ingelsson, M. "Prion-like" seeding and propagation of oligomeric protein assemblies in neurodegenerative disorders. Front Neurosci 2024, 18, 1436262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koprich, J.B.; Kalia, L.V.; Brotchie, J.M. Animal models of alpha-synucleinopathy for Parkinson disease drug development. Nat Rev Neurosci 2017, 18, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehay, B.; Fernagut, P.O. Alpha-synuclein-based models of Parkinson's disease. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2016, 172, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorn, K.J.; Moors, T.; Drukarch, B.; van de Berg, W.; Lucassen, P.J.; van Dam, A.M. Microglial phenotypes and toll-like receptor 2 in the substantia nigra and hippocampus of incidental Lewy body disease cases and Parkinson's disease patients. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2014, 2, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannaccone, S.; Cerami, C.; Alessio, M.; Garibotto, V.; Panzacchi, A.; Olivieri, S.; Gelsomino, G.; Moresco, R.M.; Perani, D. In vivo microglia activation in very early dementia with Lewy bodies, comparison with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2013, 19, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, K.; Hishikawa, N.; Sawada, M.; Nagatsu, T.; Yoshida, M.; Hashizume, Y. Distribution of major histocompatibility complex class II-positive microglia and cytokine profile of Parkinson's disease brains. Acta Neuropathol 2003, 106, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, Y.; Yoshikawa, E.; Sekine, Y.; Futatsubashi, M.; Kanno, T.; Ogusu, T.; Torizuka, T. Microglial activation and dopamine terminal loss in early Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 2005, 57, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.K.; Tao, K.X.; Wang, X.B.; Yao, X.Y.; Pang, M.Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.F. Role of alpha-synuclein in microglia: autophagy and phagocytosis balance neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease. Inflamm Res 2023, 72, 443–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Ettle, B.; Bruno, A.; Kulinich, A.; Hoffmann, A.C.; von Wittgenstein, J.; Winkler, J.; Xiang, W.; Schlachetzki, J.C.M. Alpha-synuclein activates BV2 microglia dependent on its aggregation state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 479, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Lu, M.; Hu, G. The interplay between alpha-Synuclein and NLRP3 inflammasome in Parkinson's disease. Biomed Pharmacother 2023, 168, 115735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtas, N.; Mazlumoglu, B.S.; Palabiyik Yucelik, S.S. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasomes in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Eurasian J Med 2023, 55, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease and its potential as therapeutic target. Transl Neurodegener 2015, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim-Balatan, C.; Fenyi, A.; Besnault, P.; Gomez, L.; Sepulveda-Diaz, J.E.; Michel, P.P.; Melki, R.; Hunot, S. Parkinson's disease-derived alpha-synuclein assemblies combined with chronic-type inflammatory cues promote a neurotoxic microglial phenotype. J Neuroinflammation 2024, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Minjares, K.M.; Martinez-Fong, D.; Martinez-Davila, I.A.; Banuelos, C.; Gutierrez-Castillo, M.E.; Blanco-Alvarez, V.M.; Cardenas-Aguayo, M.D.; Luna-Munoz, J.; Pacheco-Herrero, M.; Soto-Rojas, L.O. Mechanistic Insight from Preclinical Models of Parkinson's Disease Could Help Redirect Clinical Trial Efforts in GDNF Therapy. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz-Buschart, A.; Pandey, U.; Wicke, T.; Sixel-Doring, F.; Janzen, A.; Sittig-Wiegand, E.; Trenkwalder, C.; Oertel, W.H.; Mollenhauer, B.; Wilmes, P. The nasal and gut microbiome in Parkinson's disease and idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Mov Disord 2018, 33, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill-Burns, E.M.; Debelius, J.W.; Morton, J.T.; Wissemann, W.T.; Lewis, M.R.; Wallen, Z.D.; Peddada, S.D.; Factor, S.A.; Molho, E.; Zabetian, C.P.; et al. Parkinson's disease and Parkinson's disease medications have distinct signatures of the gut microbiome. Mov Disord 2017, 32, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzian, A.; Green, S.J.; Engen, P.A.; Voigt, R.M.; Naqib, A.; Forsyth, C.B.; Mutlu, E.; Shannon, K.M. Colonic bacterial composition in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2015, 30, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine Bardenhorst, S.; Cereda, E.; Severgnini, M.; Barichella, M.; Pezzoli, G.; Keshavarzian, A.; Desideri, A.; Pietrucci, D.; Aho, V.T.E.; Scheperjans, F.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in Parkinson disease: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Eur J Neurol 2023, 30, 3581–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Ge, Y. The link between the gut microbiome, inflammation, and Parkinson's disease. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2023, 107, 6737–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.G.; Stribinskis, V.; Rane, M.J.; Demuth, D.R.; Gozal, E.; Roberts, A.M.; Jagadapillai, R.; Liu, R.; Choe, K.; Shivakumar, B.; et al. Exposure to the Functional Bacterial Amyloid Protein Curli Enhances Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation in Aged Fischer 344 Rats and Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 34477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Abbas, K.; Mustafa, M.; Usmani, N.; Habib, S. Microbiome-based therapies for Parkinson's disease. Front Nutr 2024, 11, 1496616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rub, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, A.; Miglietti, M.; De Luca, C.M.G.; Cazzaniga, F.A.; Ciullini, A.; Dellarole, I.L.; Bufano, G.; Di Fonzo, A.; Giaccone, G.; Baggi, F.; et al. Approaching the Gut and Nasal Microbiota in Parkinson's Disease in the Era of the Seed Amplification Assays. Brain Sci 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaldi, A.; Fiore, M.; Oliveri Conti, G.; Pulvirenti, E.; Favara, C.; Grasso, A.; Copat, C.; Ferrante, M. Possible association between PM(2.5) and neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review. Environ Res 2022, 208, 112581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrenschee, M.; Zorenkov, D.; Bottner, M.; Lange, C.; Cossais, F.; Scharf, A.B.; Deuschl, G.; Schneider, S.A.; Ellrichmann, M.; Fritscher-Ravens, A.; et al. Distinct pattern of enteric phospho-alpha-synuclein aggregates and gene expression profiles in patients with Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2017, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, A.; Vivacqua, G.; Ceci, L.; Leone, S.; Vaccaro, R.; Tagliafierro, M.; Bassi, F.M.; Vitale, S.; Bocci, E.; Pannarale, L.; et al. TNBS colitis induces architectural changes and alpha-synuclein overexpression in mouse distal colon: A morphological study. Cell Tissue Res 2024, 10.1007/s00441-024-03932-4. [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, S.; Chutna, O.; Bousset, L.; Aldrin-Kirk, P.; Li, W.; Bjorklund, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Roybon, L.; Melki, R.; Li, J.Y. Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats. Acta Neuropathol 2014, 128, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Illigens, B.M.; McCormick, M.P.; Wang, N.; Gibbons, C.H. Alpha-Synuclein in Skin Nerve Fibers as a Biomarker for Alpha-Synucleinopathies. J Clin Neurol 2019, 15, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann Gastroenterol 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.X.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, C.F. Relationship Between Short-chain Fatty Acids and Parkinson's Disease: A Review from Pathology to Clinic. Neurosci Bull 2024, 40, 500–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killinger, B.A.; Madaj, Z.; Sikora, J.W.; Rey, N.; Haas, A.J.; Vepa, Y.; Lindqvist, D.; Chen, H.; Thomas, P.M.; Brundin, P.; et al. The vermiform appendix impacts the risk of developing Parkinson's disease. Sci Transl Med 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, A.; Goncalves, A.; Vila-Cha, N.; Moreira, I.; Fernandes, J.; Damasio, J.; Teixeira-Pinto, A.; Taipa, R.; Lima, A.B.; Cavaco, S. Appendectomy may delay Parkinson's disease Onset. Mov Disord 2015, 30, 1404–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, E.; Horvath-Puho, E.; Thomsen, R.W.; Djurhuus, J.C.; Pedersen, L.; Borghammer, P.; Sorensen, H.T. Vagotomy and subsequent risk of Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol 2015, 78, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, E.J. Gut-brain axis and environmental factors in Parkinson's disease: bidirectional link between disease onset and progression. Neural Regen Res 2024, 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00994. [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Yang, L.; Tran, H.D.; Yu, W.; Sun, A.X.; Chang, Y.Y.; Jung, B.C.; Lee, S.J.; Saw, T.Y.; Xiao, B.; et al. Lewy Body-like Inclusions in Human Midbrain Organoids Carrying Glucocerebrosidase and alpha-Synuclein Mutations. Ann Neurol 2021, 90, 490–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Schweighauser, M.; Zhang, X.; Kotecha, A.; Murzin, A.G.; Garringer, H.J.; Cullinane, P.W.; Saito, Y.; Foroud, T.; et al. Structures of alpha-synuclein filaments from human brains with Lewy pathology. Nature 2022, 610, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldez-Perez, R.; Antolin-Vallespin, M.; Munoz, M.; Sanchez-Capelo, A. Models of alpha-synuclein aggregation in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2014, 2, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovonou, A.; Bolduc, C.; Soto Linan, V.; Gora, C.; Peralta Iii, M.R.; Levesque, M. Animal models of Parkinson's disease: bridging the gap between disease hallmarks and research questions. Transl Neurodegener 2023, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feany, M.B.; Bender, W.W. A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature 2000, 404, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, P.J.; Neumann, M.; Ozmen, L.; Muller, V.; Jacobsen, H.; Schindzielorz, A.; Okochi, M.; Leimer, U.; van Der Putten, H.; Probst, A.; et al. Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson's disease-associated mutant alpha -synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J Neurosci 2000, 20, 6365–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masliah, E.; Rockenstein, E.; Veinbergs, I.; Mallory, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Takeda, A.; Sagara, Y.; Sisk, A.; Mucke, L. Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 2000, 287, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, A.L.; Feany, M.B. Glial alpha-synuclein promotes neurodegeneration characterized by a distinct transcriptional program in vivo. Glia 2019, 67, 1933–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Benito, M.; Granado, N.; Garcia-Sanz, P.; Michel, A.; Dumoulin, M.; Moratalla, R. Modeling Parkinson's Disease With the Alpha-Synuclein Protein. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulusoy, A.; Decressac, M.; Kirik, D.; Bjorklund, A. Viral vector-mediated overexpression of alpha-synuclein as a progressive model of Parkinson's disease. Prog Brain Res 2010, 184, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorklund, A.; Mattsson, B. The AAV-alpha-Synuclein Model of Parkinson's Disease: An Update. J Parkinsons Dis 2024, 14, 1077–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.K.; Ho, H.A.; Perez-Acuna, D.; Lee, S.J. Modeling alpha-Synuclein Propagation with Preformed Fibril Injections. J Mov Disord 2020, 13, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkentli, F.; Jang, I.K.; Choi, Y.; Min, Y.; Park, J.; Jo, H.; Kim, L.; Mendpara, A.; Bains, B.; Yoo, D.; et al. Quantitative proteomic analysis using a mouse model of Lewy body dementia induced by alpha-synuclein preformed fibrils injection. Front Dement 2024, 3, 1477986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.C.; Kehm, V.M.; Zhang, B.; O'Brien, P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Intracerebral inoculation of pathological alpha-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative alpha-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 2012, 209, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.C.; Song, C.; O'Brien, P.; Stieber, A.; Branch, J.R.; Brunden, K.R.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils seed the formation of Lewy body-like intracellular inclusions in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 20051–20056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadgar-Kiani, E.; Bieri, G.; Melki, R.; Hossain, A.; Gitler, A.D.; Lee, J.H. Neuromodulation modifies alpha-synuclein spreading dynamics in vivo and the pattern is predicted by changes in whole-brain function. Brain Stimul 2024, 17, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofs, L.; Geissler-Losch, D.; Wunderlich, K.M.; Szego, E.M.; Van den Haute, C.; Baekelandt, V.; Hoyer, W.; Falkenburger, B.H. Evaluation of the Effect of beta-Wrapin AS69 in a Mouse Model Based on Alpha-Synuclein Overexpression. Biomolecules 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challis, C.; Hori, A.; Sampson, T.R.; Yoo, B.B.; Challis, R.C.; Hamilton, A.M.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Gradinaru, V. Gut-seeded alpha-synuclein fibrils promote gut dysfunction and brain pathology specifically in aged mice. Nat Neurosci 2020, 23, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delenclos, M.; Burgess, J.D.; Lamprokostopoulou, A.; Outeiro, T.F.; Vekrellis, K.; McLean, P.J. Cellular models of alpha-synuclein toxicity and aggregation. J Neurochem 2019, 150, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeier, D.J.; Obeso, J.A.; Halliday, G.M. Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2017, 18, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.S.; Geng, W.S.; Jia, J.J. Neurotoxin-Induced Animal Models of Parkinson Disease: Pathogenic Mechanism and Assessment. ASN Neuro 2018, 10, 1759091418777438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Herrera, C.; Martinez-Davila, I.A.; Soto-Rojas, L.O.; Flores-Martinez, Y.M.; Fernandez-Parrilla, M.A.; Ayala-Davila, J.; Leon-Chavez, B.A.; Soto-Rodriguez, G.; Blanco-Alvarez, V.M.; Lopez-Salas, F.E.; et al. Intranigral Administration of beta-Sitosterol-beta-D-Glucoside Elicits Neurotoxic A1 Astrocyte Reactivity and Chronic Neuroinflammation in the Rat Substantia Nigra. J Immunol Res 2020, 2020, 5907591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Martinez, A.; Martinez-Gomez, P.A.; Martinez-Fong, D.; Villegas-Rojas, M.M.; Perez-Severiano, F.; Del Toro-Colin, M.A.; Delgado-Minjares, K.M.; Blanco-Alvarez, V.M.; Leon-Chavez, B.A.; Aparicio-Trejo, O.E.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Complex I Dysfunction Correlate with Neurodegeneration in an alpha-Synucleinopathy Animal Model. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, N.C.; Kenney, L.L.; Jangalwe, S.; Aryee, K.E.; Greiner, D.L.; Brehm, M.A.; Shultz, L.D. Humanized Mouse Models of Clinical Disease. Annu Rev Pathol 2017, 12, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamache, J.; Benzow, K.; Forster, C.; Kemper, L.; Hlynialuk, C.; Furrow, E.; Ashe, K.H.; Koob, M.D. Factors other than hTau overexpression that contribute to tauopathy-like phenotype in rTg4510 mice. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, S.H.; Ryu, H.G.; Kwon, S.H.; Park, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, N.S.; Ma, S.X.; Jee, H.J.; Kim, S.; Ko, H.S. Gba1 E326K renders motor and non-motor symptoms with pathological alpha-synuclein, tau and glial activation. Brain 2024, 147, 4072–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; McInnes, J.; Kim, J.; Liang, Y.H.W.; Veeraragavan, S.; Garza, A.R.; Belfort, B.D.W.; Arenkiel, B.; Samaco, R.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Olfactory deficit and gastrointestinal dysfunction precede motor abnormalities in alpha-Synuclein G51D knock-in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2024, 121, e2406479121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teil, M.; Arotcarena, M.L.; Dehay, B. A New Rise of Non-Human Primate Models of Synucleinopathies. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvian, A.T.; Koss, D.J.; Aliakbari, F.; Morshedi, D.; Outeiro, T.F. In vitro models of synucleinopathies: informing on molecular mechanisms and protective strategies. J Neurochem 2019, 150, 535–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaro, D.F.; Pavlou, M.A.S.; Outeiro, T.F. Cellular models as tools for the study of the role of alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol 2017, 298, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasili, E.; Dominguez-Meijide, A.; Outeiro, T.F. Spreading of alpha-Synuclein and Tau: A Systematic Comparison of the Mechanisms Involved. Front Mol Neurosci 2019, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, M.A.; Bjorklund, A. Animal models for preclinical Parkinson's research: An update and critical appraisal. Prog Brain Res 2020, 252, 27–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Choi, C.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, S.J. Formation and removal of alpha-synuclein aggregates in cells exposed to mitochondrial inhibitors. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 5411–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, P.J.; Kawamata, H.; Hyman, B.T. Alpha-synuclein-enhanced green fluorescent protein fusion proteins form proteasome sensitive inclusions in primary neurons. Neuroscience 2001, 104, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Gamble, K.L.; Schultheiss, C.E.; Riddle, D.M.; West, A.B.; Lee, V.M. Formation of alpha-synuclein Lewy neurite-like aggregates in axons impedes the transport of distinct endosomes. Mol Biol Cell 2014, 25, 4010–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klucken, J.; Poehler, A.M.; Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Schneider, J.; Nuber, S.; Rockenstein, E.; Schlotzer-Schrehardt, U.; Hyman, B.T.; McLean, P.J.; Masliah, E.; et al. Alpha-synuclein aggregation involves a bafilomycin A 1-sensitive autophagy pathway. Autophagy 2012, 8, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, D.F.; Rodrigues, E.F.; Langohr, R.; Shahpasandzadeh, H.; Ribeiro, T.; Guerreiro, P.; Gerhardt, E.; Krohnert, K.; Klucken, J.; Pereira, M.D.; et al. Systematic comparison of the effects of alpha-synuclein mutations on its oligomerization and aggregation. PLoS Genet 2014, 10, e1004741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outeiro, T.F.; Putcha, P.; Tetzlaff, J.E.; Spoelgen, R.; Koker, M.; Carvalho, F.; Hyman, B.T.; McLean, P.J. Formation of toxic oligomeric alpha-synuclein species in living cells. PLoS One 2008, 3, e1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh, C.L.; Lund, L.B.; Febbraro, F.; Hansen, H.D.; Gai, W.P.; El-Agnaf, O.; Richter-Landsberg, C.; Jensen, P.H. Alpha-synuclein aggregation and Ser-129 phosphorylation-dependent cell death in oligodendroglial cells. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 10211–10222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, K.A.; Lee, S.J.; Rochet, J.C.; Ding, T.T.; Harper, J.D.; Williamson, R.E.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Accelerated oligomerization by Parkinson's disease linked alpha-synuclein mutants. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2000, 920, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Pique, A.; Lopes da Fonseca, T.; Sant'Anna, R.; Szego, E.M.; Fonseca-Ornelas, L.; Pinho, R.; Carija, A.; Gerhardt, E.; Masaracchia, C.; Abad Gonzalez, E.; et al. Environmental and genetic factors support the dissociation between alpha-synuclein aggregation and toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, E6506–E6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abati, E.; Di Fonzo, A.; Corti, S. In vitro models of multiple system atrophy from primary cells to induced pluripotent stem cells. J Cell Mol Med 2018, 22, 2536–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, G.; Junn, E.; Iwatsubo, T.; Mouradian, M.M. Aggresomes formed by alpha-synuclein and synphilin-1 are cytoprotective. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 4625–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindersson, E.; Beedholm, R.; Hojrup, P.; Moos, T.; Gai, W.; Hendil, K.B.; Jensen, P.H. Proteasomal inhibition by alpha-synuclein filaments and oligomers. J Biol Chem 2004, 279, 12924–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzer, K.M.; Kranich, L.R.; Ruf, W.P.; Cagsal-Getkin, O.; Winslow, A.R.; Zhu, L.; Vanderburg, C.R.; McLean, P.J. Exosomal cell-to-cell transmission of alpha synuclein oligomers. Mol Neurodegener 2012, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Tang, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, M. CRISPR/Cas9 system and its applications in nervous system diseases. Genes Dis 2024, 11, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson's disease: etiopathogenesis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2020, 91, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, G.; Cook, L.; Schulze, J.; Verbrugge, J.; Alcalay, R.N.; Merello, M.; Sue, C.M.; Bardien, S.; Bonifati, V.; Chung, S.J.; et al. Genetic Testing in Parkinson's Disease. Mov Disord 2023, 38, 1384–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maass, F.; Schulz, I.; Lingor, P.; Mollenhauer, B.; Bahr, M. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker for Parkinson's disease: An overview. Mol Cell Neurosci 2019, 97, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eusebi, P.; Giannandrea, D.; Biscetti, L.; Abraha, I.; Chiasserini, D.; Orso, M.; Calabresi, P.; Parnetti, L. Diagnostic utility of cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov Disord 2017, 32, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyad, M.; Salim, S.; Majbour, N.; Erskine, D.; Stoops, E.; Mollenhauer, B.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Parkinson's disease biomarkers based on alpha-synuclein. J Neurochem 2019, 150, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O.; Hall, S.; Ohrfelt, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Minthon, L.; Nagga, K.; Londos, E.; Varghese, S.; Majbour, N.K.; et al. Levels of cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein oligomers are increased in Parkinson's disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies compared to Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 2014, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Chiasserini, D.; Persichetti, E.; Eusebi, P.; Varghese, S.; Qureshi, M.M.; Dardis, A.; Deganuto, M.; De Carlo, C.; Castrioto, A.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid lysosomal enzymes and alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2014, 29, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, T.; Salem, S.A.; Allsop, D.; Mizuno, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Qureshi, M.M.; Locascio, J.J.; Schlossmacher, M.G.; El-Agnaf, O.M. Decreased alpha-synuclein in cerebrospinal fluid of aged individuals and subjects with Parkinson's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 349, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, C.; Panaro, M.A.; Lofrumento, D.D.; Hasalla, E.; Trotta, T. The multiple roles of exosomes in Parkinson's disease: an overview. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2019, 41, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Caspell-Garcia, C.J.; Coffey, C.S.; Taylor, P.; Singleton, A.; Shaw, L.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Frasier, M.; Simuni, T.; Iranzo, A.; et al. Longitudinal analyses of cerebrospinal fluid alpha-Synuclein in prodromal and early Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2019, 34, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, A.G.; Vazquez-Romero, A.; Mahdi Moein, M.; Aden, J.; Elmore, C.S.; Takano, A.; Arakawa, R.; Varrone, A.; Almqvist, F.; Schou, M. Increased Brain Exposure of an Alpha-Synuclein Fibrillization Modulator by Utilization of an Activated Ester Prodrug Strategy. ACS Chem Neurosci 2018, 9, 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, K.M.; Cedarbaum, J.M.; Brundin, P.; Dave, K.D.; Eberling, J.; Espay, A.J.; Hutten, S.J.; Javidnia, M.; Luthman, J.; Maetzler, W.; et al. A Proposed Roadmap for Parkinson's Disease Proof of Concept Clinical Trials Investigating Compounds Targeting Alpha-Synuclein. J Parkinsons Dis 2019, 9, 31–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manne, S.; Kondru, N.; Hepker, M.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Lewis, M.; Huang, X.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Ultrasensitive Detection of Aggregated alpha-Synuclein in Glial Cells, Human Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Brain Tissue Using the RT-QuIC Assay: New High-Throughput Neuroimmune Biomarker Assay for Parkinsonian Disorders. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2019, 14, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saijo, E.; Groveman, B.R.; Kraus, A.; Metrick, M.; Orru, C.D.; Hughson, A.G.; Caughey, B. Ultrasensitive RT-QuIC Seed Amplification Assays for Disease-Associated Tau, alpha-Synuclein, and Prion Aggregates. Methods Mol Biol 2019, 1873, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaikath, N.N.; Hmila, I.; Gupta, V.; Erskine, D.; Ingelsson, M.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Antibodies against alpha-synuclein: tools and therapies. J Neurochem 2019, 150, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollerhage, M.; Wolff, A.; Chakroun, T.; Evsyukov, V.; Duan, L.; Chua, O.W.; Tang, Q.; Koeglsperger, T.; Hoglinger, G.U. Binding Stability of Antibody-alpha-Synuclein Complexes Predicts the Protective Efficacy of Anti-alpha-synuclein Antibodies. Mol Neurobiol 2022, 59, 3980–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covell, D.J.; Robinson, J.L.; Akhtar, R.S.; Grossman, M.; Weintraub, D.; Bucklin, H.M.; Pitkin, R.M.; Riddle, D.; Yousef, A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Novel conformation-selective alpha-synuclein antibodies raised against different in vitro fibril forms show distinct patterns of Lewy pathology in Parkinson's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2017, 43, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaikath, N.N.; Majbour, N.K.; Paleologou, K.E.; Ardah, M.T.; van Dam, E.; van de Berg, W.D.; Forrest, S.L.; Parkkinen, L.; Gai, W.P.; Hattori, N.; et al. Generation and characterization of novel conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies for alpha-synuclein pathology. Neurobiol Dis 2015, 79, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agnaf, O.; Overk, C.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Florio, J.; Adame, A.; Vaikath, N.; Majbour, N.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, C.; et al. Differential effects of immunotherapy with antibodies targeting alpha-synuclein oligomers and fibrils in a transgenic model of synucleinopathy. Neurobiol Dis 2017, 104, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, B.; Valera, E.; Rockenstein, E.; Overk, C.; Mante, M.; Adame, A.; Zago, W.; Seubert, P.; Barbour, R.; Schenk, D.; et al. Anti-alpha-synuclein immunotherapy reduces alpha-synuclein propagation in the axon and degeneration in a combined viral vector and transgenic model of synucleinopathy. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, C.; Lorenzen, N.; Lemminger, L.; Christiansen, G.; Moller, I.M.; Vesterager, L.B.; Pedersen, L.O.; Fog, K.; Kallunki, P.; Otzen, D.E. Antibodies against the C-terminus of alpha-synuclein modulate its fibrillation. Biophys Chem 2017, 220, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Sudhakaran, I.P.; Islam, Z.; Vaikath, N.N.; Hmila, I.; Lukacsovich, T.; Kolatkar, P.R.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Expression, purification and characterization of alpha-synuclein fibrillar specific scFv from inclusion bodies. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0241773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassler, M.; Benaim, C.; George, J. A Single Chain Fragment Variant Binding Misfolded Alpha-Synuclein Exhibits Neuroprotective and Antigen-Specific Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsoom, I.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Wen, H. Research Progress of alpha-Synuclein Aggregation Inhibitors for Potential Parkinson's Disease Treatment. Mini Rev Med Chem 2023, 23, 1959–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Goncalves, N.P.; Vaegter, C.B.; Jensen, P.H.; Ferreira, N. The Prion-Like Spreading of Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease: Update on Models and Hypotheses. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlushchuk, I.; Ruskoaho, H.; Domanskyi, A.; Airavaara, M.; Valimaki, M.J. Domain-Independent Inhibition of CBP/p300 Attenuates alpha-Synuclein Aggregation. ACS Chem Neurosci 2021, 12, 2273–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarutani, A.; Hasegawa, M. Prion-like propagation of alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2019, 168, 323–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujols, J.; Pena-Diaz, S.; Lazaro, D.F.; Peccati, F.; Pinheiro, F.; Gonzalez, D.; Carija, A.; Navarro, S.; Conde-Gimenez, M.; Garcia, J.; et al. Small molecule inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregation, disrupts amyloid fibrils, and prevents degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, 10481–10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Diaz, S.; Pujols, J.; Vasili, E.; Pinheiro, F.; Santos, J.; Manglano-Artunedo, Z.; Outeiro, T.F.; Ventura, S. The small aromatic compound SynuClean-D inhibits the aggregation and seeded polymerization of multiple alpha-synuclein strains. J Biol Chem 2022, 298, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, R.; Brotzakis, Z.F.; Chia, S.; Horne, R.I.; Vendruscolo, M. Optimization of a small molecule inhibitor of secondary nucleation in alpha-synuclein aggregation. Front Mol Biosci 2023, 10, 1155753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Dong, F.; Wang, Y. Enlarged Perivascular Space and Index for Diffusivity Along the Perivascular Space as Emerging Neuroimaging Biomarkers of Neurological Diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2023, 44, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Jiang, X.; Guan, X.; Guo, T.; Wu, J.; Wu, H.; Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Wen, J.; Tan, S.; et al. Glymphatic system dysfunction and risk of clinical milestones in patients with Parkinson disease. Eur J Neurol 2024, 31, e16521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, X.; Liu, Z.; Gan, Z.; Yan, Q.; Tong, L.; Qiu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.F.; Li, Z. Targeting the glymphatic system to promote alpha-synuclein clearance: a novel therapeutic strategy for Parkinson's disease. Neural Regen Res 2025, 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00764. [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Fang, Y.; Cheng, C.; He, Y.; Shao, Z.; Kong, Y.; Huang, H.; Xu, S.; Luo, X.; Wang, W.; et al. Genome-wide and phenome-wide studies provided insights into brain glymphatic system function and its clinical associations. Sci Adv 2025, 11, eadr4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padilla-Godinez, F.J.; Ruiz-Ortega, L.I.; Guerra-Crespo, M. Nanomedicine in the Face of Parkinson's Disease: From Drug Delivery Systems to Nanozymes. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, D.F.; Lee, V.M. Navigating through the complexities of synucleinopathies: Insights into pathogenesis, heterogeneity, and future perspectives. Neuron 2024, 112, 3029–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Hou, L.; Li, N. A crazy trio in Parkinson's disease: metabolism alteration, alpha-synuclein aggregation, and oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biochem 2025, 480, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yun, X.; Lo, H.H.; Song, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; et al. FBXL16: a new regulator of neuroinflammation and cognition in Alzheimer's disease through the ubiquitination-dependent degradation of amyloid precursor protein. Biomark Res 2024, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Ali, W.; Din, Z.U.; Song, S.; Sohail, M.; Shah, W.; Guo, J.; Guo, R.Y.; Ilahi, I.; Shah, S.; et al. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats as an advanced treatment for Parkinson's disease. Brain Behav 2021, 11, e2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, F.; Hatam, G.; Behbahani, A.B.; Rezaei, V.; Barekati-Mowahed, M.; Petramfar, P.; Khademi, F. CRISPR System: A High-throughput Toolbox for Research and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2020, 40, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.M.; El-Khatib, A.S. Exploring Parkinson-associated kinases for CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing: beyond alpha-synuclein. Ageing Res Rev 2023, 92, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuensche, T.E.; Pereira, P.M.; Windhorst, A.D.; Bjerregaard-Andersen, K.; Sotty, F.; Kallunki, P.; Jensen, A.; Bang-Andersen, B.; van Dongen, G.; Beaino, W.; et al. New prospects for (89)Zr-immuno-PET in brain applications - Alpha-synucleinopathies. Nucl Med Biol 2024, 140-141, 108969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, S.; Ye, K. Positron emission tomography tracers for synucleinopathies. Mol Neurodegener 2025, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaidi, M.; Barker, R.A.; Kuan, W.L. An update on immune-based alpha-synuclein trials in Parkinson's disease. J Neurol 2024, 272, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadh, M.J.; Muhammad, F.A.; Singh, A.; Mustafa, M.A.; Al Zuhairi, R.A.H.; Ghildiyal, P.; Hashim, G.; Alsaikhan, F.; Khalilollah, S.; Akhavan-Sigari, R. MicroRNAs Modulating Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease. Inflammation 2024, 10.1007/s10753-024-02125-z. [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, A.; Ali, H.; AlNaimi, A.; Yousef, M.; Rob, M.; Al-Muhannadi, N.A.; Senevirathne, D.K.L.; Chaari, A. Immunotherapy for Parkinson's Disease and Alzheimer's Disease: A Promising Disease-Modifying Therapy. Cells 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Preeti, K.; Fernandes, V.; Khatri, D.K.; Singh, S.B. Role of MicroRNAs, Aptamers in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2022, 42, 2075–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Shannon, K.M.; Kordower, J.H.; Voigt, R.M.; Shaikh, M.; Jaglin, J.A.; Estes, J.D.; Dodiya, H.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early Parkinson's disease. PLoS One 2011, 6, e28032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.B.; Malireddi, A.; Abera, M.; Noor, K.; Ansar, M.; Boddeti, S.; Nath, T.S. Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Parkinson's Disease. Cureus 2024, 16, e73150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Ru, Q.; Chen, L.; Xu, G.; Wu, Y. Advances in animal models of Parkinson's disease. Brain Res Bull 2024, 215, 111024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
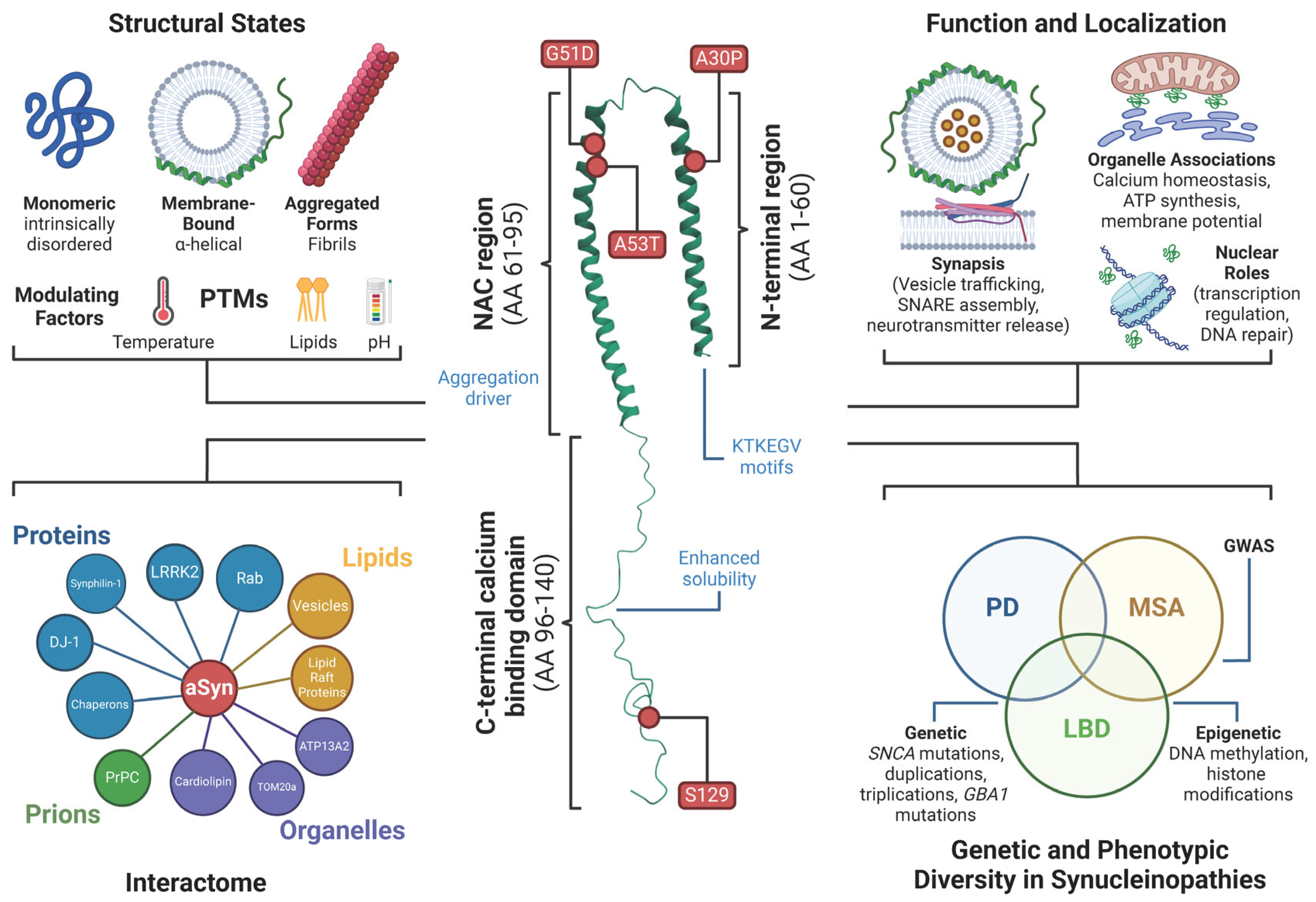
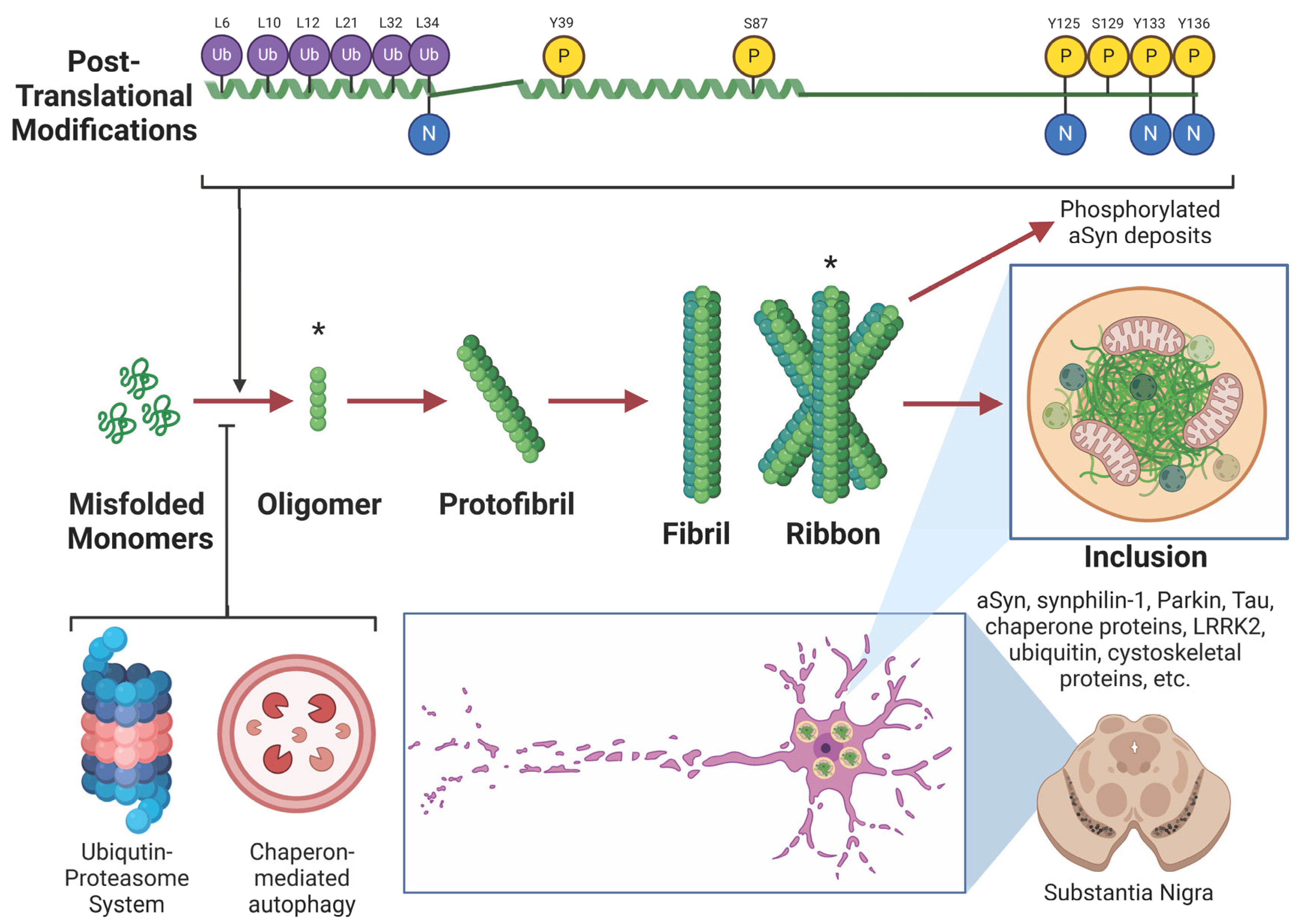
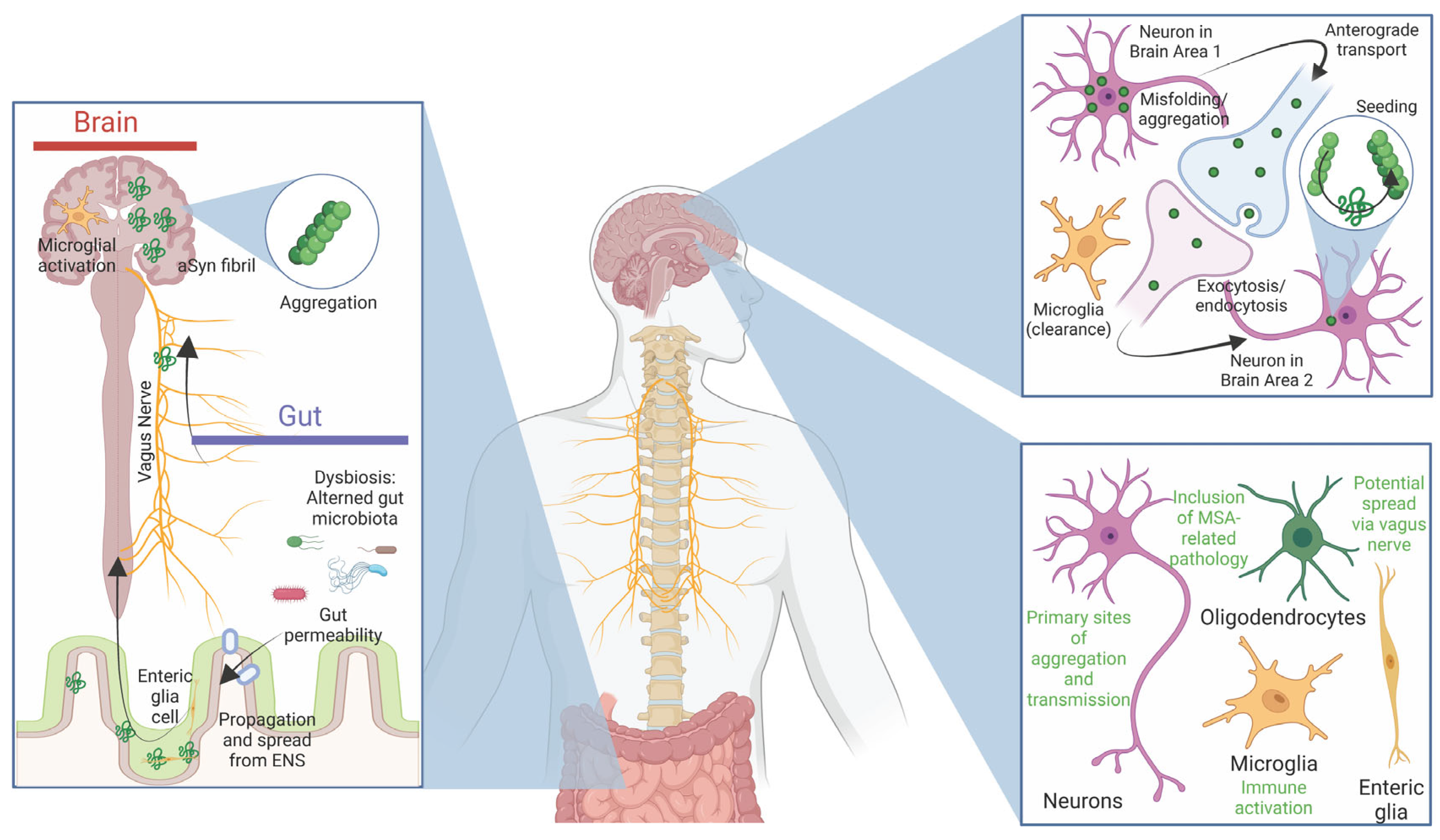
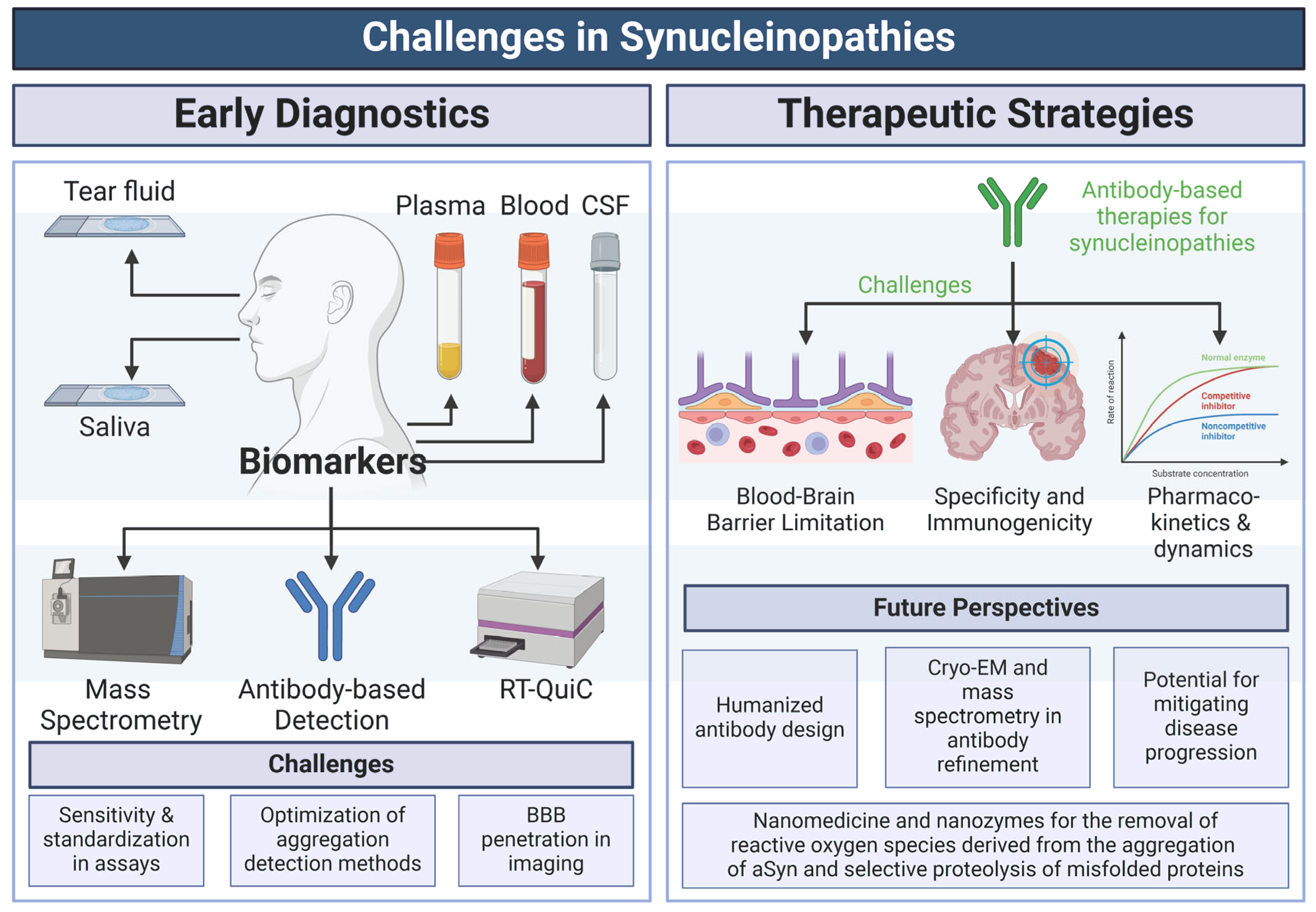
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




