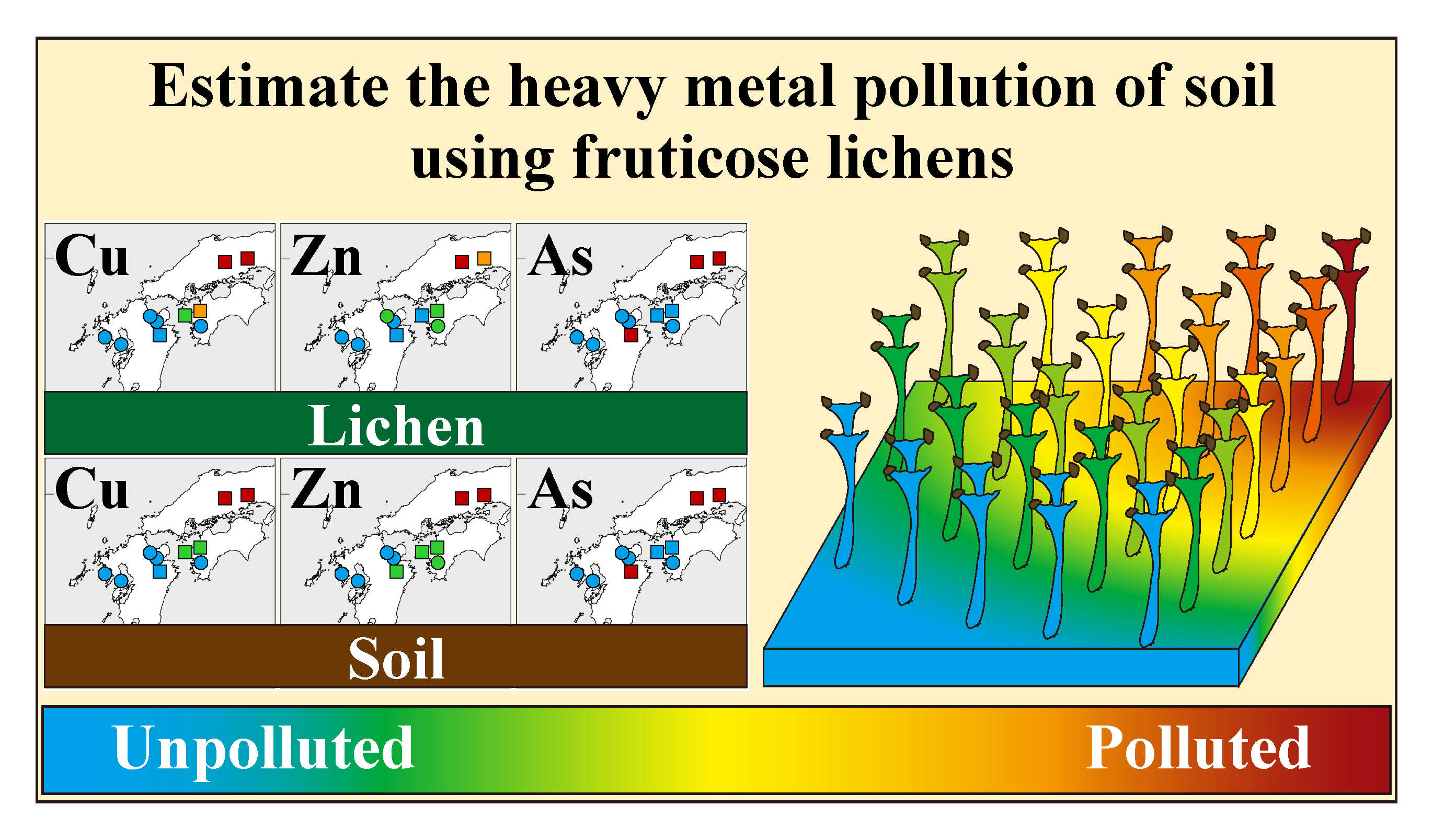
Soil pollution has been estimated using soil analysis and leaching test. These methods could show different data from reality due to effects by soil properties such as grain size and mineral composition. Therefore, this study advocates a new assessment and monitoring method of heavy metal polluted soil using fruticose lichens. Lichens growing at abandoned mine sites and unpolluted areas in southwest Japan and their substrata were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry to clarify the relationships between the heavy metal concentrations in lichens and soils, and their heavy metal absorption properties. Concentrations of Cu, Zn, As, and Pb in the lichens were positively correlated with those in the soil. Variability of the relationships did not depend on the lichen species, location, habitat, or the conditions of soils. The analyzed lichens had neither competitive nor antagonistic properties in their heavy metal absorption, which make them good biomarkers of heavy metal pollution of soil. The distribution maps of average heavy metal concentrations at each sampling region detected almost all of the Cu, Zn, and As pollution of soil. Therefore, lichens could be used in practical applications to assess Cu, Zn, and As pollution of soils.