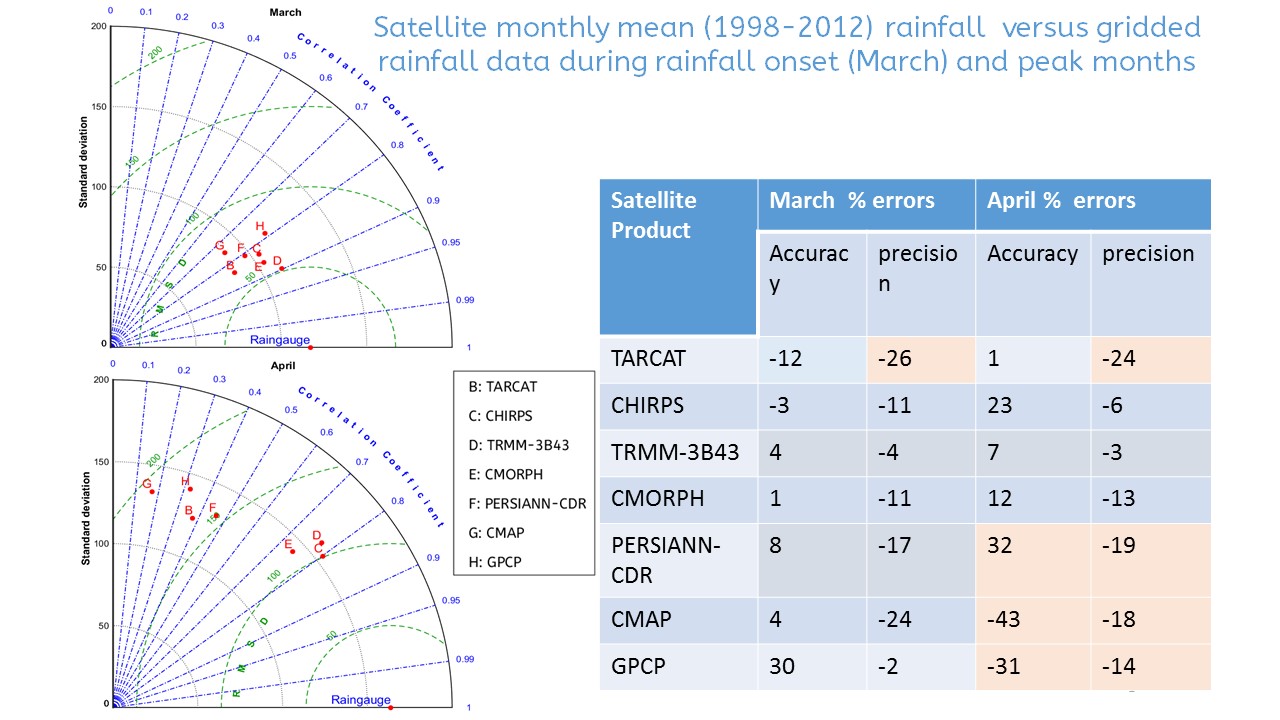
Accurate and consistent rainfall observations are vital for climatological studies in support of better planning and decision making. However, estimation of accurate spatial rainfall is limited by sparse rain gauge distributions. Satellite rainfall products can thus potentially play a role in spatial rainfall estimation but their skill and uncertainties need to be under-stood across spatial-time scales. This study aimed at assessing the temporal and spatial performance of seven satellite products (TARCAT (Tropical Applications of Meteorology using SATellite and ground-based observations (TAMSAT) African Rainfall Climatology And Time series), Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station data (CHIRPS), Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM-3B43), Climate Prediction Center (CPC) Morphing (CMORPH), the Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks- Climate Data Record (PERSIANN-CDR), CPC Merged Analysis of Precipitation (CMAP) and Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) using gridded (0.05o) rainfall data over East Africa for 15 years(1998-2012). The products’ error distributions were qualitatively compared with large scale horizontal winds (850 mb) and elevation patterns with respect to corresponding rain gauge data for each month during the ‘long’ (March-May) and ‘short’ (October-December) rainfall seasons. For validation only rainfall means extracted from 284 rain gauge stations were used, from which qualitative analysis using continuous statistics of Root Mean Squared Difference, Standard deviations, Correlations, coefficient of determinations (from scatter plots) were used to evaluate the products’ performance. Results revealed rainfall variability dependence on wind flows and modulated by topographic influences. The products’ errors showed seasonality and dependent on rainfall intensity and topography. Single sensor and coarse resolution products showed lowest performance on high ground areas. All the products showed low skills in retrieving rainfall during ‘short’ rainfall season when orographic processes were dominant. CHIRPS, CMORPH and TRMM performed well, with TRMM showing the best performance in both seasons. There is need to reduce products’ errors before applications.