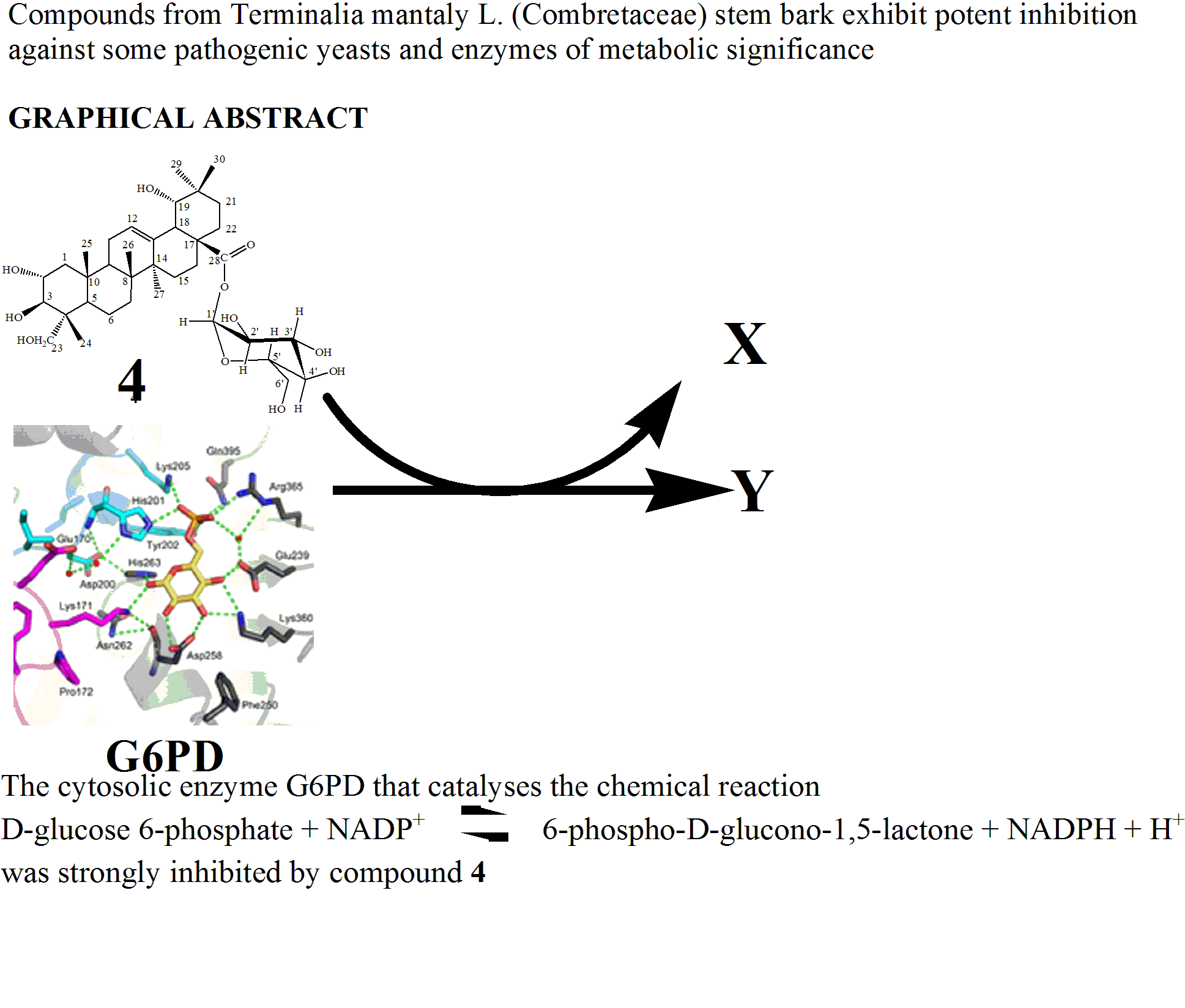
The chemical investigation of the anti-yeast methanol extract from the stem bark of Terminalia mantaly led to the isolation of seven compounds: 3-O-methyl-4-O-α-rhamnopyranoside ellagic acid (1), 3-O-mehylellagic acid (2), arjungenin or 2,3,19,23-tetrahydroxyolean-12-en-28-oïc acid (3), arjunglucoside or 2,3,19,23-tetrahydroxyolean-12-en-28-oïc acid glucopyranoside (4), 2α,3α,24-trihydroxyolean-11,13(18)-dien-28-oïc acid (5), stigmasterol (6), stigmasterol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (7). Their structures were established by means of spectroscopic analysis and comparison with published data. Compounds 1-5 were tested in vitro for activity against three pathogenic yeast isolates, Candida albicans, Candida parapsilosis and Candida krusei. The activity of compounds 1, 2 and 4 were comparable to that of the reference compound fluconazole (MIC values below 32 µg/ml) against the three tested yeast isolates. They were also tested for inhibitory properties against four enzymes of metabolic significance: Glucose-6-Phosphate Deshydrogenase (G6PD), human erythrocyte Carbonic anhydrase I and II (hCA I and hCA II), Glutathione S-transferase (GST). Compound 4 showed highly potent inhibitory property against the four tested enzymes with overall IC50 values below 4 µM and inhibitory constant (Ki) <3 µM.