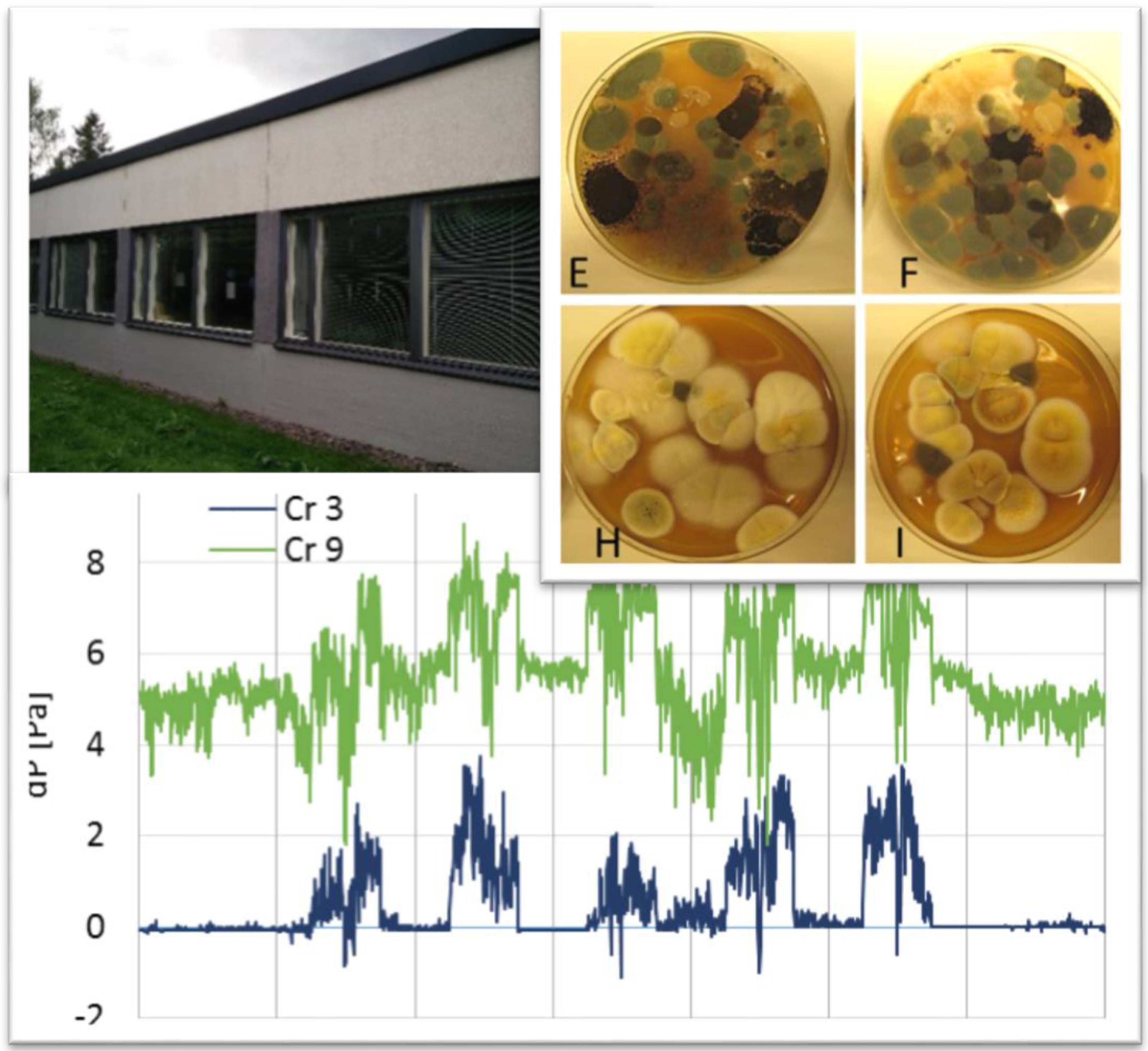
This case study investigates the effects of ventilation intervention on measured and perceived indoor air quality (IAQ) in a repaired school where occupants reported IAQ problems. Occupants´ symptoms were suspected to be related to the impurities leaked indoors through the building envelope. The study’s aim was to determine whether a positive pressure of 5-7 Pa prevents the infiltration of harmful chemical and microbiological agents from structures, thus decreasing symptoms and discomfort. Ventilation intervention was conducted in a building section comprising 12 classrooms and was completed with IAQ measurements and occupants´ questionnaires. After intervention, the concentration of total volatile organic compounds (TVOC) and fine particulate matter (PM2.5) decreased, and occupants´ negative perceptions became more moderate compared to those for other parts of the building. The indoor mycobiota differed in species composition from the outdoor mycobiota, and changed remarkably with the intervention, indicating that some species may have emanated from an indoor source before the intervention.