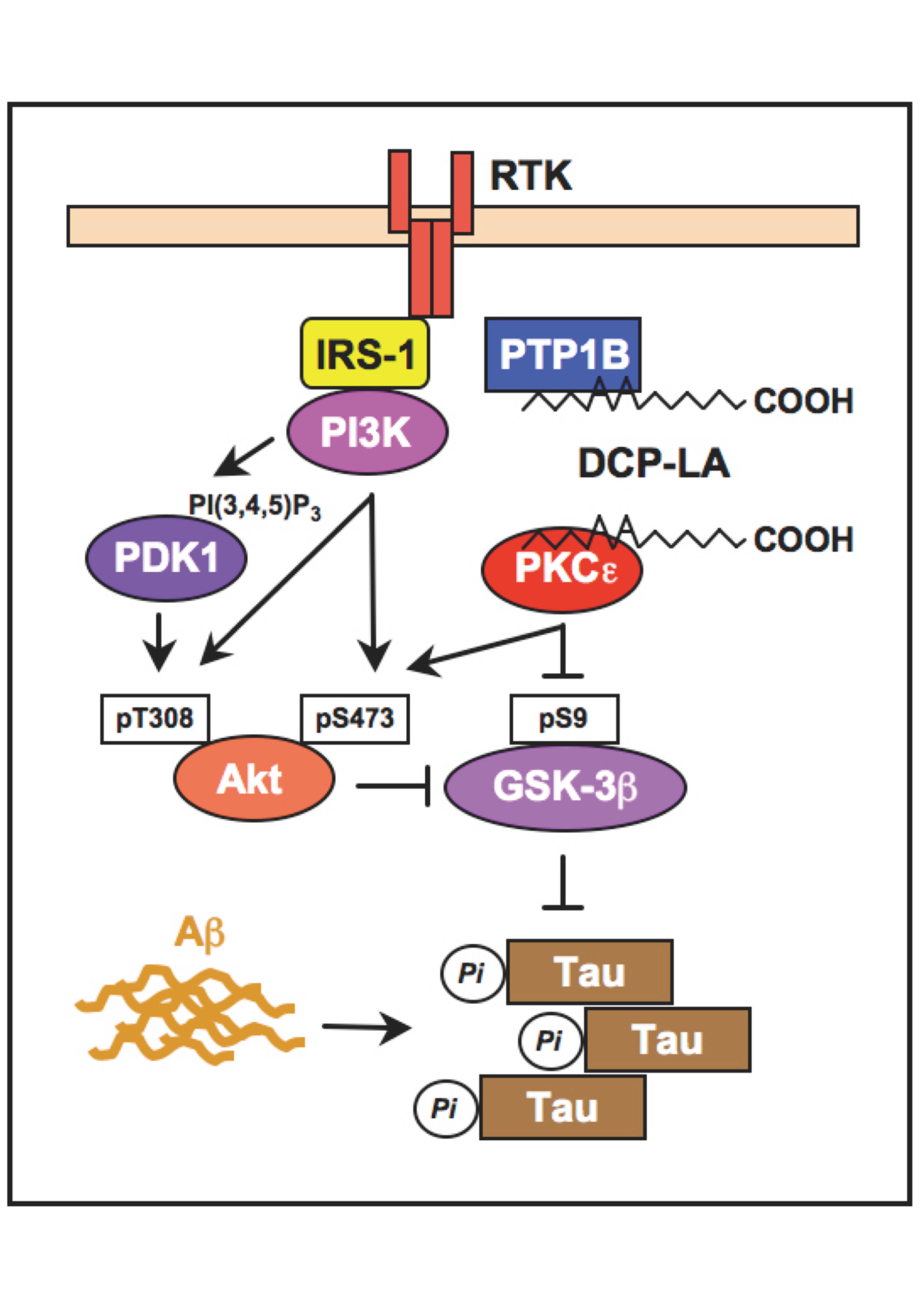
Abnormal Tau phosphorylation and aggregation into neuronal paired helical filaments and neurofibrillary tangles cause tauopathies, a class of neurodegenerative diseases, that include Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17, progressive supranuclear palsy, Pick's disease, and corticobasal degeneration. Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) is the most critical kinase to phosphorylate Tau. We have developed the linoleic acid derivative 8-[2-(2-pentyl-cyclopropylmethyl)-cyclopropyl]-octanoic acid (DCP-LA), with cyclopropane rings instead of cis-double bonds, as an anti-dementia drug. DCP-LA serves as a selective activator of PKCε and a potent inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B). DCP-LA prevents Tau phosphorylation due to PKCε-mediated direct inactivation of GSK-3β, to PKCε/Akt-mediated inactivation of GSK-3β, and to receptor tyrosine kinase-mediated inactivation of GSK-3β in association with PTP1B inhibition. DCP-LA targeting GSK-3β, thus, could become a valid drug for treatment of tauopathies.