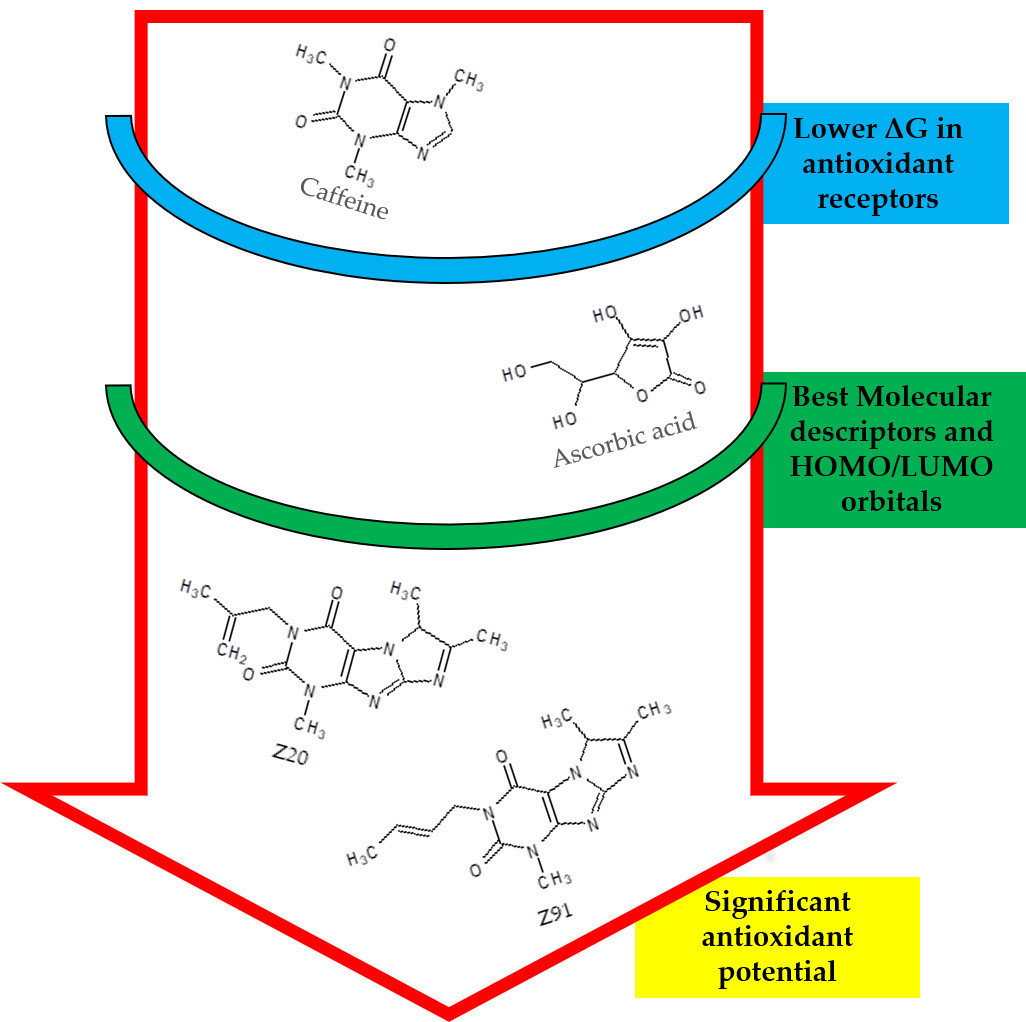
The antioxidant activity of molecules constitutes an important factor for the regulation of redox homeostasis and reduction of oxidative stress. Cells affected by oxidative stress can undergo genetic alteration, causing structural changes and promoting the onset of chronic diseases, such as cancer. The in silico study performed here was developed to evaluate the antioxidant potential of two molecules, ZINC08706191 (Z91) and ZINC08992920 (Z20), with recognized epithelial anticancer potential. Molecular docking, chemical-quantum calculations and Pearson's correlation were performed. The Z91 and Z20 molecules showed lower binding free energy (ΔG) values for the receptor-ligand interaction than the reference molecules (caffeine – CAF and ascorbic acid – AA), and better results for values of molecular descriptors correlated with ΔG, resulting in a decrease of ΔG. Strong correlations were observed between ΔG values for the five receptors evaluated and ΔG values of the potential epithelial anticancer activity available in literature. These results attest to the significant antioxidant potential of the Z91 and Z20 molecules and their strong relation with the potential epithelial anticancer activity and may be indicated for further analysis in relation to the control of oxidative stress and epithelial anticancer activity.