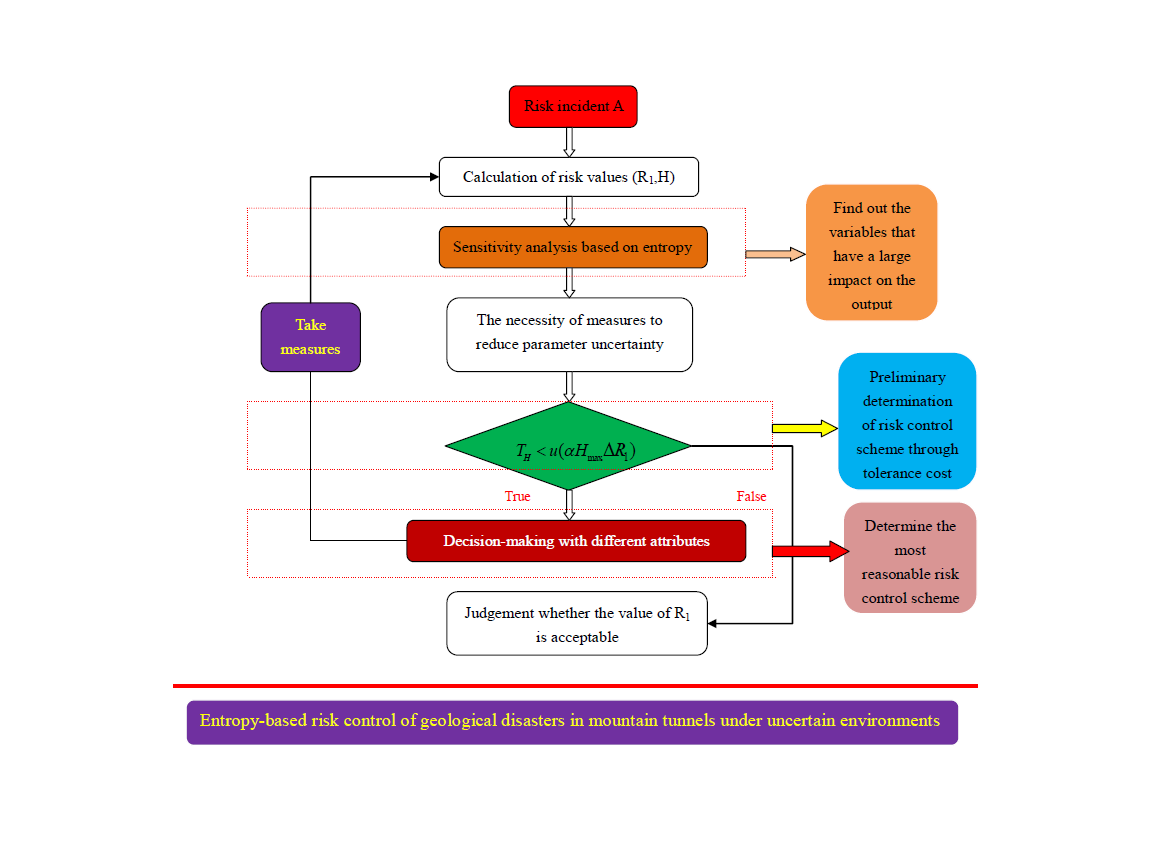
Uncertainty is the main source of risk of geological hazards in tunnel engineering. Uncertainty information not only affects the accuracy of evaluation results, but also affects the reliability of decision-making schemes. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate and control the impact of uncertainty on risk. In this study, the problems in existing entropy-hazard model such as inefficient decision-making and failure of decision-making are analysed, and an improved uncertainty evaluation and control process are proposed. Then the tolerance cost, the key factor in the decision-making model, is also discussed. It is considered that the amount of change in risk value (R1) can better reflect the psychological behaviour of decision-makers. Thirdly, common attribute decision models, such as the expected utility-entropy model, are analysed, and then the viewpoint of different types of decision-making issues that require different decision methods is proposed. The well-known Allais paradox is explained by the proposed methods. Finally, the engineering application results show that the uncertainty control idea proposed here is accurate and effective. This research indicates a direction for further research into uncertainty, and risk control, issues affecting underground engineering works.