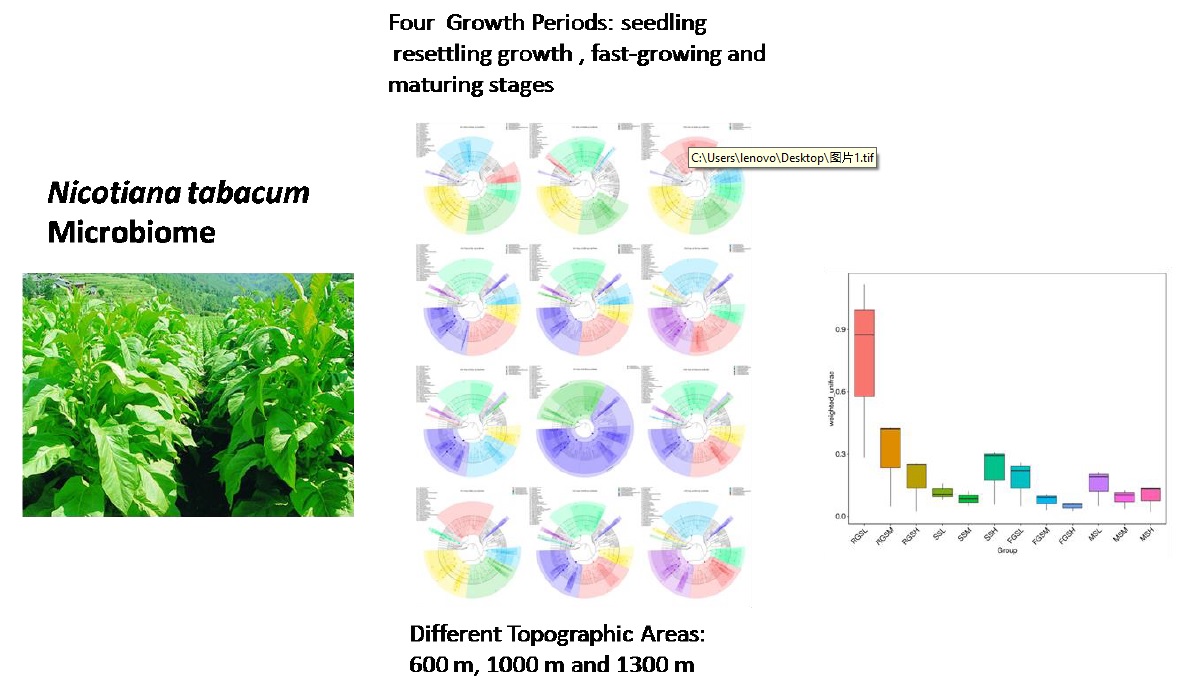
Fungal endophytes are the most ubiquitous plant symbionts on earth and are phylogenetically diverse. Studies on the fungal endophytes in tobacco have shown that they are widely distributed in the leaves, stems, and roots, and play important roles in the composition of the microbial ecosystem of tobacco. Herein, we analyzed and quantified the endophytic fungi of healthy tobacco leaves at the seedling (SS), resettling growth (RGS), fast-growing (FGS), and maturing (MS) stages at three altitudes [600 (L), 1000 (M), and 1300 m (H)]. We sequenced the ITS region of fungal samples to delimit operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and phylogenetically characterize the communities. The result showed the number of clustering OTUs at SS, RGS, FGS and MS were greater than 170, 245, 140, and 164, respectively. At the phylum level, species in Ascomycota and Basidiomycota had absolute predominance, representing 97.8% and 2.0 % of the total number of species. We also found the number of unique fungi at the RGS and FGS stages were higher than those in the other two stages. Additionally, OTU richness was determined by calculating the Observed Species, Shannon, Simpson, Chao1, ACE, Goods coverage and PD_whole_tree indices based on the total number of species. Our results showed RGS samples had the highest diversity indices. Furthermore, we found that the diversity of fungal communities tended to decrease with increasing tobacco growth altitude. The results from this study indicated that the tobacco harbors an abundant and diverse endophytic fungal population, which provides new opportunities for exploration their potential utilization.