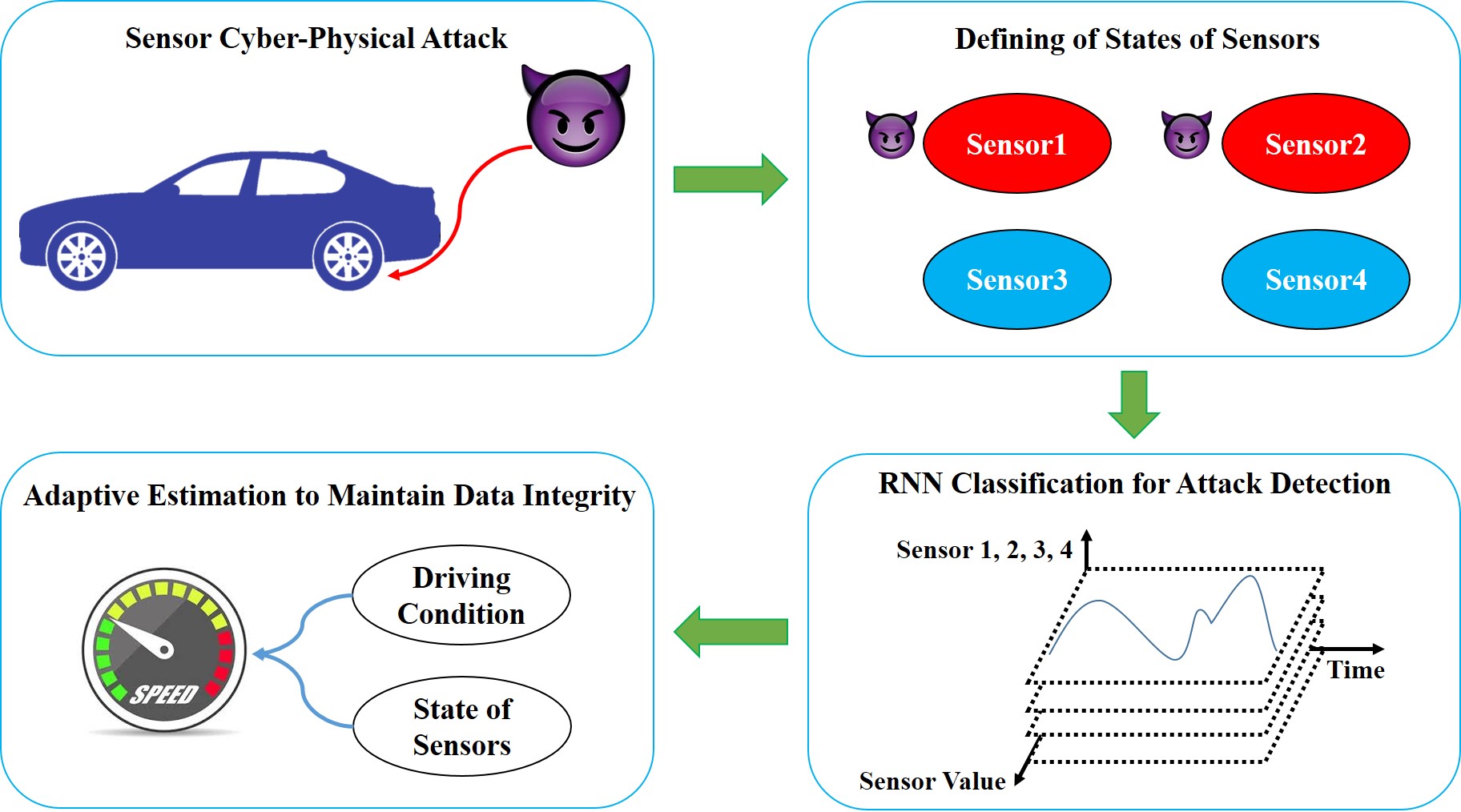
The violation of data integrity in automotive Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) may lead to dangerous situations for drivers and pedestrians in terms of safety. In particular, cyber-attacks on the sensor could easily degrade data accuracy and consistency over any other attack, we investigate attack detection and identification based on a deep learning technology on wheel speed sensors of automotive CPS. For faster recovery of a physical system with detection of the cyber-attacks, estimation of a specific value is conducted to substitute false data. To the best of our knowledge, there has not been a case of joining sensor attack detection and vehicle speed estimation in existing literatures. In this work, we design a novel method to combine attack detection and identification, vehicle speed estimation of wheel speed sensors to improve the safety of CPS even under the attacks. First, we define states of the sensors based on the cases of attacks that can occur in the sensors. Second, Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) is applied to detect and identify wheel speed sensor attacks. Third, in order to estimate the vehicle speeds accurately, we employ Weighted Average (WA), as one of the fusion algorithms, in order to assign a different weight to each sensor. Since environment uncertainty while driving has an impact on different characteristics of vehicles and cause performance degradation, the recovery mechanism needs the ability adaptive to changing environments. Therefore, we estimate the vehicle speeds after assigning a different weight to each sensor depending on driving situations classified by analyzing driving data. Experiments including training, validation, and test are carried out with actual measurements obtained while driving on the real road. In case of the fault detection and identification, classification accuracy is evaluated. Mean Squared Error (MSE) is calculated to verify that the speed is estimated accurately. The classification accuracy about test additive attack data is 99.4978%. MSE of our proposed speed estimation algorithm is 1.7786. It is about 0.2 lower than MSEs of other algorithms. We demonstrate that our system maintains data integrity well and is safe relatively in comparison with systems which apply other algorithms.