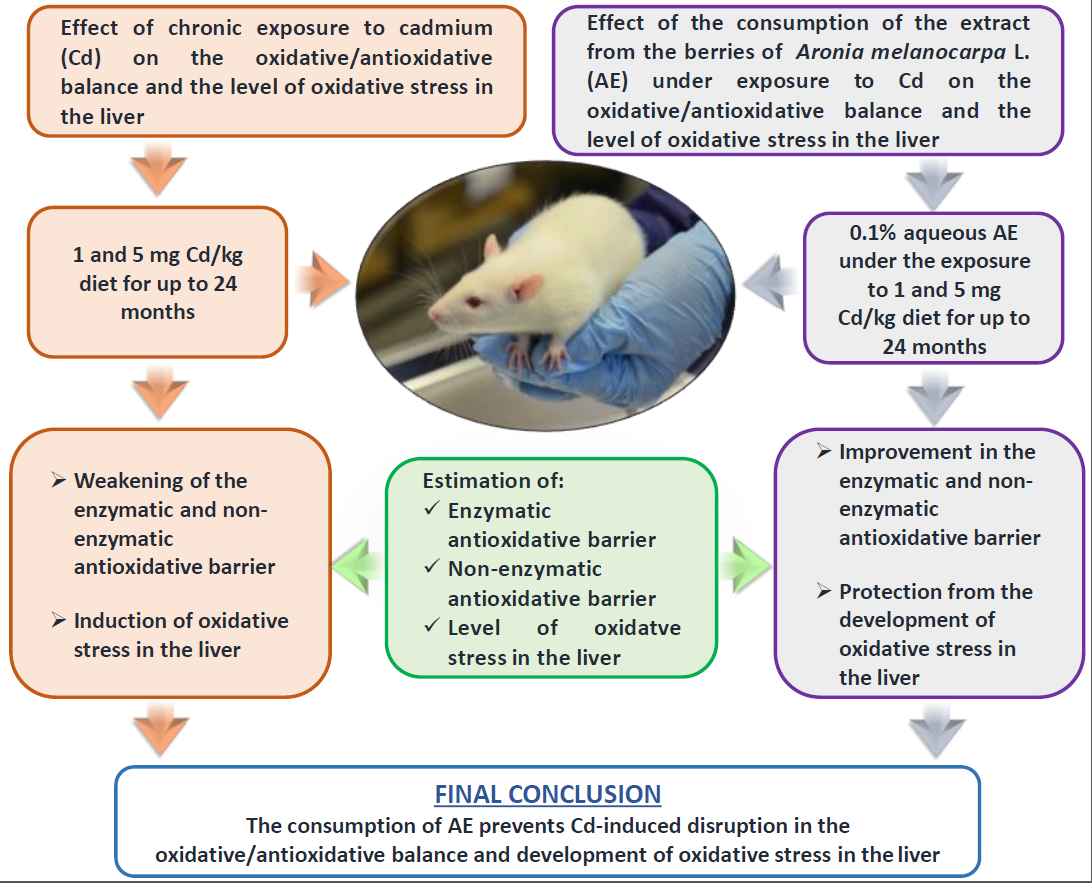
The study investigated, in a rat model of low-level and moderate environmental exposure to cadmium (Cd; 1 or 5 mg Cd/kg diet, respectively, for 3-24 months), whether the co-administration of 0.1% extract from Aronia melanocarpa L. berries (AE) may protect against oxidative stress in the liver. The intoxication with Cd, dose- and duration-dependently, weakened the enzymatic antioxidative barrier (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione S-transferase), decreased the concentrations of non-enzymatic antioxidants (reduced glutathione and total thiol groups), and increased the concentrations of oxidized glutathione, hydrogen peroxide, xanthine oxidase, and myeloperoxidase in this organ. These resulted in a decrease in the total antioxidative status (TAS), an increase in the total oxidative status (TOS), and development of oxidative stress in the liver (evaluated based on the index of oxidative stress calculated as the ratio of TOS and TAS). The administration of AE at both levels of Cd treatment significantly improved the enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidative barrier, decreased the concentration of pro-oxidants, and protected from the development of oxidative stress in the liver. In conclusion, consumption of aronia products may prevent Cd-induced destroying the oxidative/antioxidative balance and development of oxidative stress in the liver protecting against this organ damage.