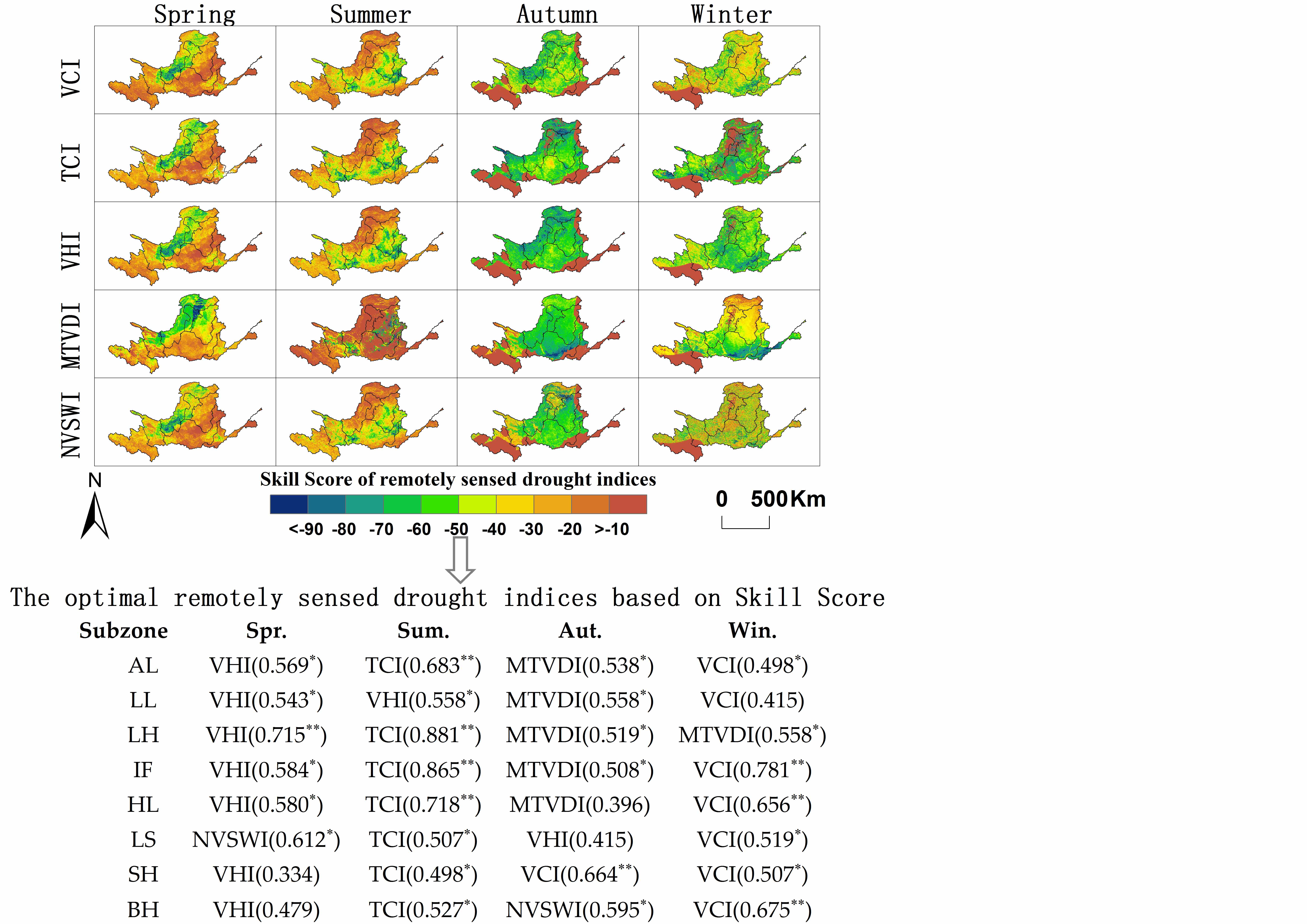
Due to the advantages of wide coverage and continuity, remotely sensed data are widely used for large-scale drought monitoring to compensate the deficiency and discontinuity of meteorological data. However, few researches have focused on the capability of various remotely sensed drought indices (RSDIs) for representing the spatio-temporal variations of the meteorological droughts. In this study, five RSDIs, namely Vegetation Condition Index (VCI), Temperature Condition Index (TCI), Vegetation Health Index (VHI), Modified Temperature Vegetation Dryness Index (MTVDI) and Normalized Vegetation Supply Water Index (NVSWI) were calculated using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) monthly NDVI and LST. The monthly NDVI and LST data were filtered by Savitzky-Golay (S-G) filtering method. Meteorological station-based drought index represented by Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) was compared with RSDIs. And the dimensionless Skill Score (SS) method was adopted to identify the spatiotemporally optimal RSDIs for presenting the meteorological droughts in the Yellow River basin (YRB) from 2000 to 2015. The results indicated that (1) RSDIs revealed a decreasing trend to the overall YRB consistent with SPEI except for in winter, and different variations of seasonal trends spatially; (2) the optimal RSDIs in spring, summer, autumn and winter were VHI, TCI, MTVDI and VCI, respectively, and the average correlation coefficient between the RSDIs and SPEI was 0.577 (=0.05); (3) different RSDIs have a 0–3 months’ time-lags compared with meteorological drought index.