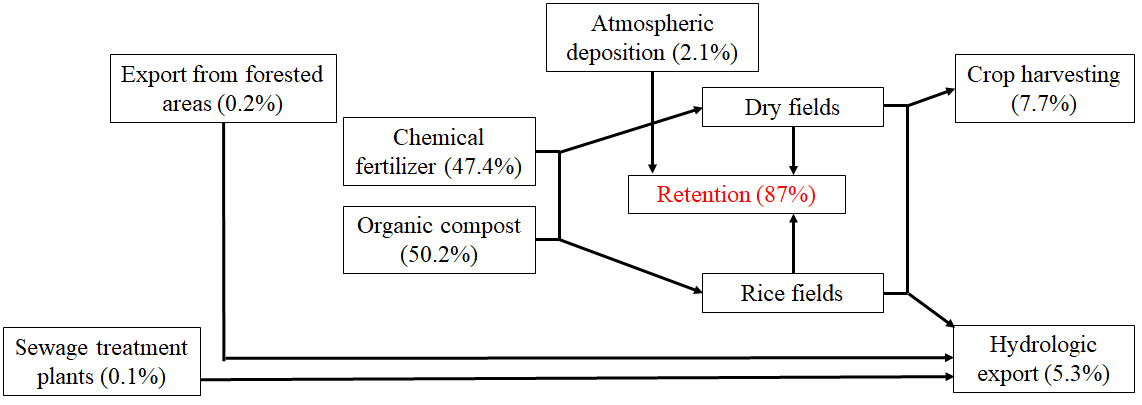
Despite increased awareness of and attention to the need for sustainable agriculture, fertilizers and compost application in excess of crop requirements remain common agricultural practices in South Korea, causing eutrophication of freshwater and coastal ecosystems. In this study, a phosphorus (P) budget was developed to quantify P inputs, outputs, and retention in a forested- agricultural watershed. The P budget showed that chemical fertilizers and organic compost were the largest source of P (97.6% of the total) followed by atmospheric deposition (2.1% of the total P), whereas forest export (0.2% of the total) and sewage treatment plants (STPs) (0.1% of the total) were negligible. The dominant P outputs were crop harvesting and hydrologic export to surface water. The P balance showed a significant accumulation of P in the watershed; approximately 87% of the total P input was retained in the soils within the watershed. However, P concentrations in drainage water were still high enough to cause eutrophication of downstream reservoirs. The results provide useful information on the proportion of P export and retention in soils and will help support efforts to improve water quality and design better management of agricultural non-point source pollution.