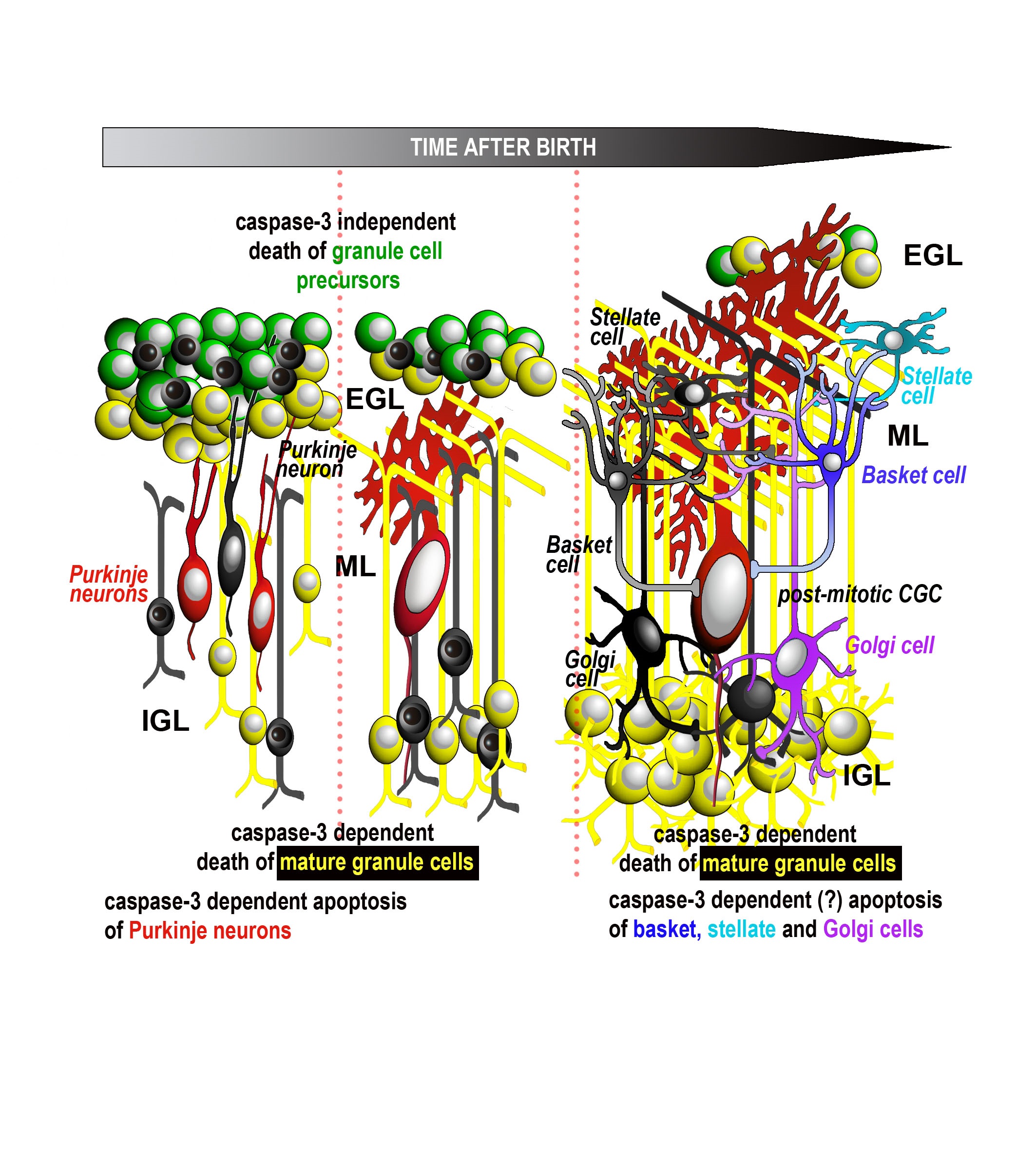
Caspase-3, onto which there is a convergence of the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways, is the main executioner of apoptosis. We here review the current literature on the intervention of the protease in the execution of naturally occurring neuronal death (NOND) during cerebellar development. We will consider data on the most common altricial species (rat, mouse and rabbit), as well as humans. Among the different types of neurons and glia in cerebellum, there is ample evidence for an intervention of caspase-3 in the regulation of NOND of the post-mitotic cerebellar granule cells (CGCs) and Purkinje neurons as a consequence of failure to establish proper synaptic contacts with target (secondary cell death). It seems possible that also the GABAergic interneurons undergo a similar type of secondary cell death, but the intervention of caspase-3 in this case still remains to be clarified in full. Remarkably, CGCs also undergo primary cell death at the precursor/pre-migratory stage of differentiation, in this case without the intervention of caspase-3. Glial cells as well undergo a process of regulated cell death, but it seems possible that expression of caspase-3, at least in the Bergmann glia, is related to differentiation rather than death.