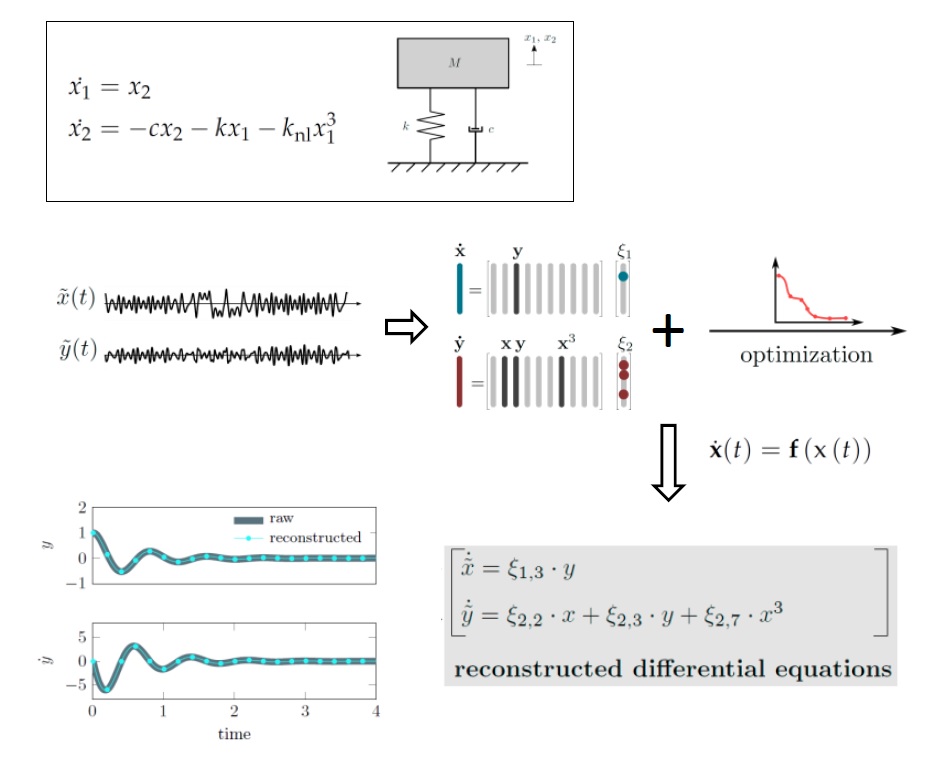
Time recordings of impulse-type oscillation responses are short and highly transient. These characteristics may complicate the usage of classical spectral signal processing techniques for a) describing the dynamics and b) deriving discriminative features from the data. However, common model identification and validation techniques mostly rely on steady-state recordings, characteristic spectral properties and non-transient behavior. In this work, a recent method, which allows reconstructing differential equations from time series data, is extended for higher degrees of automation. With special focus on short and strongly damped oscillations, an optimization procedure is proposed that fine-tunes the reconstructed dynamical models with respect to model simplicity and error reduction. This framework is analyzed with particular focus on the amount of information available to the reconstruction, noise contamination and non-linearities contained in the time series input. Using the example of a mechanical oscillator, we illustrate how the optimized reconstruction method can be used to identify a suitable model and to extract features from uni-variate and multivariate time series recordings in an engineering-compliant environment. Moreover, the determined minimal models allow for identifying the qualitative nature of the underlying dynamical systems as well as testing for the degree and strength of non-linearity. The reconstructed differential equations would then be potentially available for classical numerical studies, such as bifurcation analysis. These results represent a physically interpretable enhancement of data-driven modeling approaches in structural dynamics.