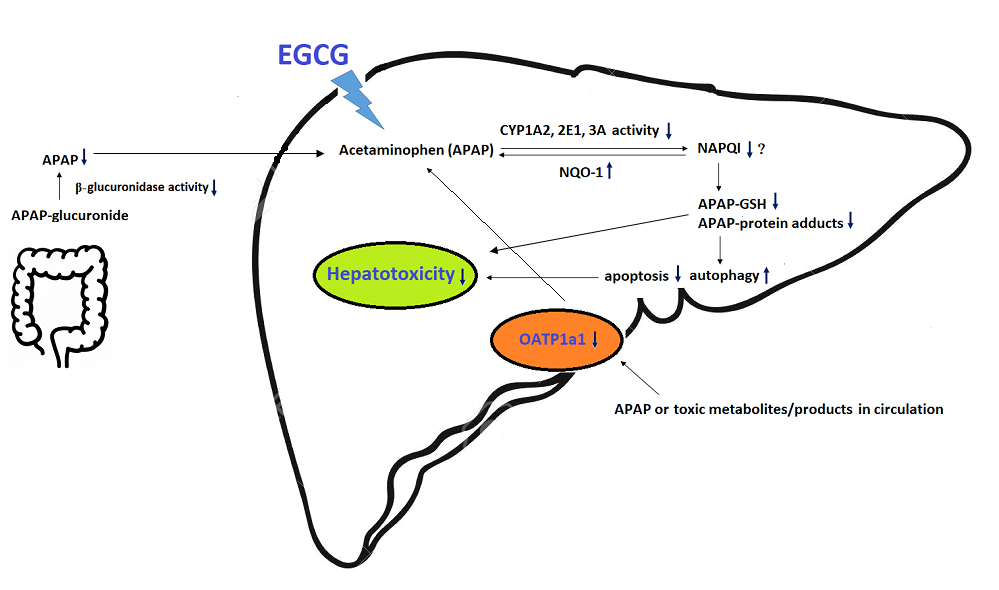
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is the most abundant polyphenol in green tea. In this study, the effects of dietary EGCG on oxidative stress and the metabolism and toxicity of acetaminophen in liver were investigated. Rats were fed the diets with (0.54 %) or without EGCG supplementation for four weeks and were then intraperitoneally injected with acetaminophen (1g/kg). Results showed EGCG lowered hepatic oxidative stress and cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, 2E1, and 3A, and UDP-glucurosyltransferase activities prior to acetaminophen injection. After acetaminophen challenge, the elevations in plasma alanine aminotransferase activity and histological changes in liver were ameliorated by EGCG treatment. EGCG reduced acetaminophen-induced apoptosis by increasing the Bax/Bcl2 ratio in liver. EGCG mildly increased autophagy by increasing the LC3B II/I ratio. Lower hepatic acetaminophen-glutathione and acetaminophen-protein adducts contents were observed after EGCG treatment. EGCG increased glutathione peroxidase and NAD(P)H quinone 1 oxidoreductase activities and reduced organic anion-transporting polypeptides 1a1 expression in liver after acetaminophen treatment. Our results indicate that EGCG may lower oxidative stress and reduce the metabolism and toxicity of acetaminophen. The reductions in CYP-mediated acetaminophen bioactivation and uptake transporter, as well as enhanced antioxidant enzyme activity, may limit the accumulation of toxic products in liver and thus lower hepatotoxicity