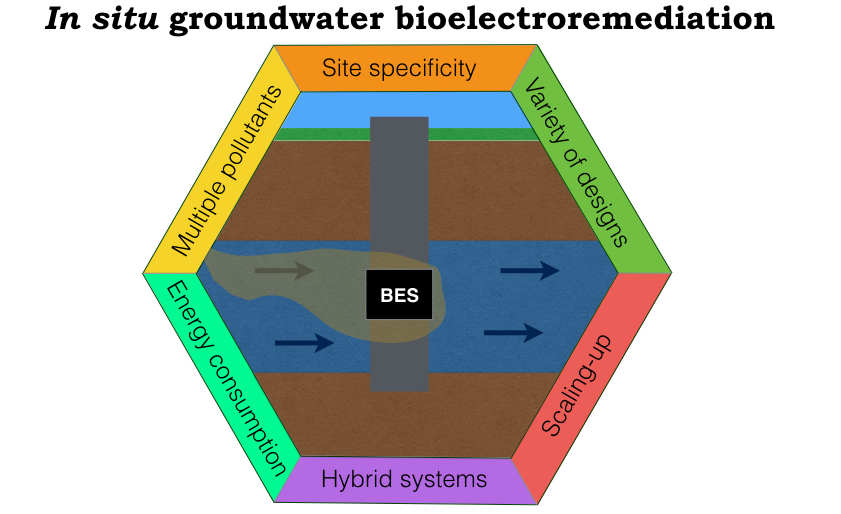
Groundwater contamination is an ever-growing environmental issue that has attracted much and undiminished attention for the past half century. Groundwater contamination may originate from both anthropogenic (e.g., hydrocarbons) and natural compounds (e.g., nitrate and arsenic); to tackle the removal of these contaminants, different technologies have been developed and implemented. Recently, bioelectrochemical systems (BES) have emerged as a potential treatment for groundwater contamination, with reported in situ applications that showed promising results. Nitrate and hydrocarbons (toluene, phenanthrene, benzene, BTEX and light PAHs) have been successfully removed, due to the interaction of microbial metabolism with poised electrodes, in addition to physical migration due to the electric field generated in a BES. The selection of proper BESs relies on several factors and problems, such as the complexity of groundwater and subsoil environment, scale-up issues, and energy requirements that need to be accounted for. Modeling efforts could help predict case scenarios and select a proper design and approach, while BES-based biosensing could help monitoring remediation processes. In this review, we critically analyze in situ BES applications for groundwater remediation, focusing in particular on different proposed setups, and we identify and discuss the existing research gaps in the field.