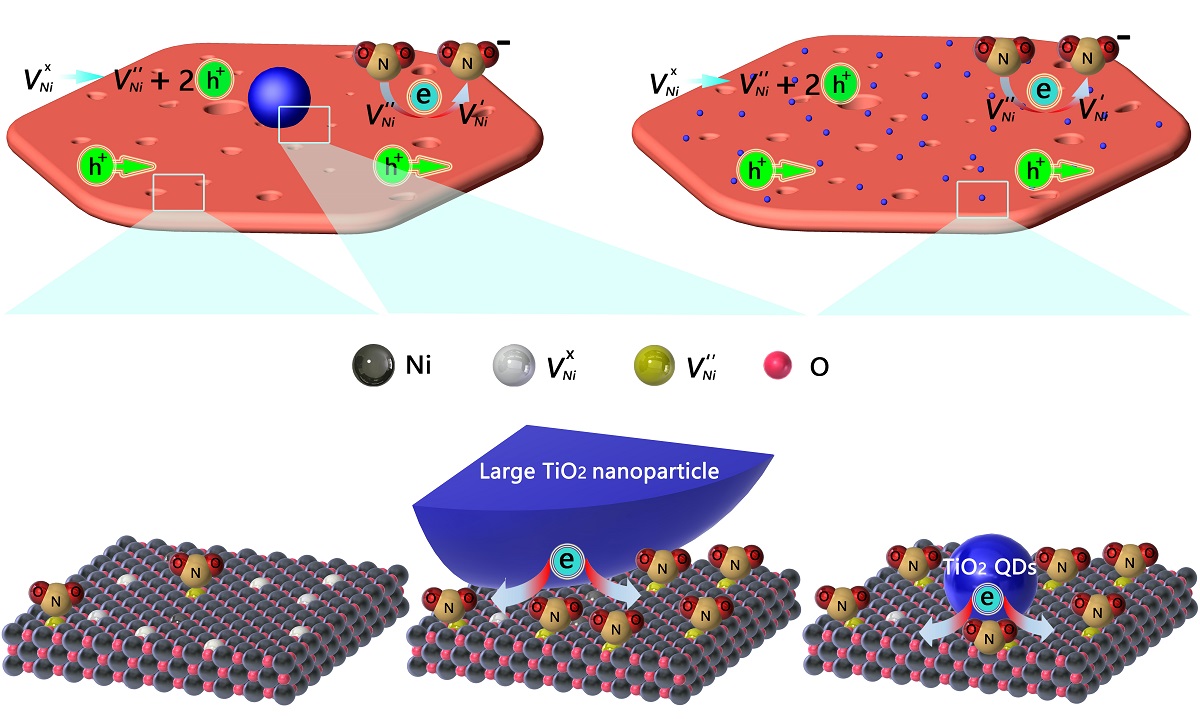
In this work, TiO2 QDs modifed NiO nanosheets was employed to imporve the room-temperature NO2 sensing properties of NiO. The gas-sensing studies showed that the response of nanocomposites with the optimal ratio to 60 ppm NO2 was nearly 10 times larger than that of bare NiO, exhibiting potential application in gas-sensing. Considering the commonly reported immature mechanism that the effective charge transfer between two phases contribute to enhanced sensitivity, QDs sensitization mechanism was further detailed by designing a seirs of contrast experiments. First, the important role of QDs size effect was revealed by comparing a little enhanced sensitivity of TiO2 particle-modified NiO with largely enhanced senstivity of TiO2 QDs-NiO. Second, and more important, the direct evidence of heterointerface charge transfer efficiency was detailed by extracted interface bond (Ti-O-Ni) using XPS peak fitting. We hope this work can provide guideline to design more QDs-modified nanocomposites with the higher sensitivty for practical application.