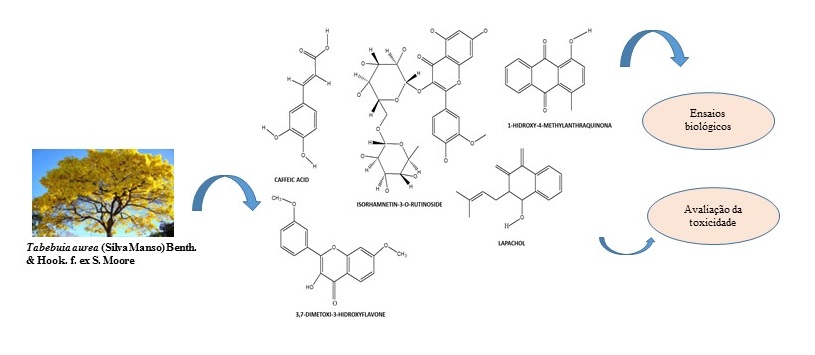
Tabebuia aurea (Silva Manso) Benth. & Hook. f. The ex S.Moore (yellow ipe), belonging to the Bignoniaceae family, used in the popular for fever, inflammation and healing of skin wounds. The extract was prepared by maceration, using 70% ethanol. Through HPLC analysis, it was possible to identify substances, mainly phenolic, such as lapachol, present in Bignoniaceae. The phenolic content was 21.36 mg / Eag in the antioxidant activity, the effective concentration of 50% was 53.03 ± 1.14 µg / mL. The antimicrobial activity against S.aureus, E. coli and C. albicans was evaluated by microdilution in broth, which verified action against the tested microorganisms. Cell viability has been inhibited for tumor cells, although this has not been observed for normal cells. The LD50 against A.aegypti mosquito larvae was 3504.6 mg / L and there was no mortality in the concentration tested for the snail B.glabrata. Nontoxic or low toxicity for A. salina and T. molitor, respectively, and did not exhibit hemolytic action at concentrations of antibacterial effect. Given the above, it was concluded that the bark extract of the studied species has bioprospecting potential for the future development of antimicrobial products.