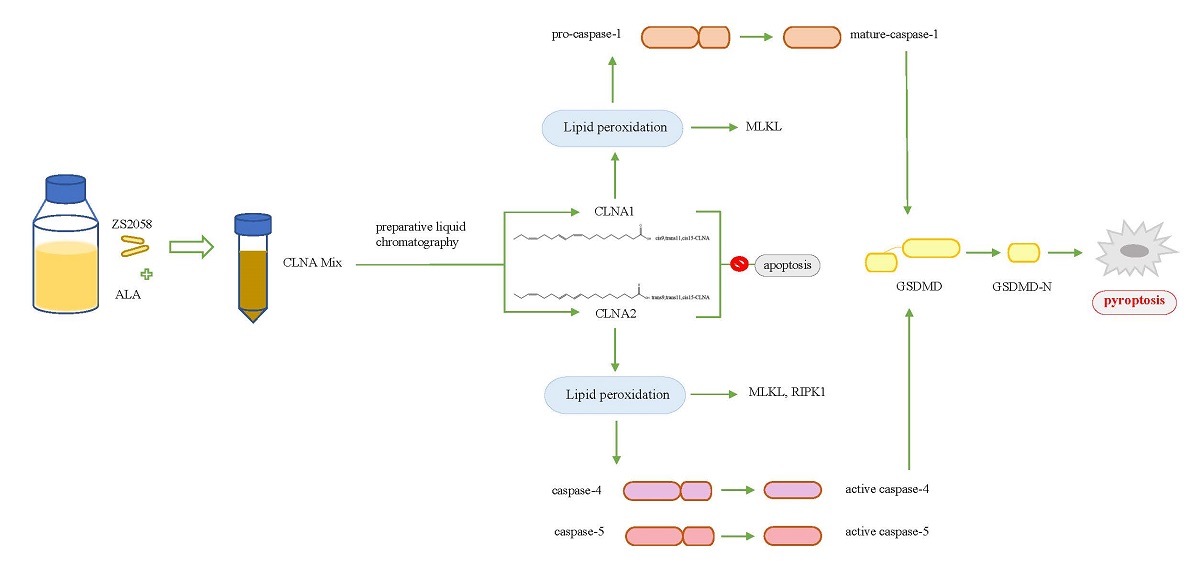
The probiotic bacterial strain Lactobacillus plantarum ZS2058 has been proved to manifest comprehensive functions, which were due to ability to synthesise conjugated fatty acids (CFAs). To investigate the specific functions of CFAs produced by this probiotic bacterium, α-linolenic acid was isomerized by Lactobacillus plantarum strain ZS2058, and two different conjugated α-linolenic acid (CLNA) isomers were successfully isolated. These isoforms, CLNA1 (c9, t11, c15-CLNA, purity 97.48%) and CLNA2 (c9, t11, t15-CLNA, purity 99.00%), both showed the ability to inhibit the growth of three types of colon cancer cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. In addition, the expression of MDA in Caco-2 cells was increased by CLNA1 or CLNA2, which indicated lipid peroxidation was related to the antiproliferation activity of CLNAs. Examination of the key protein of pyroptosis showed that CLNA1 induced the cleavage of caspase-1 and gasdermin-D, while CLNA2 induced the cleavage of caspase-4, 5 and gasdermin-D. The addition of relative inhibitors could alleviate the pyroptosis by CLNAs. CLNA1 and CLNA2 showed no effect on caspase-3, 7, 9 and PARP-1, which were key proteins associated with apoptosis. And no sub-diploid apoptotic peak appeared in the result of PI single staining test. In conclusion, CLNA1 activated caspase-1 and induced Caco-2 cell pyroptosis, whereas CLNA2 induced pyroptosis through the caspase-4/5-mediated pathway. The inhibition of Caco-2 cells by the two isomers was not related to apoptosis. This is the first report showing the ability of CLNAs to activate antioxidant defenses resulting in pyroptosis.