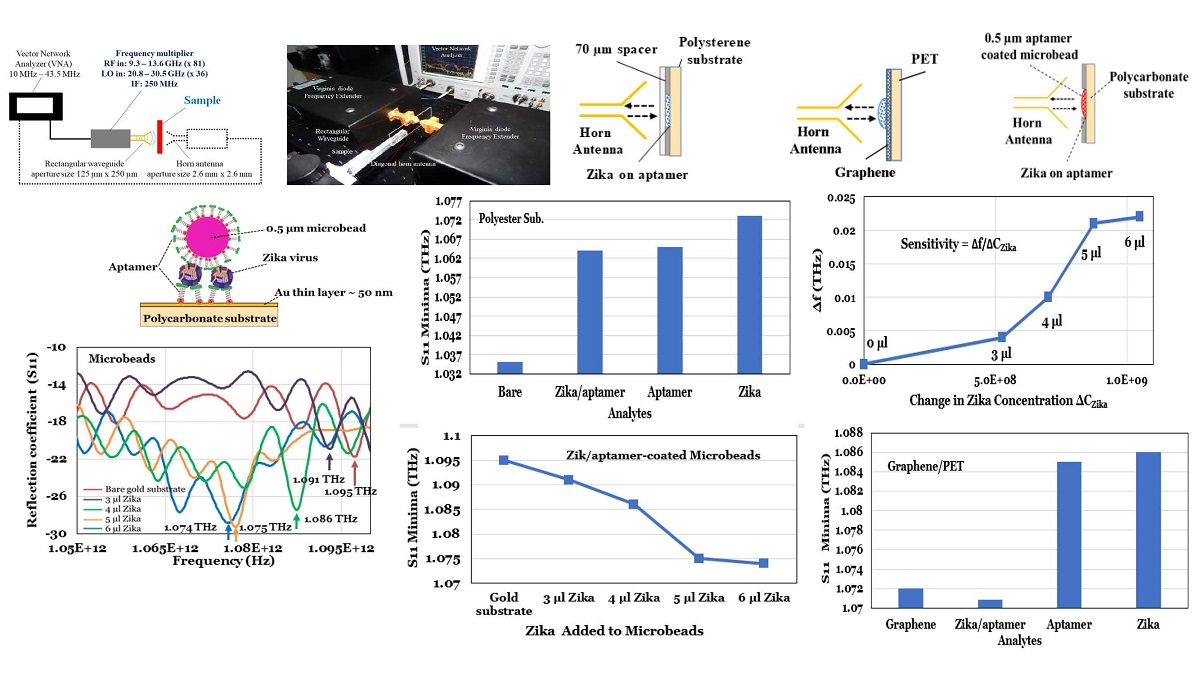
Our main objective in this work was to examine the possibility of non-intrusive, label-free, detection of whole Zika viruses using terahertz signals with or without a targeting/binding oligonucleotide (aptamers). We report for the first time the use of terahertz electromagnetic waves (0.75 THz – 1.1 THz) to detect Zika viruses. The Zika/aptamer complexes showed a reproducible terahertz reflection coefficient minimum at 1.064 THz while the Zika virus’s reflection minimum was at 1.073 THz. Of different substrates we examined, the polyester petri dish provided a very low loss and excellent terahertz transmission. To increase the interaction between the terahertz signal and the sample we also used polyester microbeads coated with aptamers. We then measured the terahertz reflection from the microbeads as a function of Zika concentration. The resulting terahertz Zika sensor had sensitivity of 63 Hz/Zika and minimum detectable signal of ~ 16x103 Zika. Other substrates such as Graphene on polyethylene terephthalate (PET), 50 nm-thick gold film on polycarbonate, thin (30 um-thick) glass slide and Teflon were also examined. Graphene substrate enabled direct detection of the Zika without any aptamers.