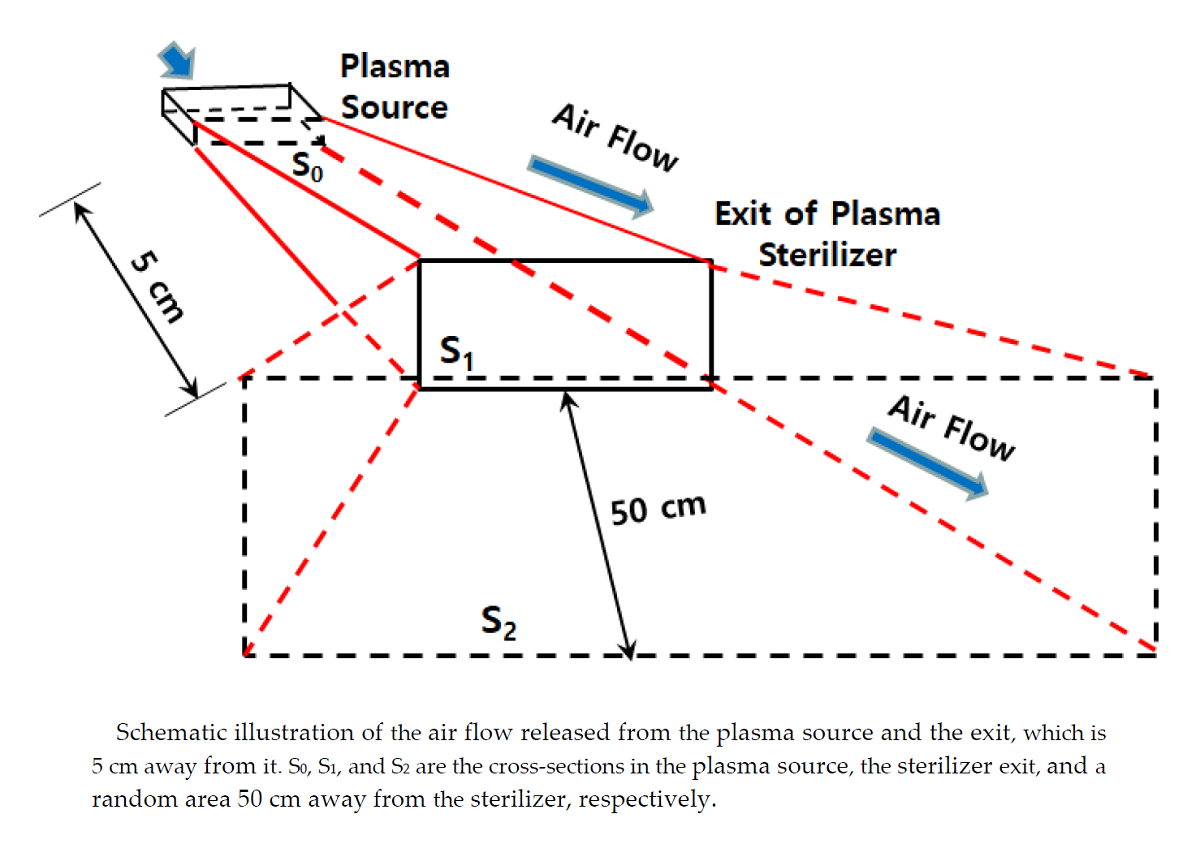
Medical institutions, where several patients are treated and medical workers engaged, are always exposed to secondary viral and bacterial infections. It is critical to prevent infection transmission by indirect as well as direct contact through air or splash. The infections of most diseases can be transmitted through the air. HEPA filters installed in air conditioning equipment are used to prevent infection transmission through air in medical institutions, but air circulation takes a long time in a large space. Virus and bacteria smaller than 0.3 μm cannot be removed by the HEPA filter; hence, those microbes remain alive throughout the air ventilation. A plasma sterilizer has the capability to provide environmental friendly sterilization by employing reactive oxide species and reactive nitrogen species at a low cost. We developed an excellent plasma sterilizer by using a non-thermal atmospheric-pressure biocompatible plasma (NBP). Ozone concentration in plasma sources has been derived by Kuhn et al. [1]. The diffusion coefficients inside (D0) and outside (D1) the plasma sterilizer have been calculated to be 0.0641 m2 s-1 and 0.717 m2 s-1, respectively. To sustain high O3 concentrations over 121 ppm inside the plasma source and low O3 concentrations below 0.05 ppm outside the sterilizer, it is necessary to keep O3 concentrations at the exit of plasma sterilizer below 0.28 ppm. so that diffusion coefficient D1 has been designed to be as large as 11 times of D0.