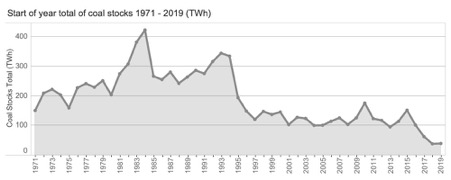
Great Britain’s stocks of coal, natural gas, and petroleum have seen major changes to the levels of stored energy over the years 2005 to 2019, a reduction of 200 TWh (35%) from 570 TWh to 370 TWh. The transformation of its electrical system over this timeframe saw a reduction in coal generation, leading to a corresponding reduction of the levels of stockpiled coal of 85 TWh (68%), partially offset by an increase in the stocks of biomass for electrical generation. The reduction in natural gas storage of 24 TWh (44%) was primarily due to the closure of Britain’s only long-term seasonal natural gas storage facility in January 2018. This was partially offset by the construction of medium-term natural gas storage facilities and the use of LNG storage in the years preceding its closure. For stocks of crude oil and oil products the reduction was 35 TWh (21%), linked to the overall reduction in demand.