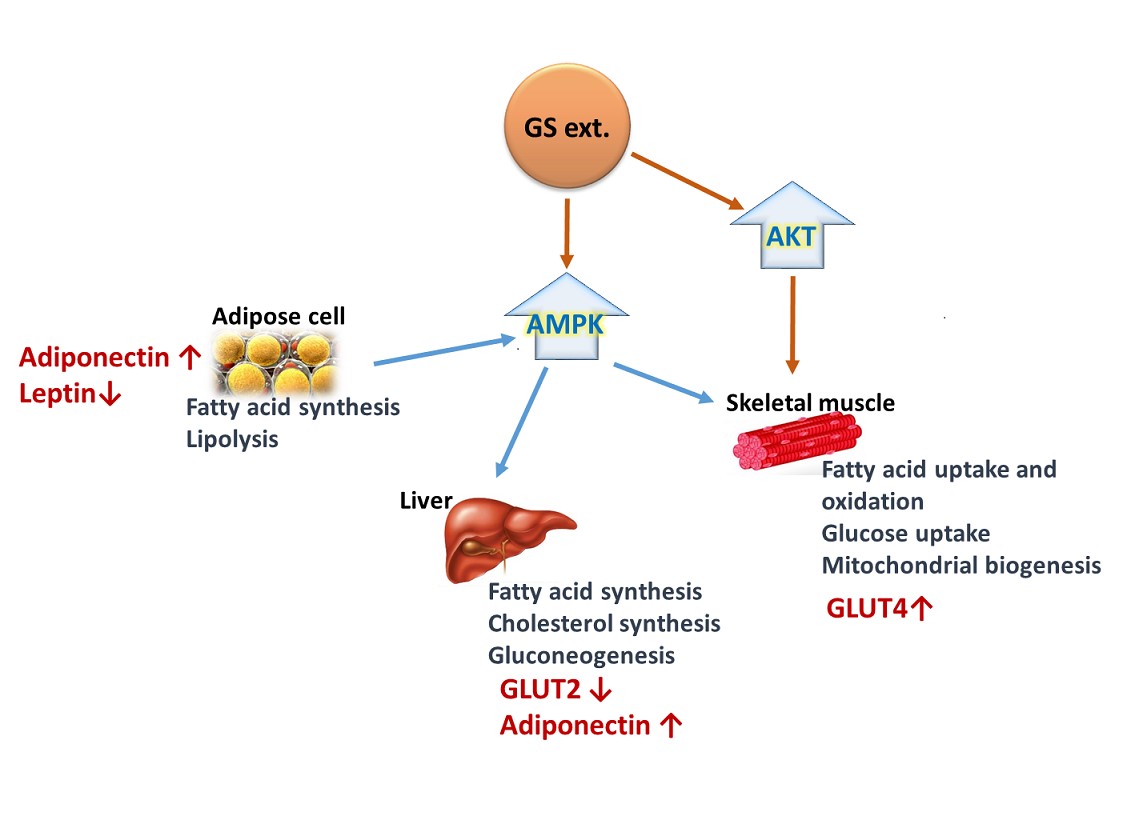
Anti-diabetic effects of Glycine soja seed extract (GS) on Type 2 diabetes mellitus mouse model and human hepatocytes induced insulin resistance were investigated. 3 weeks old db/db mice were divided into 5 groups (n = 6) including two control groups and 3 GS treated groups with different doses. Oral administration of GS for 6 weeks to diabetic db/db mice reduced blood glucose level significantly in a dose dependent manner by 44.7% (300 mg/kg/day), 30.9% (150 mg/kg/day) and 21.1% (75 mg/kg/day). GS treatment also lowered significantly plasma level of HbA1c, insulin, IGF-1 and leptin, and increased that of adiponectin. GS treatment activated AMPK, and down-regulated GLUT2 in liver tissues of mice while up-regulated GLUT4 in muscle tissues of mice. In in vitro study with insulin resistance induced human hepatocyte, GS treatment increased glucose uptake and increased the activities of Akt and PPAR-γ in response to insulin. Treatment of GS appears to reduce blood glucose level by regulating energy metabolism positively through various metabolic pathways and reducing insulin resistance in Type 2 diabetes mellitus.