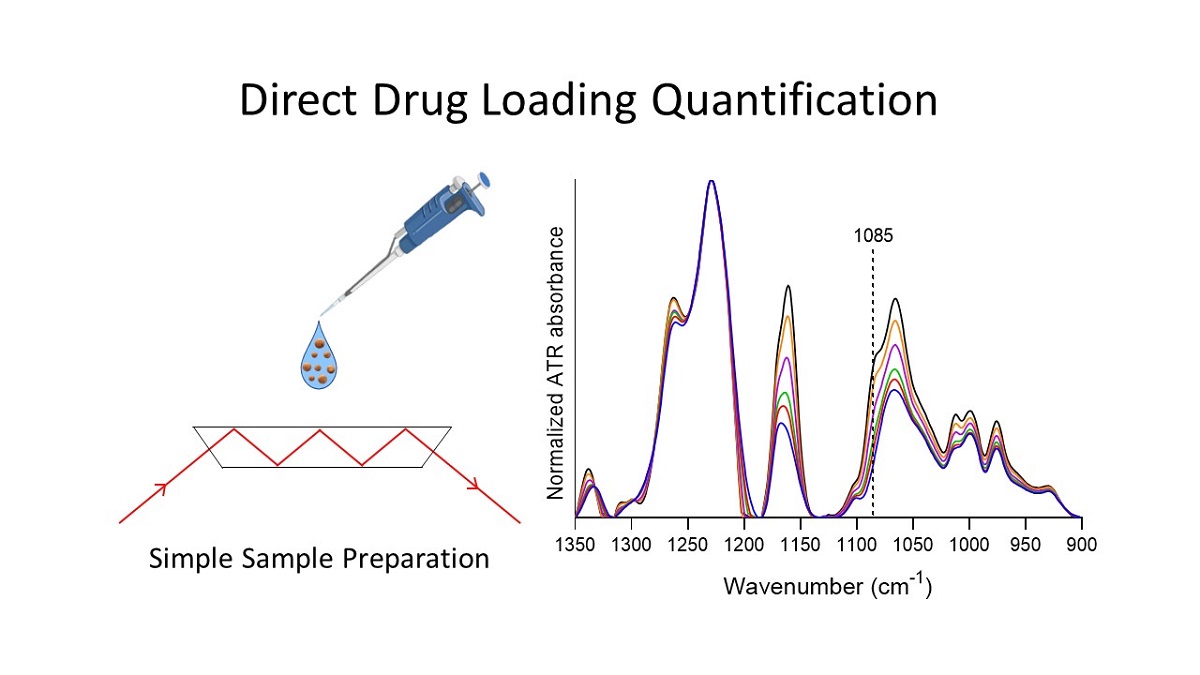
Nanotechnology has enabled the development of novel therapeutic strategies such as targeted nanodrug delivery systems, control and stimulus-responsive release mechanisms, and the production of theranostic agents. As a prerequisite for the use of nanoparticles as drug delivery systems, the amount of loaded drug must be precisely quantified, a task for which two approaches are currently used. However, both approaches suffer from the inefficiencies of drug extraction and of the solid-liquid separation process, as well as from dilution errors. This work describes a new, reliable, and simple method for direct drug quantification in polymeric nanoparticles using attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, which can be adapted for a wide variety of drug delivery systems. Silk fibroin nanoparticles and naringenin were used as model polymeric nanoparticle carrier and drug, respectively. The specificity, linearity, detection limit, precision and accuracy of the spectroscopic approach were determined in order to validate the method. A good linear relation was observed within 0.00 to 7.89 % of naringenin relative mass with an R2 of 0.973. The accuracy was determined by the spike and recovery method. Results showed an average 104% recovery. The limit of detection and limit of quantification of the drug loading content were determined to be 0.3 and 1.0 %, respectively. The method's robustness is demonstrated by the notable similarities between the calibrations carried out in two different equipment and institutions.