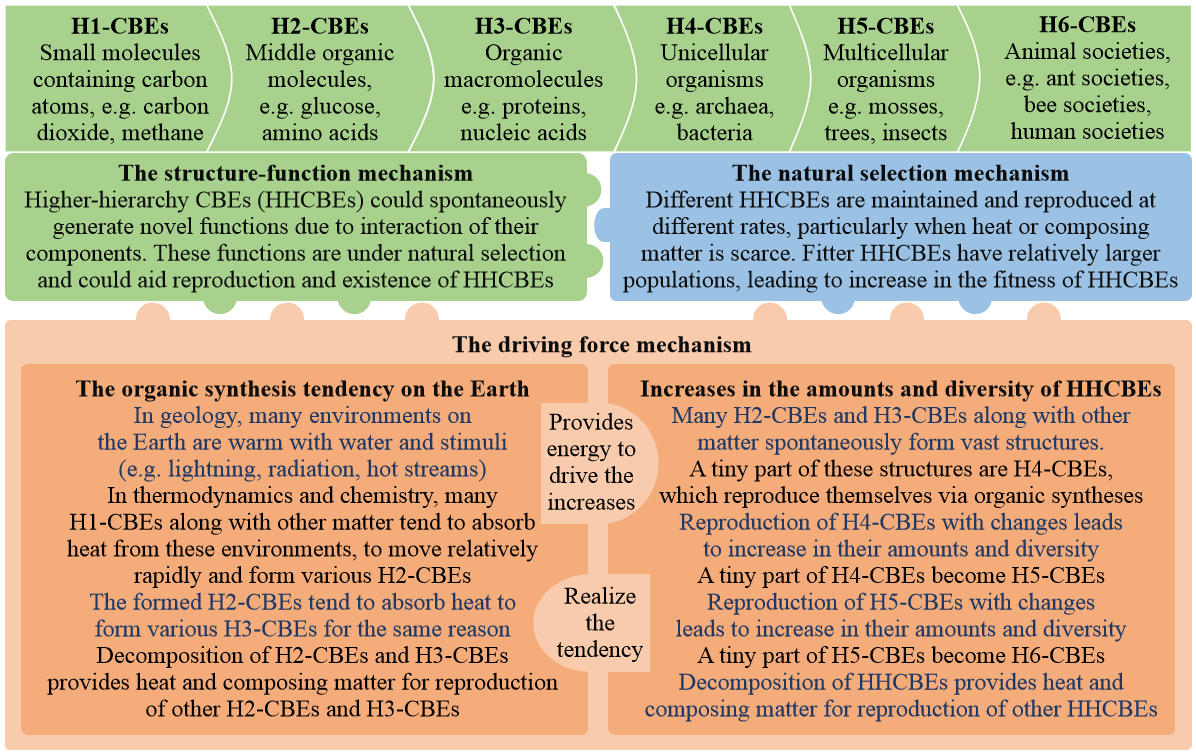
To establish a comprehensive and comprehensible evolutionary theory, and to use this theory to bridge physics, biology, and social sciences, we employ the concept carbon-based entities (CBEs), which include methane, glucose, proteins, organisms, and other entities chemically containing carbon atoms. We deduce the steps, driving forces, and mechanisms of evolution of CBEs through integration of geology, physics, chemistry, and biology. We hence establish the Carbon-Based Evolutionary Theory (CBET), which suggests that evolution is the increase in the amount, diversity, and fitness of higher-hierarchy CBEs under natural selection and driven by the organic synthesis tendency on the Earth from the thermodynamic features of the Earth. It provides better explanations for various evolutionary issues and social issues (e.g. life origin, natural selection, neutral mutation, diversity importance, and altruism) than previous theories. It refutes some incorrect views (e.g. negative entropy) in thermodynamics on evolution. The CBET could have great significance in various sciences.