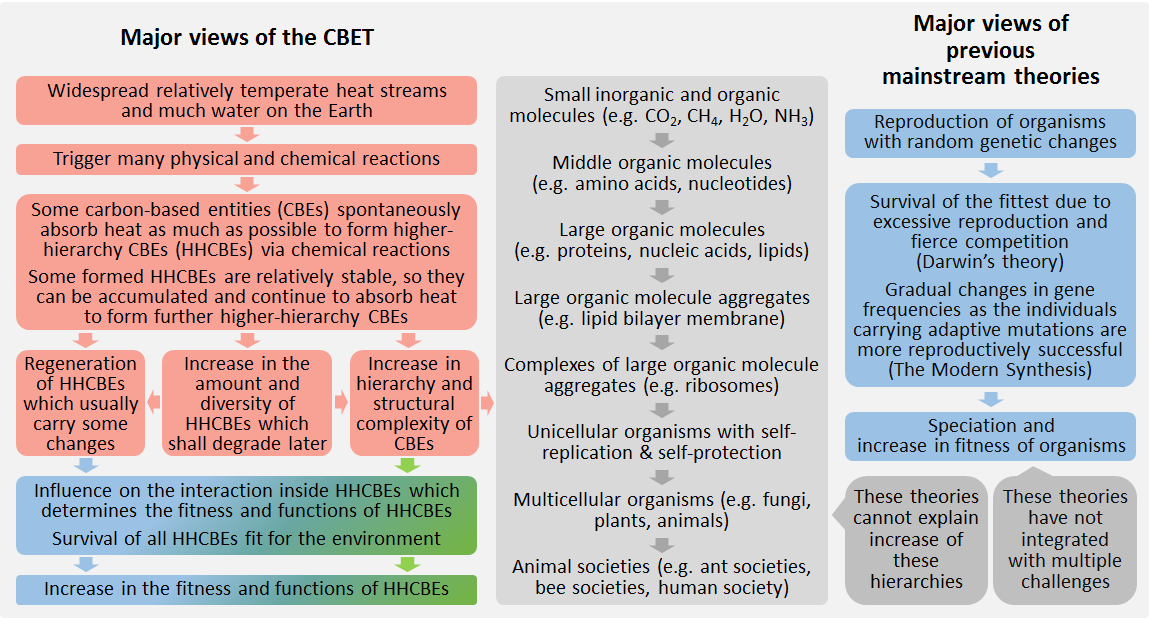
It is desirable to upgrade previous evolutionary theories, which have remained incomplete and controversial for decades. Here we employ the concept of carbon-based entities (CBEs), which include methane, amino acids, proteins, organisms, and other entities containing relatively many carbon atoms. We deduce the driving force, mechanisms, steps, modes, tempos of CBE evolution, through integration of biology, physics, and chemistry using logics for complex issues. We hence establish the Carbon-Based Evolutionary Theory (CBET). The CBET suggests that evolution is the increase in hierarchy, diversity, fitness of CBEs under natural selection and driven by thermodynamics due to the chemical effect of the thermodynamic features of the Earth on CBEs. It provides better explanations for life origin, macroevolution events, natural selection, sympatric speciation, and evolution tempos than previous evolutionary theories. It reveals the evolutionary basis of multiple important social notions, including diversity, collaboration, altruism, obeying rules, and proper increase in freedom. It refutes some wrong notions in thermodynamics, including negative entropy (negentropy) and that biological order is equal to thermodynamic order, which have misled many people. The CBET is supported by its deduction and application. It could be a rare bridge linking laws of thermodynamics, evolution of life, and development of human society, and could have great significance in various sciences.