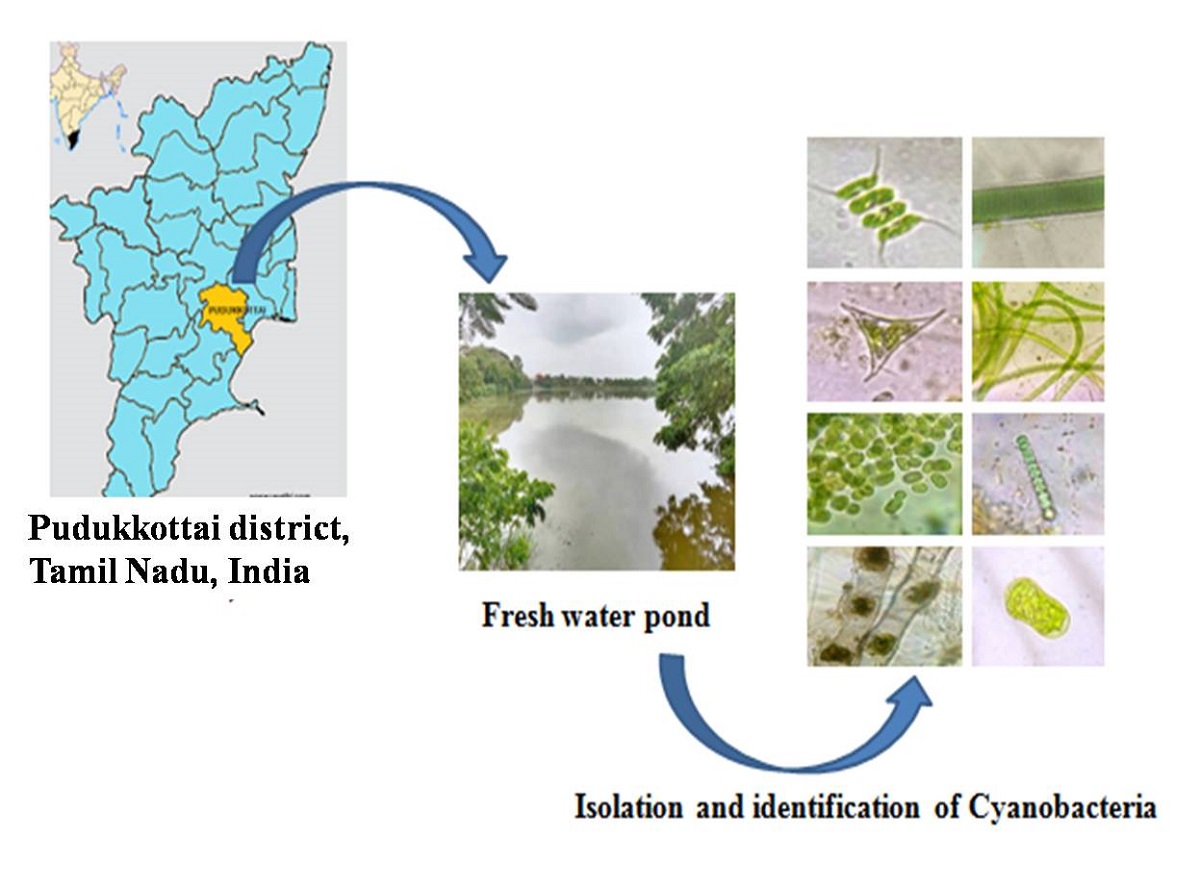
Cyanobacterial species (blue-green algae) constitute the major part of the phytoplanktonic biomass during the summer in freshwater ponds. The aim of the research work was to study the biodiversity of cyanobacteria among 20 different freshwater ponds of the Pudukkottai district of Tamil Nadu, India. The morphological identification of cyanobacterial species was carried out using a trinocular microscope. The results showed that the maximum number of cyanobacterial species belonged to Oscillatoriaceae, Nostocaceae, Microcystaceae, Scenedesmaceae, and Desmidiaceae families. Among 25 different families of Cyanobacteria about 42 distinct species were identified. These results showed that the freshwater ponds of the Pudukkottai district have an abundance of cyanobacteria species.