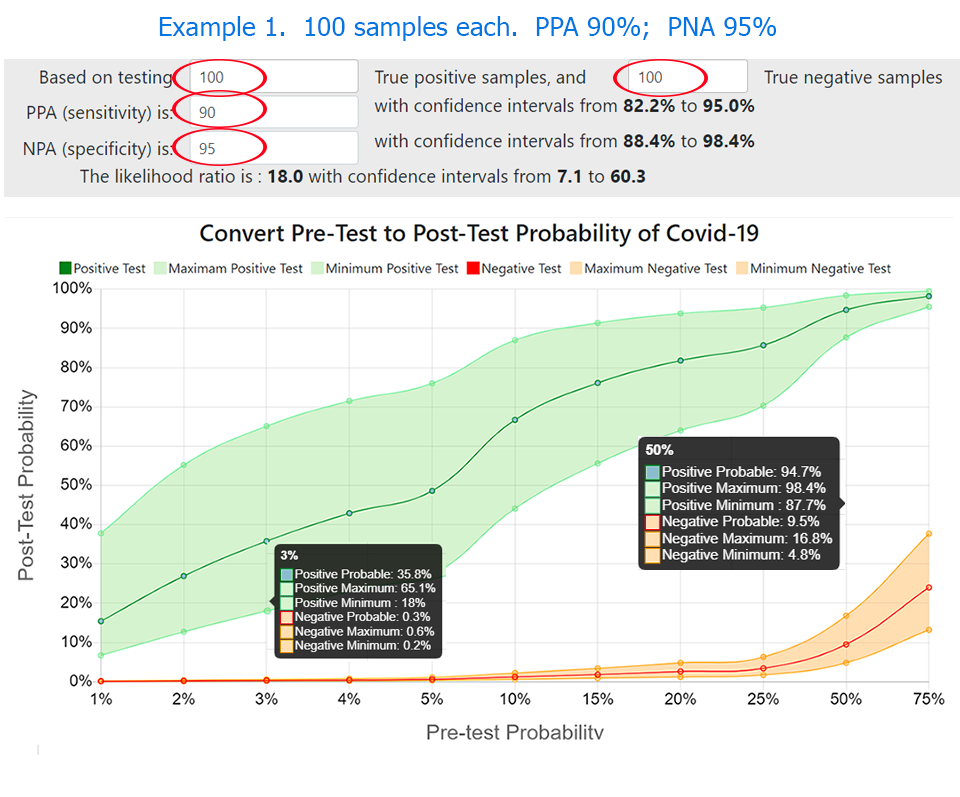
During coronavirus pandemic testing and identifying the virus has been a unique and constant challenge for the scientific community. In this paper, we discuss a practical solution to help guide clinicians and public health staff with the interpretation of the probability that a positive, or negative, COVID-19 test result indicates an infected person, based on their clinical estimate of pre-test probability of infection. The LinkedIn survey confirmed that the pre-test probability of COVID-19 increases with patient age, known contact, and severity of symptoms, as well as prevalence of disease in the local population. PPA (Positive Percent Agreement, PPA) and NPA (Negative Percent Agreement, specificity), differ between individual methods. Results vary between laboratories and the manufacturer for the same method. The confidence intervals of results vary with the number of samples tested, often adding a large range of possibilities to the reported test result. The online calculator met the objective.The authors postulated that the clinical pre-test probability of COVID-19 increases relative to local prevalence of disease plus patient age, known contact, and severity of symptoms. We conducted a small survey on LinkedIn to confirm that hypothesis. We examined results of PPA (Positive Percent Agreement, sensitivity) and NPA (Negative Percent Agreement, specificity) from 73 individual laboratory experiments for molecular tests for SARS-CoV-2as reported to the FIND database,(1) and for selected methods in FDA EUA submissions (2,3). We calculated likelihood ratios to convert pre-test to post-test probability of disease, then further calculated the number of true and false results expected in every ten positive or negative test results, plus an estimate that one in ‘x’ test results is true. We designed an online calculator to create graphics and text to fulfill the objective. A positive or negative test result from one laboratory conveys a higher probability for the presence or absence of COVID-19 than the same result from another laboratory, depending on clinical pre-test probability of disease plus proven method PPA and NPA in each laboratory. Likelihood ratios and confidence intervals provide valuable information but are seldom used in clinical settings. We recommend that testing laboratories verify PPA and NPA, and utilize a tool such as the “Clinician’s Probability Calculator” to verify acceptable test performance and create reports to help guide clinicians and public health staff with estimation of post-test probability of COVID-19 .