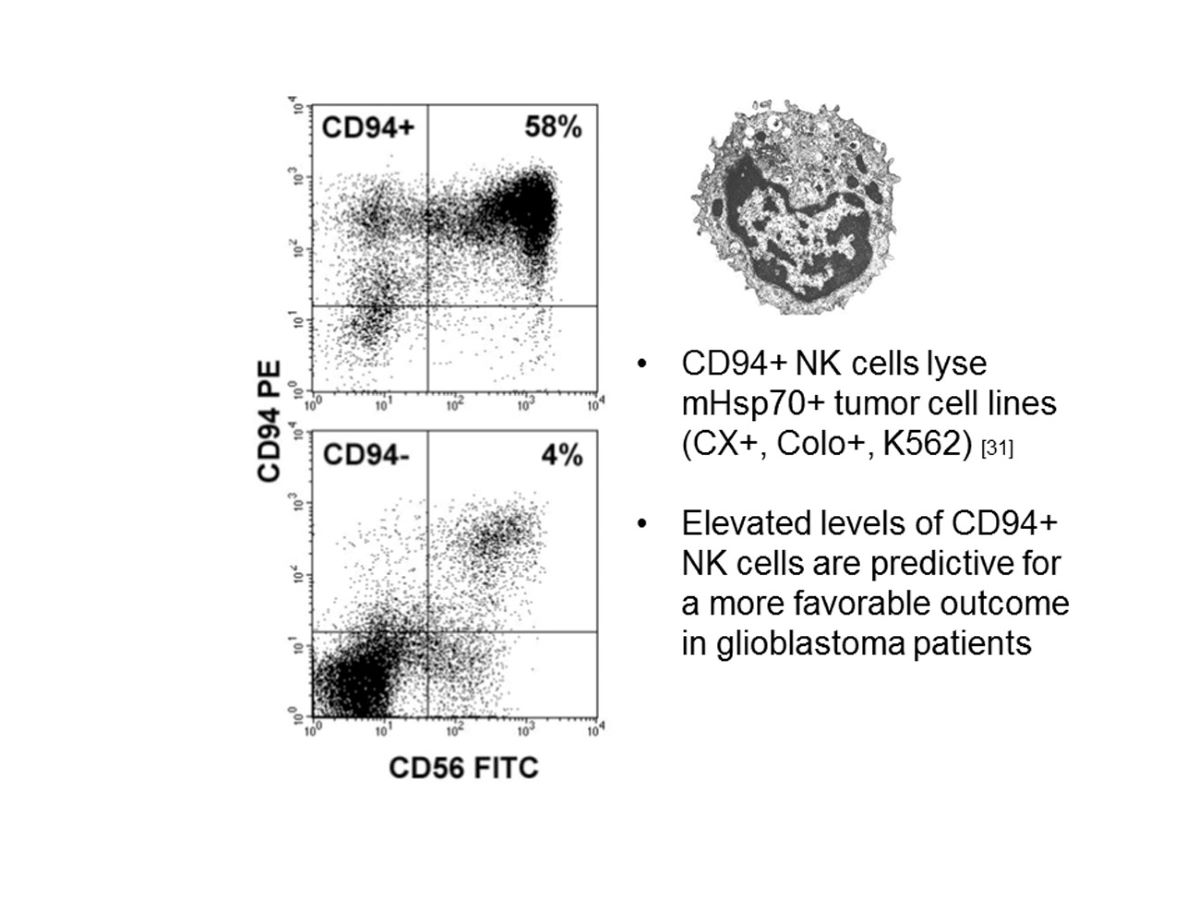
Despite rapid progress in the treatment of many cancers, glioblastoma remains a devastating disease with dismal prognosis. The aim of this study was to identify immune-related biomarkers that more effectively predict outcome of glioblastoma. Since heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) and IL-2 are known to increase the expression of activatory NK cell receptors, recognizing aggressive human tumor cells that present Hsp70 on their cell surface, extracellular Hsp70 levels were determined in glioma patients together with activatory NK cell receptors. All gliomas are membrane Hsp70-positive (mHsp70+) and high grade gliomas more frequently show an overexpression of Hsp70 in the nucleus and cytosol. Significantly increased extracellular Hsp70 levels are detected predominantly in glioblastomas with large necrotic areas. Overall survival (OS) is more favorable in patients with low Hsp70 serum levels indicating that a high Hsp70 expression is associated with an unfavorable prognosis. Elevated frequencies of NK cells are associated with a more favorable outcome. Of caution, a glucocorticoid therapy reduces the prevalence of NK cells. In summary, elevated frequencies of Hsp70-reactive NK cells at diagnosis and lower Hsp70 levels predict a more favorable prognosis in glioblastoma patients.