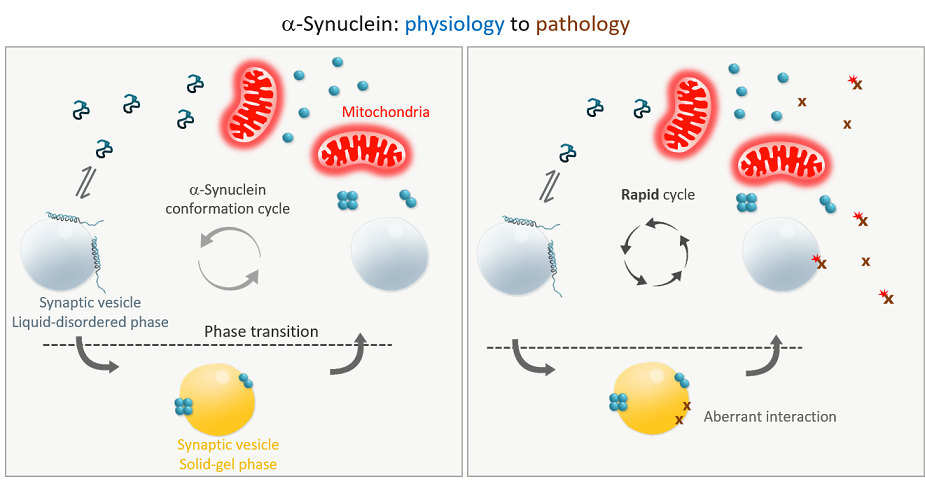
I wish to suggest a physiological function for alpha-synuclein (a-syn) that has the potential to explain its role in pathology. Intraneuronal proteinaceous Lewy Bodies (LBs), the pathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies, consist majorly of a-syn. Ample evidence suggests that LBs are not the result of simple amyloidosis of cytosolic a-syn. Benign soluble unstructured a-syn gets converted into toxic species which preferentially accumulates in LBs. But how these aberrant a-syn molecules are produced in the cytosol, is still not clear. The present hypothesis is an effort to relate a metabolic reaction specific to neuronal function, that is, phase transition, with the pathobiology of a-syn. During high frequency stimulation, which entails rapid phase transition reactions at the presynaptic compartment, aberrant interaction of a-syn with the membrane occasionally generates toxic a-syn molecules. My conjecture is that the physiological function of a-syn is to modulate membrane fluidity by a process wherein it goes through a conformation cycle driven by a flux of energy from mitochondria. It is the range of toxic a-syn produced during aberrant phase transition reaction that is responsible for pathology, not the normal a-syn that reenters the conformation cycle, thereby, resolving the paradox of the Janus-face of a-syn.