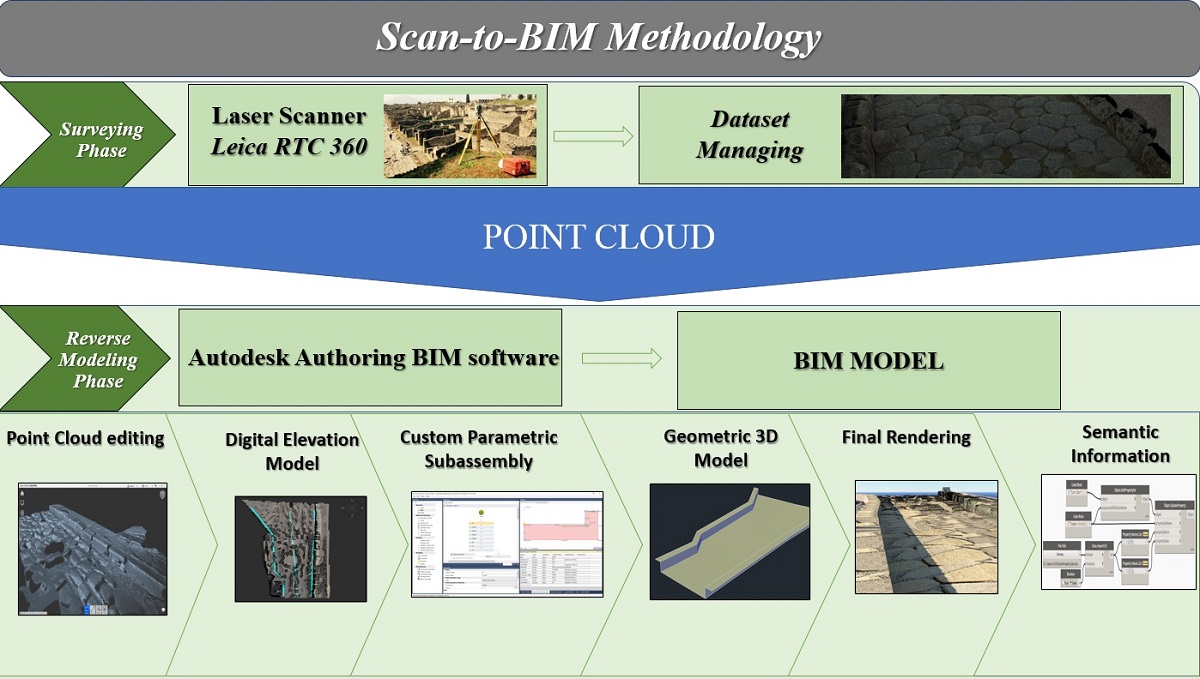
The transition from Building Information Modelling (BIM) to Heritage Building Information Modelling (H-BIM) is intended to pursue an adequate knowledge of the artefact that is to be preserved, progressively replacing the traditional methods of the restoration and structural reinforcement projects with new tools for managing both existing information and new interventions. The aim of the paper is to show the application of the H-BIM method to a stone pavement road located in the Archaeological Site of Pompeii. In detail, starting from a Laser Scanner based survey, juxtaposed by coordinated points georeferenced through a total station, points clouds were handled by means of several BIM-based tools to perform the road design process, starting from the digital elevation model (DEM) to the corridor representation. Subsequently, a visual programming application based on Python language was adopted to update corridor information by means of the object property set. As preliminary results, a tool, complete with graphical and non-graphical information, is proposed to be used in conservation, maintenance and restoration project.