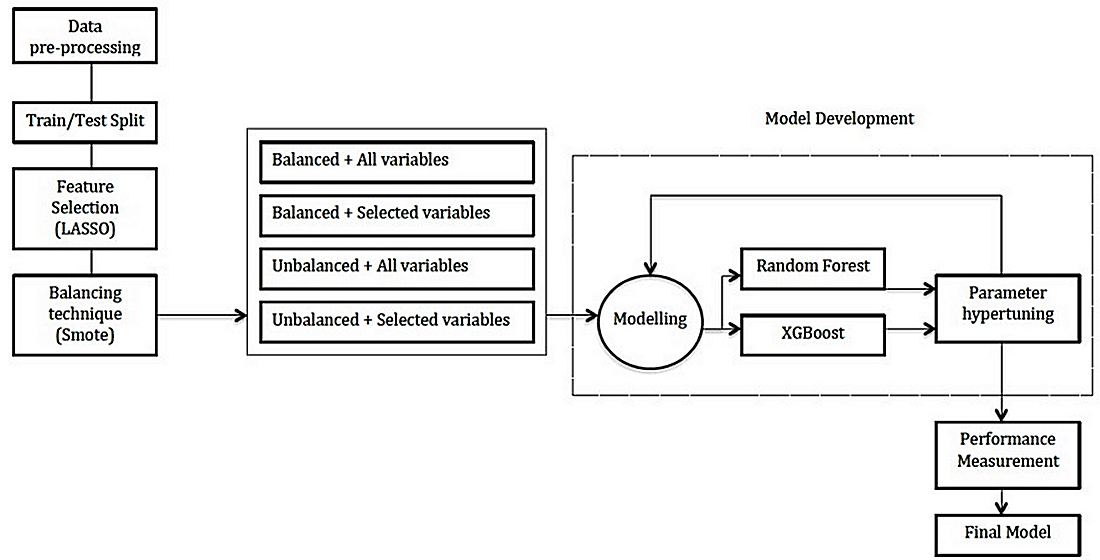
Artificial Intelligence are creating a paradigm shift in health care, being phenotyping patients through clustering techniques one of the areas of interest. Objective: To develop a predictive model to classify heart failure (HF) patients according to their left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), by using available data in Electronic Health Records (EHR). Subjects and methods: 2854 subjects more than 25 years old with diagnose of HF and LVEF measured by echocardiography were selected to develop an algorithm to predict patients with reduced EF using supervised analysis. Performance of the algorithm developed were tested in heart failure patients from Primary Care. To select the most influencing variables, LASSO algorithm setting was used and to tackle the issue of one class exceed the other one by a large proportion we used the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE). Finally, Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost models were constructed. Results: Full XGBoost model obtained the maximized accuracy, a high negative predictive value and the highest positive predictive value. Gender, age, unstable angina, atrial fibrillation and acute myocardial infarct are the variables that most influence FE value. Applied in the EHR data set with a total 25594 patients with an ICD-code of HF and no regular follow-up in Cardiology clinics, 6170 (21.1%) were identified as those pertaining to the reduced EF group. Conclusion: The algorithm obtained is able to rescue a number of HF patients with reduced ejection fraction that can be take benefit for a protocol with strong recommendation to succeed. Furthermore, the methodology can be used for studies with data extracted from the Electronic Health Records.