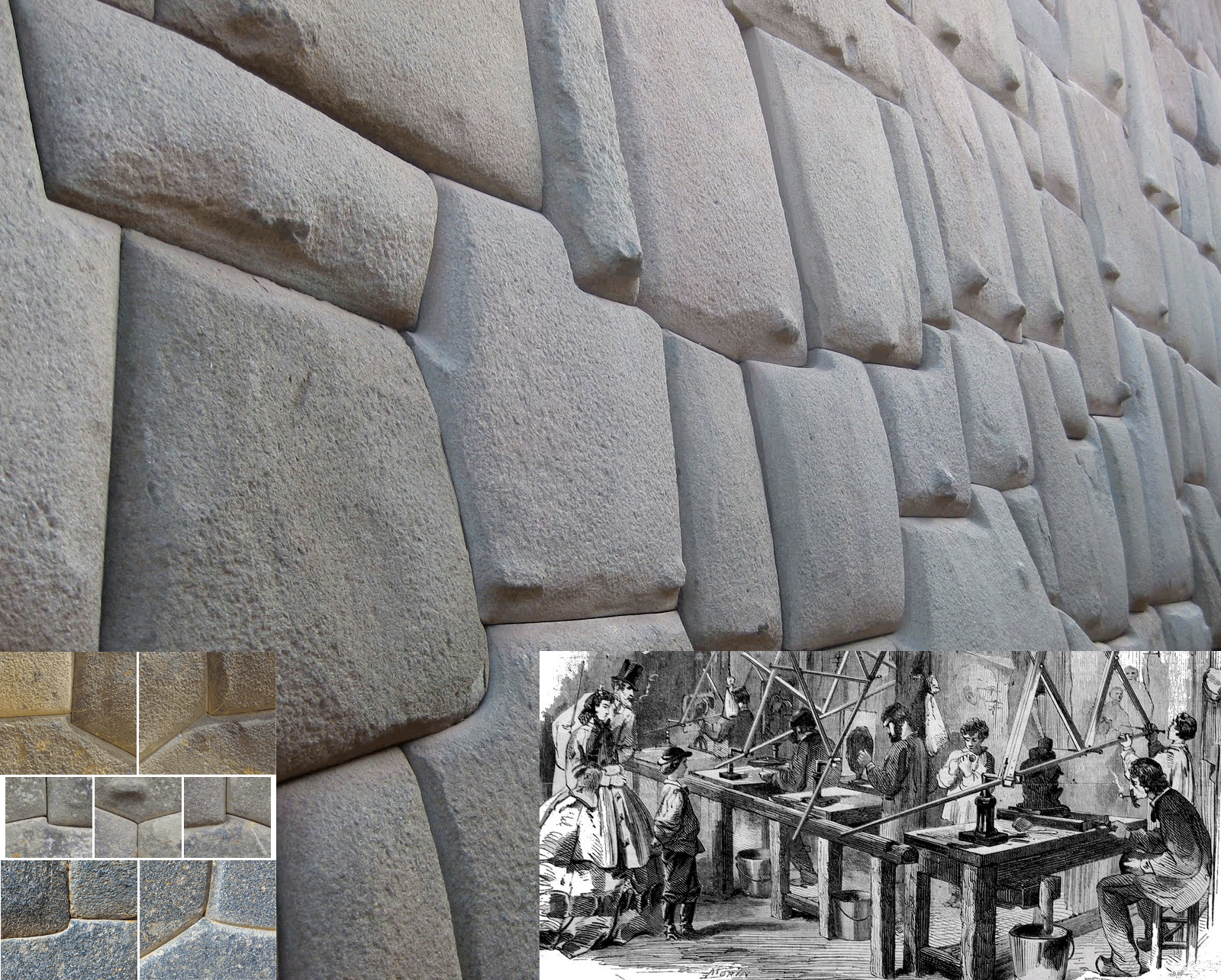
The article suggests methods that allow creating the most complicated type of polygonal masonry found in Peru. This masonry type consists of large stone blocks weighing from several hundred kilograms to several tons fitted close to each other almost without a gap between complicated curved surfaces over a large area. The work provides a description of techniques, which apparently were used by builders who arrived from Europe. The techniques under discussion are based on the use of a reduced clay model, 3D-pantograph, topography translator and replicas. The use of a reduced clay model and a pantograph provides not only the unique appearance and high quality of masonry with large blocks, but also allows to significantly increase the productivity of the builders. As machines coping-scaling three-dimensional objects are known since the beginning of the 18th century, the stone structures under consideration should be approximately dated by this time. The remaining simpler types of polygonal masonry with smaller stones or fitted surfaces are almost flat, or stones contact with each other by a small area, or there are significant gaps between stones, are quite consistent with the well-known methods of stone processing of those and earlier years, and, therefore, they do not require any additional explanations.