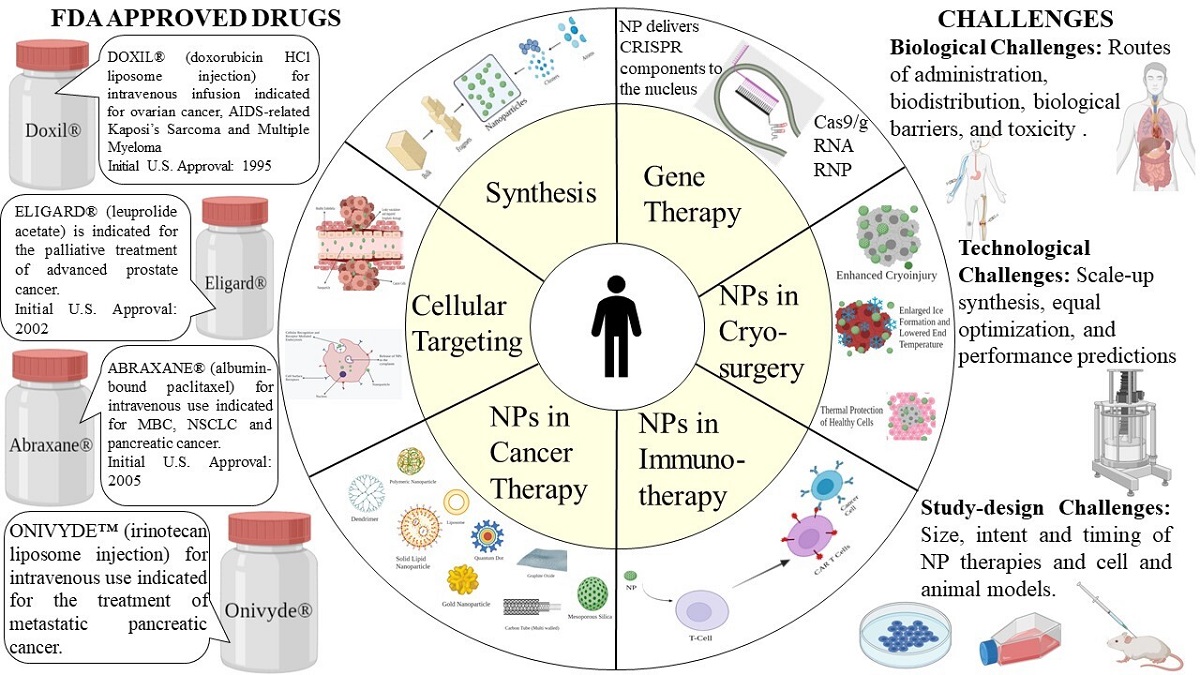
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death and morbidity with a complex pathophysiology. Traditional cancer therapies include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. However, limitations such as lack of specificity, cytotoxicity, and multi-drug resistance pose a substantial challenge for favorable cancer treatment. The advent of nanotechnology has revolutionized the arena of cancer diagnosis and treatment. Nanoparticles (1-100nm) can be used in the treatment of cancer owing to their specific advantages such as biocompatibility, reduced toxicity, more excellent stability, enhanced permeability and retention effect, and precise targeting. Nanoparticles are classified into several main categories. The nanoparticle drug delivery system is particular and utilizes tumor and tumor environment characteristics. Nanoparticles not only solve the limitations of conventional cancer treatment but also overcome multidrug resistance. Additionally, as new multidrug resistance mechanisms are unraveled and studied, nanoparticles are being investigated more vigorously. Various therapeutic implications of nano-formulations have created brand new perspectives for cancer treatment. However, a majority of the research is limited to in vivo and in vitro studies, and the number of nano-drugs that are approved has not much amplified over the years. In this review, we discuss numerous types of nanoparticles, targeting mechanisms along with approved nanotherapeutics for oncological implications in cancer treatment. Further, we also summarize the current perspective, advantages, and challenges in clinical translation.