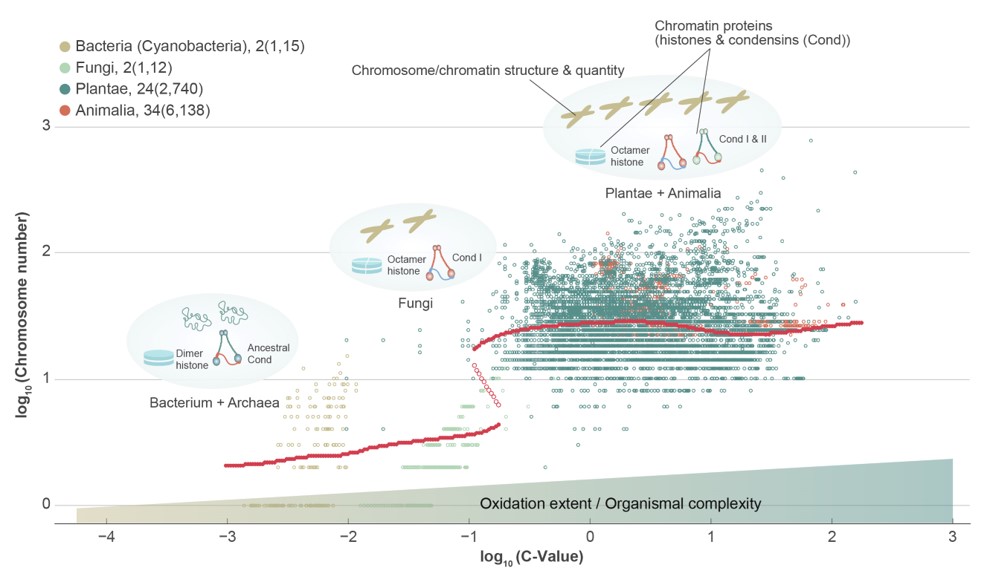
The origin of the nucleus remains a great mystery in life science, although nearly two centuries have passed since the discovery of nuclei. To date, studies of eukaryogenesis have focused largely on micro-evolutionary explanations. Here, we examined macro-patterns of C-values (the total amount of DNA within the haploid chromosome set of an organism) for over 110,000 species and the chromosome numbers for over 11,000 species and their potential links with the state of atmospheric oxidation over geological time. Eukaryogenesis was in sync with an over 2.5 order-of-magnitude increase in genome size from prokaryote to eukaryote, and also with a rapid rise of atmospheric oxidation, suggesting that eukaryogenesis would have resulted from a regime shift of genomes driven by the oxidation-driven complexification and structuralization (e.g. chromatin packing).