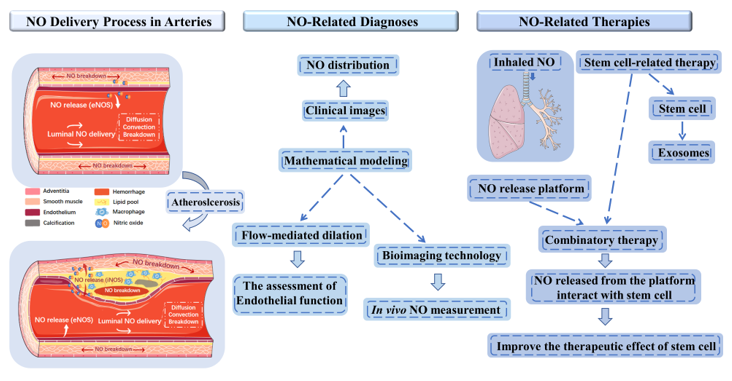
Nitric oxide (NO) is a key molecule in cardiovascular homeostasis and its abnormal delivery is highly associated with the occurrence and development of cardiovascular disease (CVD). The assessment and manipulation of NO delivery is crucial to the diagnosis and therapy of CVD, such as endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerotic progression, pulmonary hypertension, and cardiovascular manifestations of Coronavirus (COVID-19). However, due to the low concentration and fast reaction characteristics of NO in cardiovascular system, the clinical applications centered on the NO delivery are challenging. In this tutorial review, we first summarized the methods to estimate the in vivo NO delivery process based on the clinical images and mathematical modeling to assess the endothelial function and vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaque. Then, the emerging bioimaging technologies that have the potential to directly measure the arterial NO concentration were discussed, including the Raman spectroscopy and electrochemical sensor. Aside from the diagnostic methods, therapies aimed at controlling NO delivery to regulate CVD were reviewed, including the inhaled NO therapy to treat the pulmonary hypertension and COVID-19, stem cell therapy and NO-releasing platform to treat endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis.