You are currently viewing a beta version of our website. If you spot anything unusual, kindly let us know.
Preprint
Article
Mechanical Property Analysis of Cuttlebone-like Structure under Compression and Shearing
Altmetrics
Downloads
220
Views
208
Comments
0
Abstract
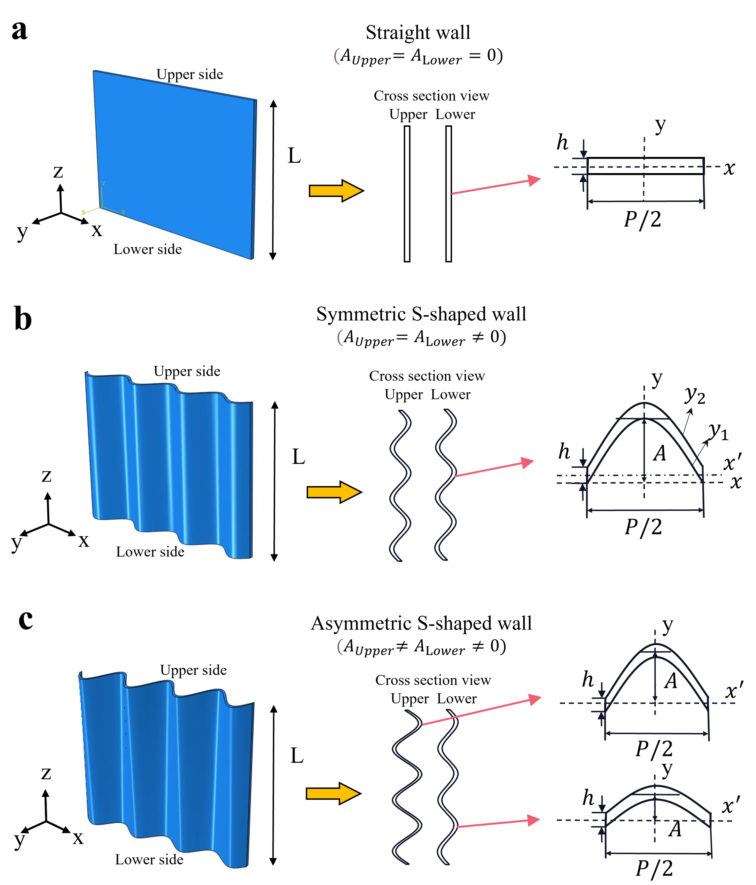
The cuttlebone-like structure is a complex porous bionic structure with asymmetric sinusoidal S-shaped wall structure connecting laminar septa, and studies have shown that the cuttlebone-like structure has light weight, high strength and excellent energy absorption capability. It has become an important research to investigate the mechanical mechanism of cuttlebone-like structure and to design a bionic structure beyond nature structure based on it. In order to investigate the mechanical properties of the static compression and shearing processes of the cuttlebone-like structure, this paper establishes theoretical formulas and analyzes the influence of dimensionless parameters such as height-to-thickness ratio $\lambda$, period-to-thickness ratio $\xi$ and amplitude to period ratio $\eta$ on the compression and shearing processes with the help of ABAQUS finite element software.The parameter sensitivity analysis method was used to compare the important influence degree of each dimensionless parameter on the mechanical properties of the structure and to determine the relative optimal parameters of the structural mechanical properties under compression and shearing. Based on the relatively optimal parameter of the cuttlebone-like structure, the cross-sectional geometry of the structure is improved to build a new cuttlebone-like structure.The experimental results showed that the new cuttlebone-like structure with revised cross-section improved the mechanical properties of the cuttlebone-like structure.The study results are of theoretical guidance to enhance the mechanical properties and geometric design of cuttlebone-like structures.
Keywords:
Subject: Physical Sciences - Applied Physics
Copyright: This open access article is published under a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, which permit the free download, distribution, and reuse, provided that the author and preprint are cited in any reuse.
Submitted:
28 April 2022
Posted:
29 April 2022
You are already at the latest version
Alerts
Submitted:
28 April 2022
Posted:
29 April 2022
You are already at the latest version
Alerts
Abstract
The cuttlebone-like structure is a complex porous bionic structure with asymmetric sinusoidal S-shaped wall structure connecting laminar septa, and studies have shown that the cuttlebone-like structure has light weight, high strength and excellent energy absorption capability. It has become an important research to investigate the mechanical mechanism of cuttlebone-like structure and to design a bionic structure beyond nature structure based on it. In order to investigate the mechanical properties of the static compression and shearing processes of the cuttlebone-like structure, this paper establishes theoretical formulas and analyzes the influence of dimensionless parameters such as height-to-thickness ratio $\lambda$, period-to-thickness ratio $\xi$ and amplitude to period ratio $\eta$ on the compression and shearing processes with the help of ABAQUS finite element software.The parameter sensitivity analysis method was used to compare the important influence degree of each dimensionless parameter on the mechanical properties of the structure and to determine the relative optimal parameters of the structural mechanical properties under compression and shearing. Based on the relatively optimal parameter of the cuttlebone-like structure, the cross-sectional geometry of the structure is improved to build a new cuttlebone-like structure.The experimental results showed that the new cuttlebone-like structure with revised cross-section improved the mechanical properties of the cuttlebone-like structure.The study results are of theoretical guidance to enhance the mechanical properties and geometric design of cuttlebone-like structures.

Keywords:
Subject: Physical Sciences - Applied Physics
Copyright: This open access article is published under a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, which permit the free download, distribution, and reuse, provided that the author and preprint are cited in any reuse.
A Numerical Study of the Effect of Component Dimensions on the Critical Buckling Load of a GFRP Composite Strut under Uniaxial Compression
Quoc Doan
et al.
Materials,
2020
Impact Resistant Structure Design and Optimization Inspired by Turtle Carapace
Baoqing Pei
et al.
Materials,
2022
Crushing Behaviors and Energy Absorption Evaluation Methods of Hexagonal Steel Tubular Columns with Triangular Cells
Weiwei Li
et al.
Materials,
2022
MDPI Initiatives
Important Links
© 2024 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated





