Preprint
Article
Extracellular Alterations in Ph and K+ Modify the Murine Brain Endothelial Cell Total and Phospho-Proteome
Altmetrics
Downloads
168
Views
215
Comments
0
A peer-reviewed article of this preprint also exists.
supplementary.zip (57.07MB )
This version is not peer-reviewed
Submitted:
03 June 2022
Posted:
06 June 2022
You are already at the latest version
Alerts
Abstract
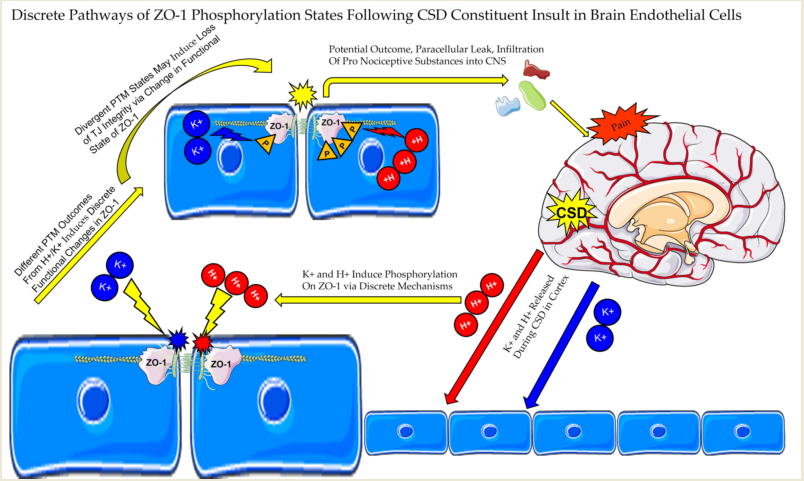
Pathologies of the blood brain barrier (BBB) have been linked to a multitude of CNS disorders whose pathology is poorly understood. Cortical spreading depression (CSD) has long been postulated to be involved in the underlying mechanisms of these disease states, yet full understanding remains elusive. This study utilized an in vitro model of the BBB with b.End3 murine endothelial cells to investigate the role of CSD in BBB pathology by characterizing effects of the release of major pronociceptive substances on BBB functional integrity using TEER screening, transcellular uptake, and immunoreactive methods in concert with global proteome and phospho-proteomic approaches. Findings demonstrated relocalization and functional alteration to proteins associated with the cytoskeleton and endothelial tight junctions. Pathologic mechanisms induced by individual substances released during CSD were found to have unique phosphorylation signatures in phospho-proteome analysis, identifying Zona Occludens 1 as a possible pathologic “checkpoint” of the BBB. Utilizing these phosphorylation signatures, possible novel diagnostic methods may be developed for neurological diseases and warrants further investigation.
Keywords:
Subject: Medicine and Pharmacology - Pathology and Pathobiology
Copyright: This open access article is published under a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, which permit the free download, distribution, and reuse, provided that the author and preprint are cited in any reuse.
MDPI Initiatives
Important Links
© 2024 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated





