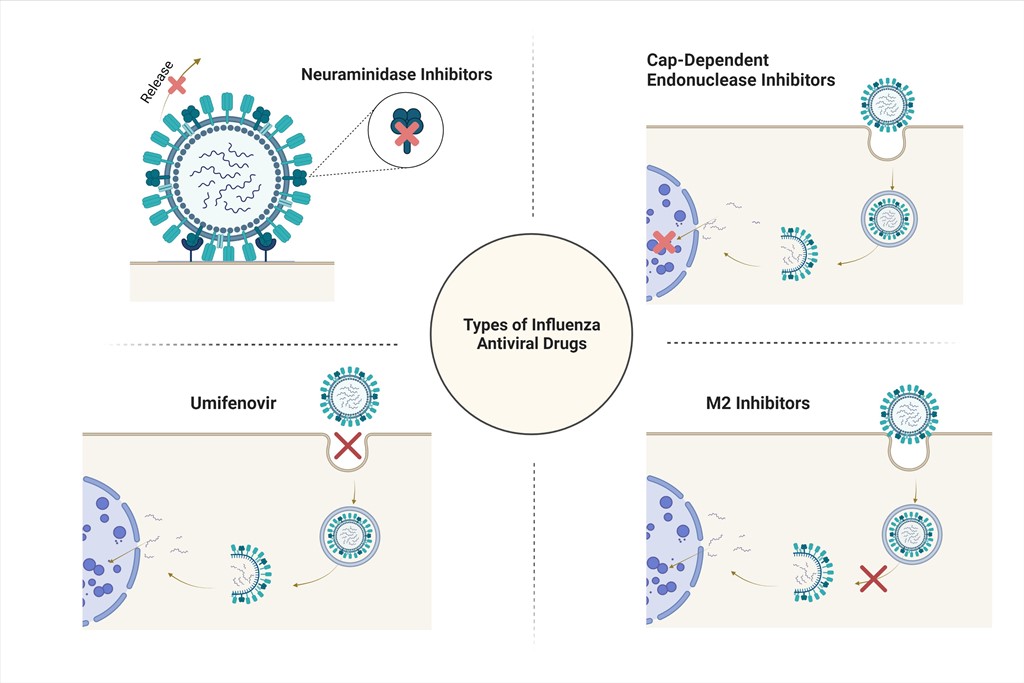
Antigenic drift in influenza strains allows viruses to avoid being fully suppressed by seasonal vaccines. As a result, public interest has led to increased scrutiny and reevaluation of anti-influenza antiviral drugs as possible solutions. Unfortunately, many anti-influenza drugs developed around the globe suffer from a lack of sufficient clinical trials, as well as a lack of toxicity data. This is especially true of Arbidol, a popularly used drug for the prevention and treatment of influenza strains in China and Russia. Neuraminidase inhibitors, which were developed in the United States, also fall victim to inconclusive clinical trials and adverse effects. Adamantanes, while proven to be effective in treating influenza A, are encountering rapid, widespread cross-resistance. Baloxavir marboxil, a newer anti-influenza medication, shows promise in treating acute uncomplicated influenza, and may avoid the development of resistance when coadministered with other antiviral drugs. This review explores the antivirals available for influenzas treatment at this time.