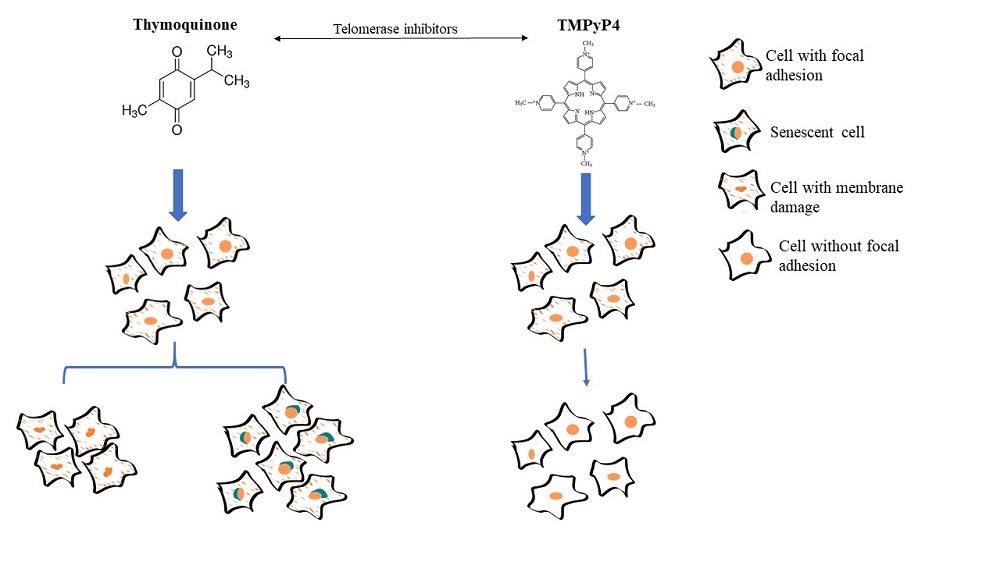
G‐quadruplexes (G4) are structures formed at the ends of the telomere, these are rich in guanines and were stabilized by molecules that bind to specific sites. TMPyP4 and Thymoquinone (TQ) are small molecules that bind to the G4, they have drawn attention because of their role as telomerase inhibitors. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of telomerase inhibitors on cellular proliferation, senescence, and death. Two cell lines LC‐HK2 (NSCLC) and RPE‐1 were treated with TMPyP4 (5μM) and TQ (10μM). Both inhibitors were effective in decreasing telomerase activity. TMPyP4 increased the percentage of cells with membrane damage associated with cell death and decreased the frequency of cells in the S‐phase. TMPyP4 changed the cell adhesion ability and modified the pattern of focal adhesion. TQ acted in a dose‐dependent manner, increasing the frequency of senescent cells, and inducing cell cycle arrest in the G1. In conclusion, the effects of both drugs on LC-HK2 and RPE-1 cell lines were different although both are telomerase inhibitors, because TMPyP4 decreased proteins of cell adhesion and TQ induces a decrease in cell viability.