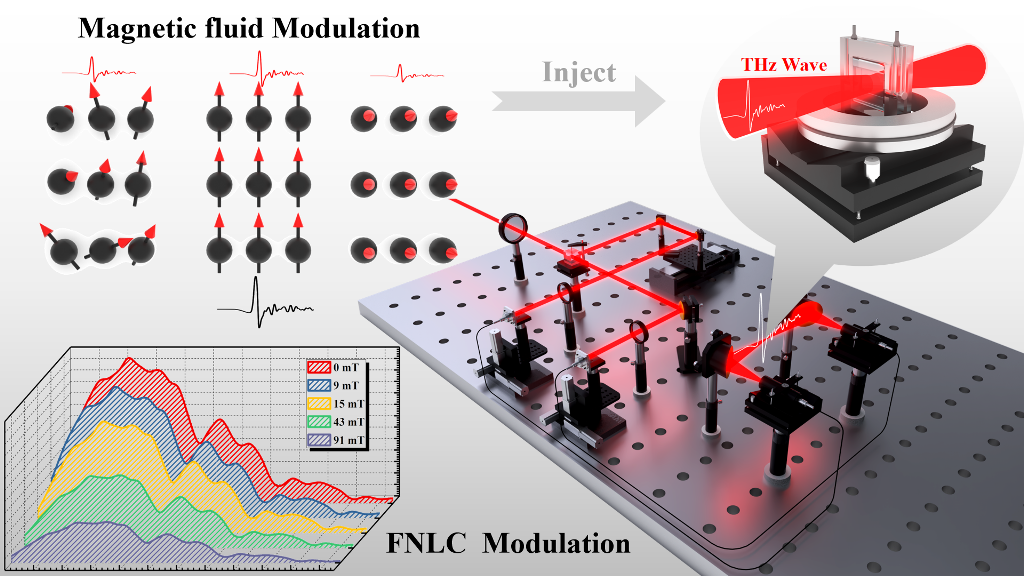
In recent years, solid state terahertz (THz) modulators have obtained rapid progress with the widespread use of two-dimensional (2D) materials in the field of THz; however, challenges remain in preparing flexible THz modulators. In this study, flexible ferromagnetic nematic materials were prepared by doping thermotropic nematic liquid crystals 5CB into magnetic fluids, and the influence of hydrogen bonding in water was reduced by a self-made cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) microfluidic chip. THz modulation characteristics of magnetic fluid and ferromagnetic nematic liquid crystal (FNLC) under the induction of external magnetic field were compared using a THz time domain spectroscopy system. Under the action of a 91 mT magnetic field, the magnetic fluid has a maximum modulation depth (MD) of 54%. Under the same magnetic field, the maximum MD of the ferromagnetic nematic liquid crystal materials increase to 78% because of the rearrangement of Fe3O4 nanoparticles induced by the topological defect of the liquid crystal. We demonstrate that the magneto-optical effect is significantly enhanced in the ferromagnetic nematic liquid crystal hybrid system. This strategy of doping thermotropic nematic liquid crystals to enhance the magneto-optical effect has great potential for THz filtering, modulation, and sensing applications.